94
10.1 Sampling Overview
To understand the sampling and sampling modes of the oscilloscope, you need to understand the sampling
principle, aliasing, oscilloscope bandwidth and sampling rate, oscilloscope rise time, required oscilloscope
bandwidth, and the influence of memory depth on the sampling rate.
Sampling principle
According to the Nyquist sampling principle, for a bandwidth-limited signal with the maximum frequency f
MAX
,
the equidistant sampling frequency f
S
must be twice as large as the maximum frequency f
MAX
, so that a unique
signal can be reconstructed without aliasing.
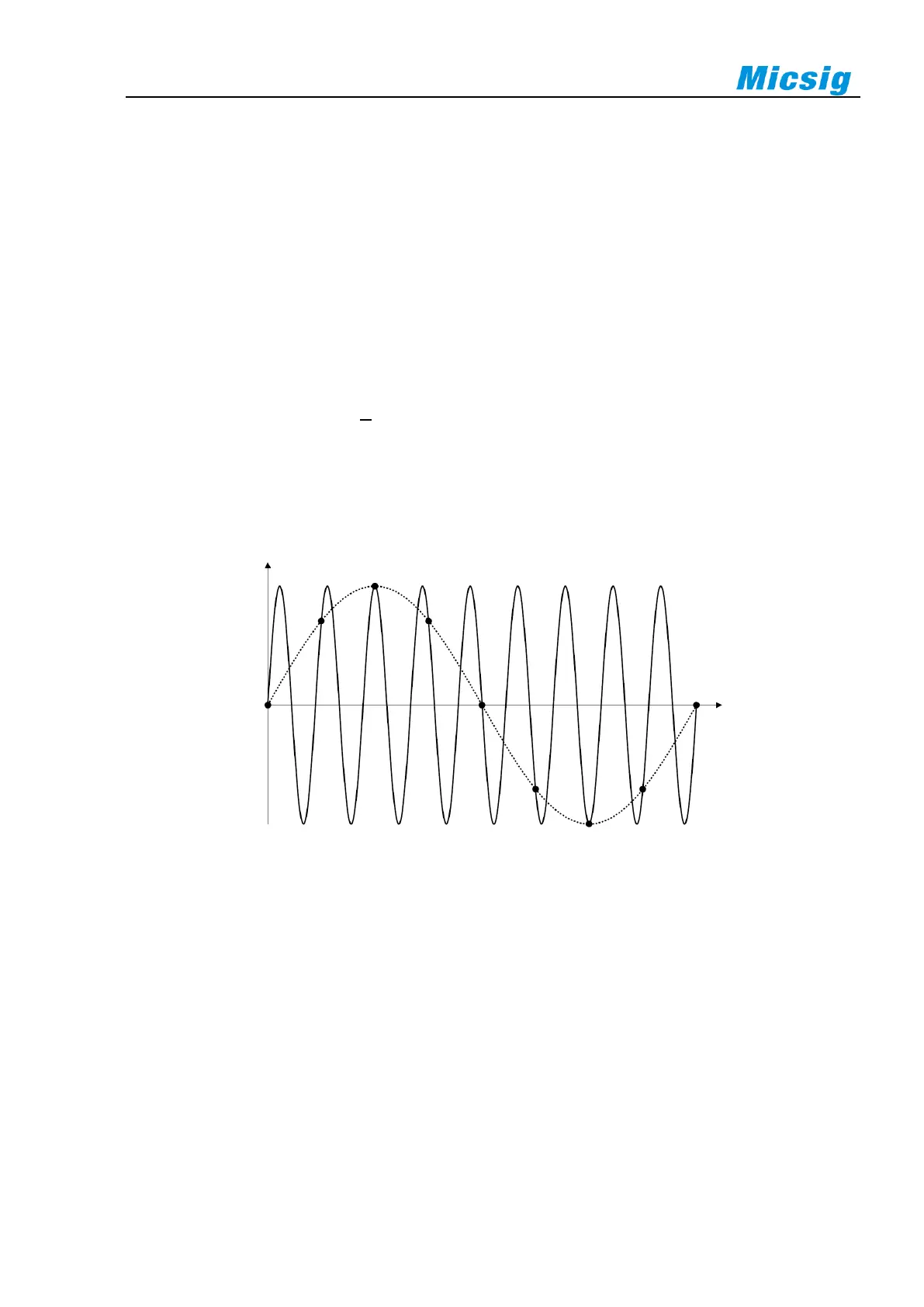
Aliasing
Aliasing occurs when the signal is under sampled (f
S
<2f
MAX
). Aliasing is signal distortion caused by incorrectly
reconstructing low frequencies from a small number of sampling points.
Figure 10-1 Aliasing
Oscilloscope bandwidth and sampling rate
The oscilloscope bandwidth usually refers to the lowest frequency at which the input signal sine wave is
attenuated by 3dB (-30% amplitude error).
For oscilloscope bandwidth, according to the sampling principle, the required sampling rate is f
S
=2f
BW
. However,
this principle assumes that there is no frequency component exceeding f
MAX
(f
BW
in this case) and requires a
system with ideal brick-wall frequency response.
 Loading...
Loading...