Basic Electricity 1:12
CP 1 – Cathodic Protection Tester Course Manual
© NACE International, 2000
02/01/05
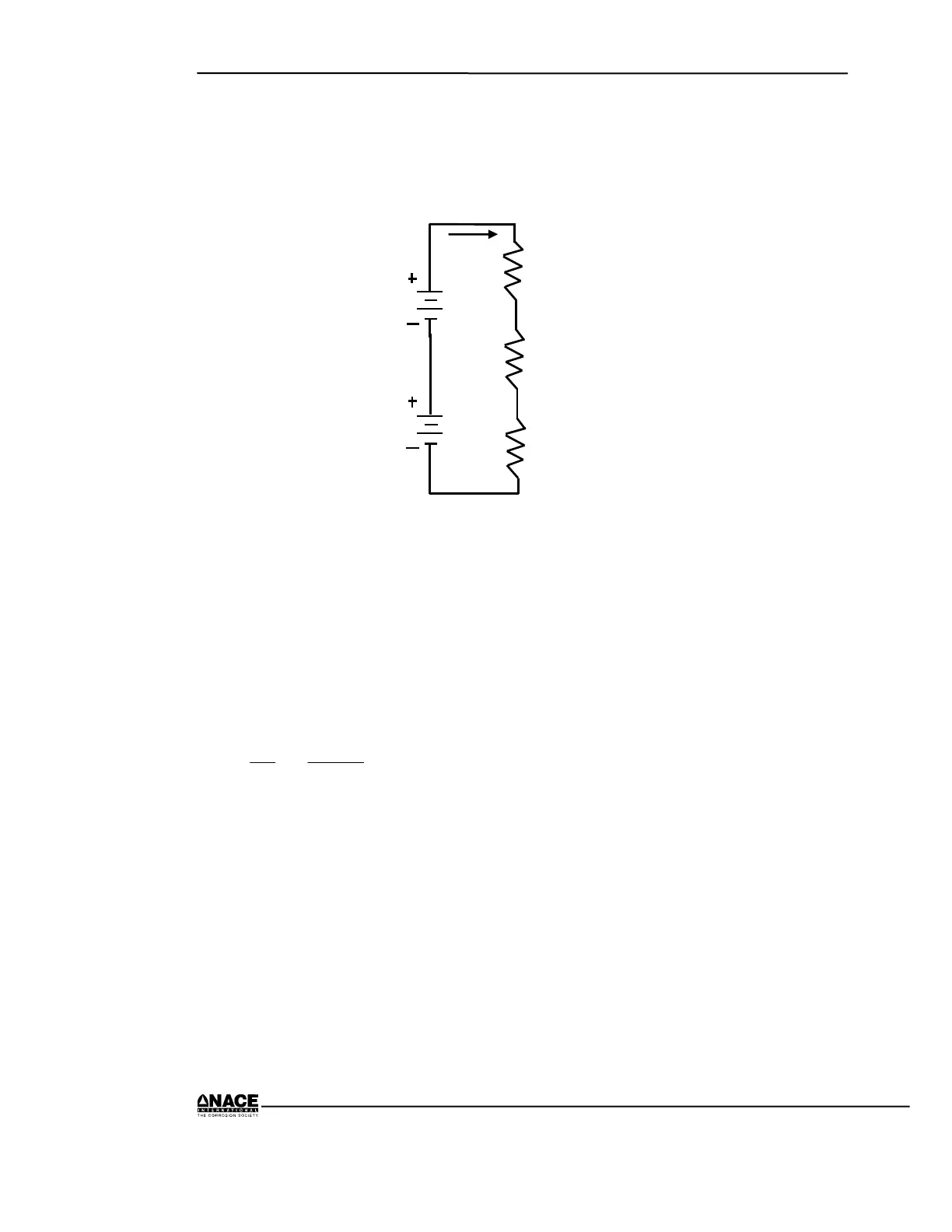
For example, consider the following circuit, where:
E
T
= Total Voltage Across the Circuit
R
T
= Total Resistance in the Circuit
I
T
= Total Current in the Circuit
E
1
E
2
R
1
R
2
R
3
I
E
2
E
1
R
3
R
2
R
1
Figure 1.6 Series Circuit
Given E
1
= 5 V
E
2
= 5 V
R
1
= 5
R
2
= 3
R
3
= 2
Ω+
= 10235R T
A1
10
V10
R
E
IT =
Ω
==
I
1
= 1 A I
T
R
1
= 1 A x 5 Ω = 5 V
I
2
= 1 A I
T
R
2
= 1 A x 3 Ω = 3 V
I
3
= 1 A I
T
R
3
= 1 A x 2 Ω = 2 V
Total IR Drop = 10 V
OR
IR
T
= 1 A x 10 Ω = 10 V
E
T
= 10 V
Note that Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law is fulfilled.
 Loading...
Loading...