152 IBM System Storage N series Hardware Guide
Better system performance
Read/write operations are faster over large RAID groups than over smaller RAID groups.
Advantages of small RAID groups
Small RAID group configurations offer the following advantages:
Shorter disk reconstruction times
During disk failure within a small RAID group, data reconstruction time is shorter than it is
within a large RAID group.
Decreased risk of data loss because of multiple disk failures
Data loss through double disk failure within a RAID 4 group is less likely than during a
triple disk failure within a RAID-DP group.
10.4 RAID-DP and double parity
It is well-known that parity generally improves fault tolerance, and that single-parity RAID
improves data protection. Because traditional single-parity RAID has a good track record to
date, the concept of double-parity RAID sounds like a better protection scheme. This is borne
out in the earlier example that used the MTTDL formula. But what exactly is RAID-DP?
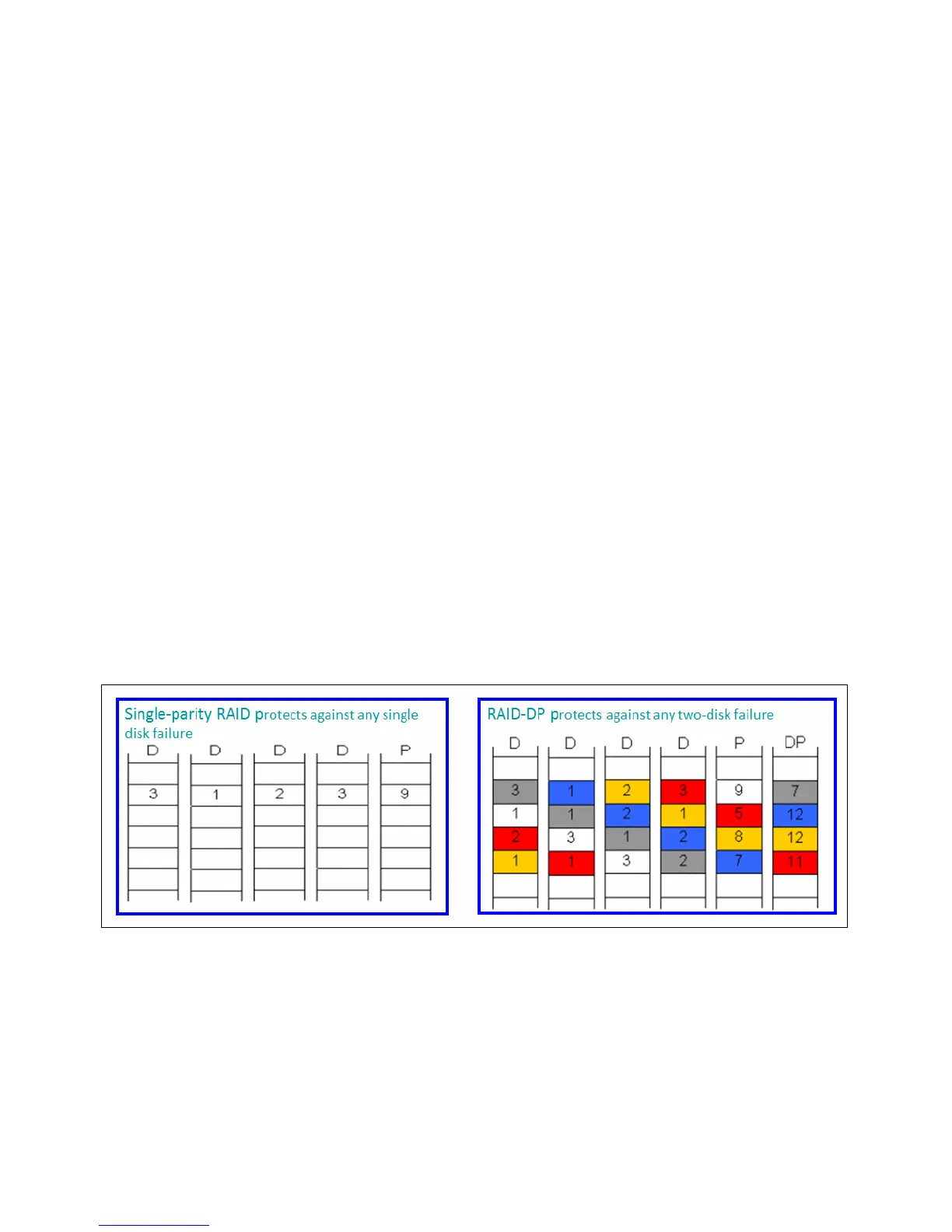
At the most basic layer, RAID-DP adds a second parity disk to each RAID group in a volume.
A
RAID group is an underlying construct on which volumes are built. Each traditional RAID 4
group has data disks and one parity disk, with volumes that contain one or more RAID 4
groups. The parity disk in a RAID 4 volume stores row parity across the disks in a RAID 4
group. The additional RAID-DP parity disk stores diagonal parity across the disks in a
RAID-DP group, as shown in Figure 10-6. These two parity stripes in RAID-DP provide data
protection if two disk failures occur in the same RAID group.
Figure 10-6 RAID 4 and RAID-DP

 Loading...
Loading...











