Chapter 10 Sampling System
95
Figure 10-2 Theoretical Brick-Wall Frequency Response
However, digital signals have frequency components that exceed the fundamental frequency (the square wave
consists of sine waves at fundamental frequency and an infinite number of odd harmonics), and for bandwidths
of 500MHz and below, the oscilloscope typically has Gaussian frequency response.
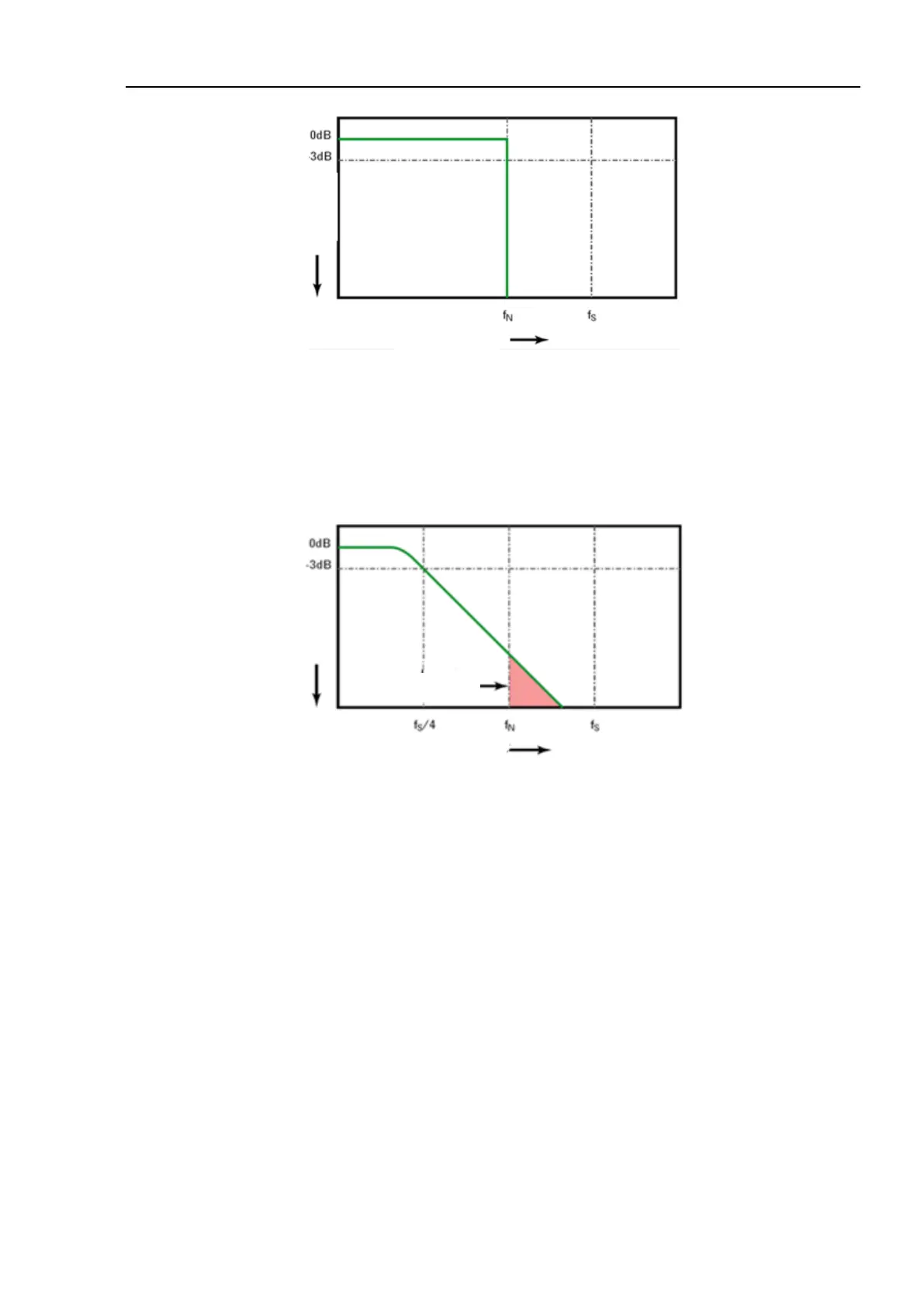
Figure 10-3 Sampling Rate and Oscilloscope Bandwidth
The oscilloscope bandwidth is limited to 1/4 sampling frequency and reduces the frequency response above the
Nyquist frequency.
Therefore, in fact, the oscilloscope sampling rate should be 4 times or more of its bandwidth: f
S
≥4f
BW
. This can
reduce aliasing and cause greater attenuation in the aliased frequency components.
Oscilloscope rise time
The oscilloscope rise time is closely related to its bandwidth. The rise time of an oscilloscope with Gaussian type
frequency response is approximately 0.35/f
BW
(based on the standard from 10% to 90%).
The oscilloscope rise time is not the fastest edge speed that an oscilloscope can accurately measure. It is the
fastest edge speed that the oscilloscope can produce.
Desired oscilloscope bandwidth
The oscilloscope bandwidth required to accurately measure signal is primarily determined by the rise time of the
 Loading...
Loading...