240 IBM System Storage N series Hardware Guide
The infrastructure and equipment that is used in the examples consists of the hardware and
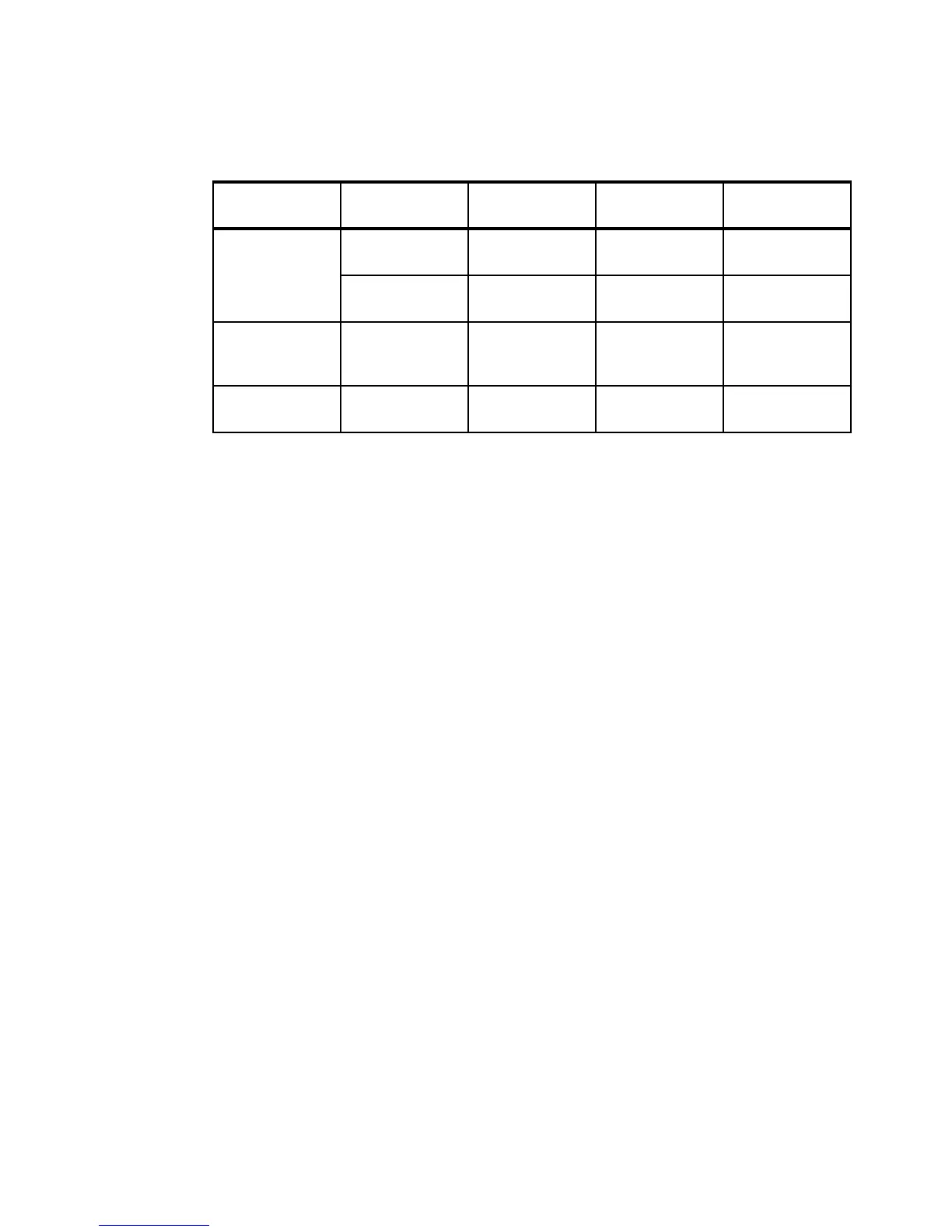
software that is listed in Table 18-1.
Table 18-1 Hardware and software configuration
18.2.2 Preferred practices
The following guidelines help you get the most out of your N series:
Fibre Channel queue depth: To avoid host queuing, the host queue depths should not
exceed the target queue depths on a per-target basis. For more information about target
queue depths and system storage controllers, see the FCP Configuration Guide at this
website:
http://www.ibm.com/storage/support/nas/
Check the appropriate interoperability matrix at the following website for the latest SAN
booting requirements for your operating system:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/storage/network/interophome.html
Volume layout: Volumes that contain boot LUNs must be separated from application data
to preserve Snapshot data integrity and prevent Snapshot locking when LUN clones are
used. Although volumes that contain boot LUNs might not require much physical disk
space, give the volume enough spindles so that performance is not bound by disk activity.
With Data ONTAP Version 7 and later, volumes with boot LUNs can be created on the
same aggregate in which the data volumes are located. This configuration maximizes
storage usage without sacrificing performance.
RHEL5 can now detect, create, and install to dm-multipath devices during installation. To
enable this feature, add the parameter mpath to the kernel boot line. At the initial Linux
installation panel, enter Linux mpath and press Enter to start the Red Hat installation.
Windows operating system pagefile placement: For Windows 2003 and 2008
configurations, store the pagesys.sys file on the local disk if you suspect pagefile latency
issues. For more information about pagefiles, see this website:
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;q305547
The operating system pagefile is where Windows writes seldom-used blocks from memory
to disk to free physical memory. This operation is called
paging. Placing the pagefile on a
SAN device can cause the following issues:
– If systems share common resources on the SAN, heavy paging operations of one
system can affect storage system responsiveness for both operating system and
application data for all connected systems. These commons resources include disk
spindles, switch bandwidth, and controller processor and cache.
Server Operating
system
HBA model N series Data ONTAP
version
IBM System
x3655 (7985)
Windows 2003
Enterprise SP2
QLOGIC
QLE2462
N series 5500
(2865-A20)
7.3
Windows 2008
Enterprise Server
QLOGIC
QLE2462
N series 5500
(2865-A20)
7.3
IBM xSeries 3850
(8863)
Red Hat
Enterprise Linux
5.2
QLOGIC
QLA2340
N series 5500
(2865-A20)
7.3
IBM xSeries 225
(8647)
Windows 2003
Enterprise SP2
Emulex LP9802 N series 5500
(2865-A20)
7.3

 Loading...
Loading...











