System Management Intel® 5000 Series Chipsets Server Board Family Datasheet
Revision 1.1
Intel order number D38960-004
132
4.26 Host to BMC Communication Interface
4.26.1 LPC / KCS Interface
The BMC has three 8042 keyboard controller style (KCS) interface ports as described in the
IPMI 2.0 specification. These interfaces are mapped into the host I/O space and accessed via
the chipset low pin count (LPC) bus.
These interfaces are assigned with the following uses and addresses:
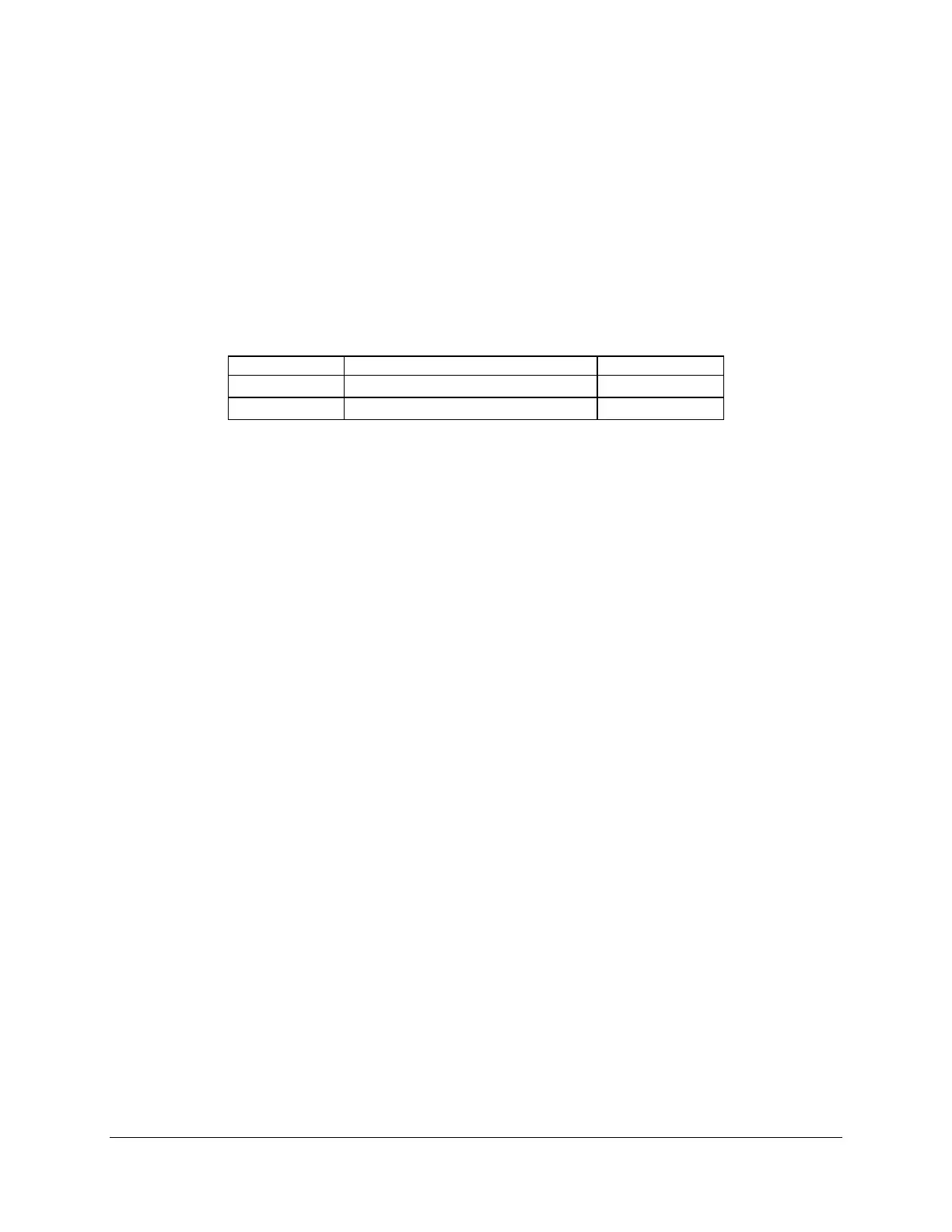
Table 43. Keyboard Controller Style Interfaces
Name Use
Address
SMS Interface SMS, BIOS POST, and utility access 0CA2h – 0CA3h
SMM Interface SMI handling for error logging 0CA4h – 0CA5h
The BMC gives higher priority to transfers occurring through the server management mode
(SMM) interface. This provides minimum latency during SMI accesses. The BMC acts as a
bridge between the server management software (SMS) and the IPMB interfaces. Interface
registers provide a mechanism for communications between the BMC and the host system.
Most platforms implement the interfaces as host I/O space mapped registers. The interfaces
consist of three sets of two 1-byte-wide registers.
4.26.2 Receive Message Queue
The receive message queue is only accessible via the SMS interface since that interface is the
BMC’s host / system interface. The queue size is platform-dependent, but is guaranteed to be at
least two entries in size. It does not support the IPMI 2.0 suggested implementation of providing
per-channel queue slots to avoid starvation.
4.26.3 Server Management Software (SMS) Interface
The SMS interface is the BMC host interface. The BMC implements the SMS KCS interface as
described in the IPMI 2.0 specification.
4.26.4 SMM Interface
The SMM interface is a KCS interface that is used by the BIOS when interface response time is
a concern, such as with the BIOS SMI handler. The BMC gives this interface priority over other
communication interfaces.
Only a relatively small subset of BMC commands is supported through the SMM interface. In
addition to utilizing the faster SMM interface, the code to execute these commands is optimized
so that the command is executed and responded to during a single BMC interrupt.

 Loading...
Loading...