274 IBM System Storage N series Hardware Guide
19.1 Overview
Multipath I/O (MPIO) provides multiple storage paths from hosts (initiators) to their IBM
System Storage N series targets. The multiple paths provide redundancy against failures of
hardware, such as cabling, switches, and adapters. They also provide higher performance
thresholds by aggregation or optimum path selection.
Multipathing solutions provide the host-side logic to use the multiple paths of a redundant
network to provide highly available and higher bandwidth connectivity between hosts and
block level devices. Multipath software has the following main objectives:
Present the OS with a single virtualized path to the storage.
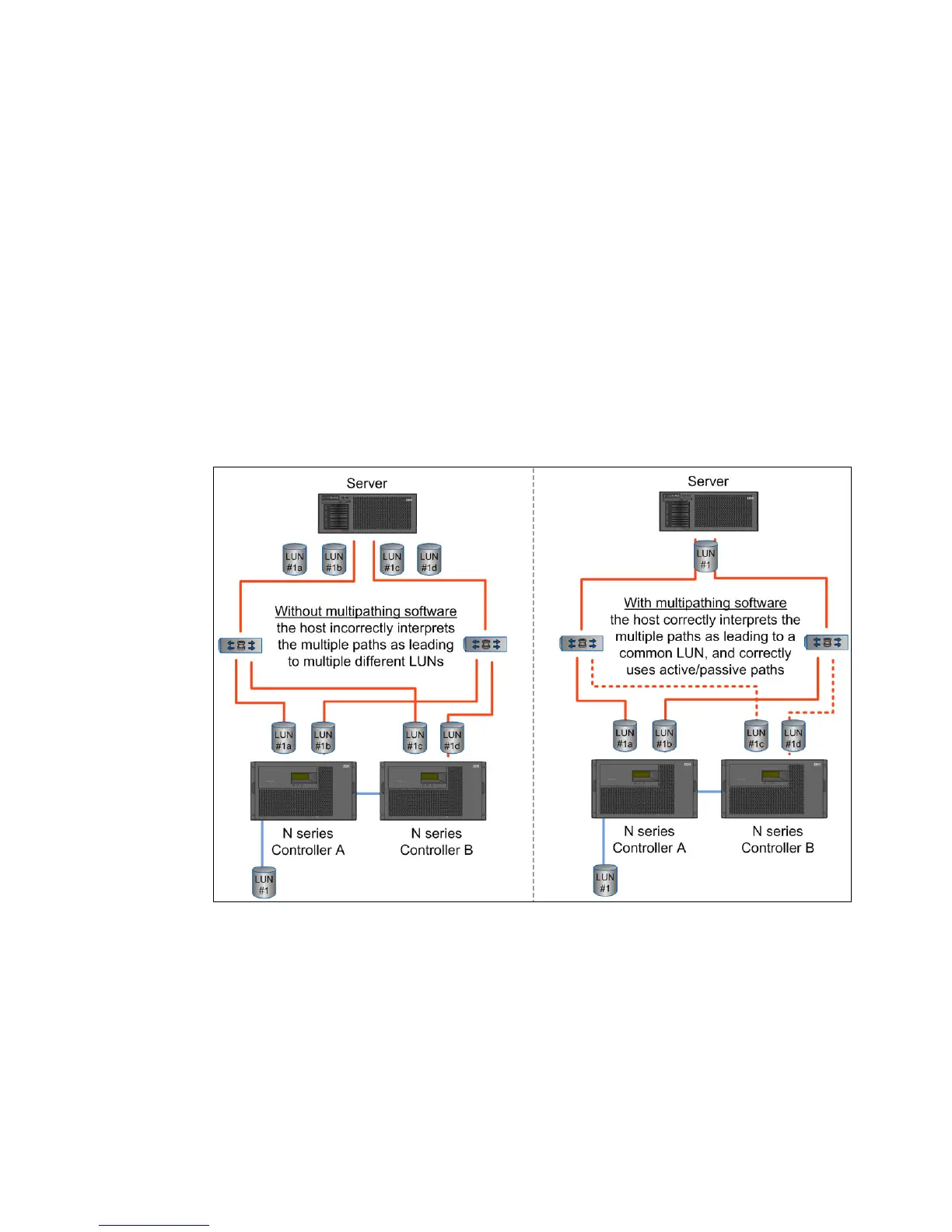
Figure 19-1 includes two scenarios: OS with no multipath management software and OS
with multipath management software.
Without multipath management software, the OS believes that it is connected to two
different physical storage devices. With multipath management software, the OS correctly
interprets that both HBAs are connected to the same storage device.
Figure 19-1 With and without host multipathing
Seamlessly recover from a path failure.
Multipath software detects failed paths and recovers from the failure by routing traffic
through another available path. The recovery is automatic, usually fast, and not apparent
to the IT organization. The data ideally remains available always.
Enable load balancing.
Load balancing is the use of multiple data paths between server and storage to provide
greater throughput of data than with only one connection. Multipathing software improves
throughput by enabling load balancing across multiple paths between server and storage.

 Loading...
Loading...











