Basic Electricity 1:18
CP 1 – Cathodic Protection Tester Course Manual
© NACE International, 2000
02/01/05
Direct Current (DC)
Direct current flows in only one direction. Pure direct current is
produced by a battery and appears as a straight line when viewed on
an oscilloscope. See Figure 1.10. The circuits we have been
discussing above are all based on direct current.
(+)
0
(–)
Figure 1.10 Pure Direct Current
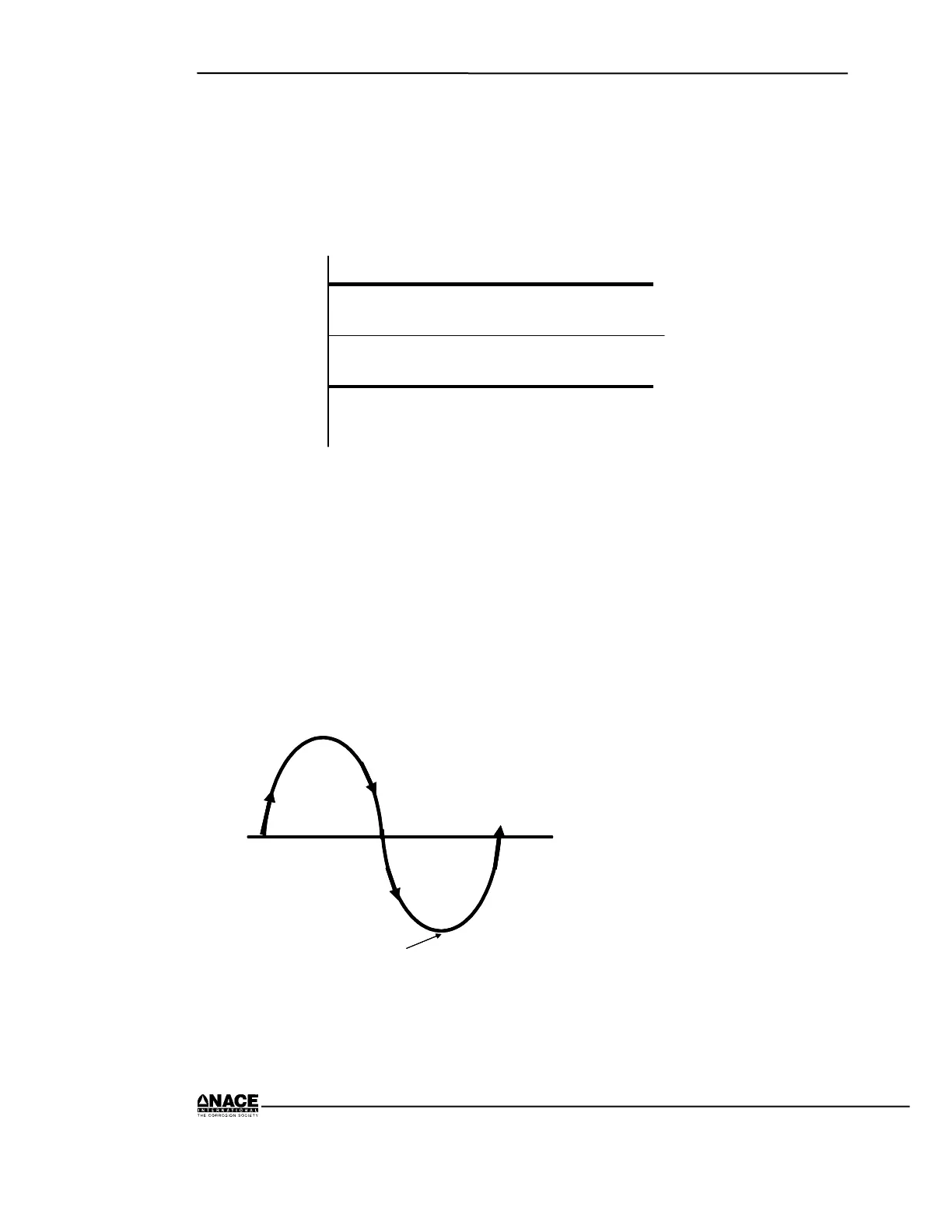
Alternating Current (AC)
Alternating current, such as that which we have in our homes and
buildings, reverses direction on a cyclic basis, most commonly 100
or 120 times a second. A full cycle is completed in a 50
th
or 60
th
of a
second. The word hertz (hz) is used to represent a cycle, so AC is
known as 50 hz or 60 hz current. Figure 1.11 shows a typical
alternating current.
Half Cycle
Zero Current
Half Cycle
Maximum Reverse Current
Half Cycle
Zero Current
Half Cycle
Maximum Reverse Current
Figure 1.11 Typical Alternating Current
 Loading...
Loading...