Basic Chemistry and Basic Corrosion Theory 2:7
CP 1 – Cathodic Protection Tester Course Manual
© NACE International, 2000
02/01/05
Reduction
Reduction is the term applied to the gain of one or more electrons to an
atom or molecule, which then forms a negatively charged ion or neutral
element.
A reduction reaction occurs any time that electrons are gained by an atom
or molecule. The atom or molecule increases in negative charge.
For example, when a hydrogen ion (H
+
) is reduced, it gains one electron,
producing a neutral hydrogen atom (H).
H
+
+ e
–
→ H
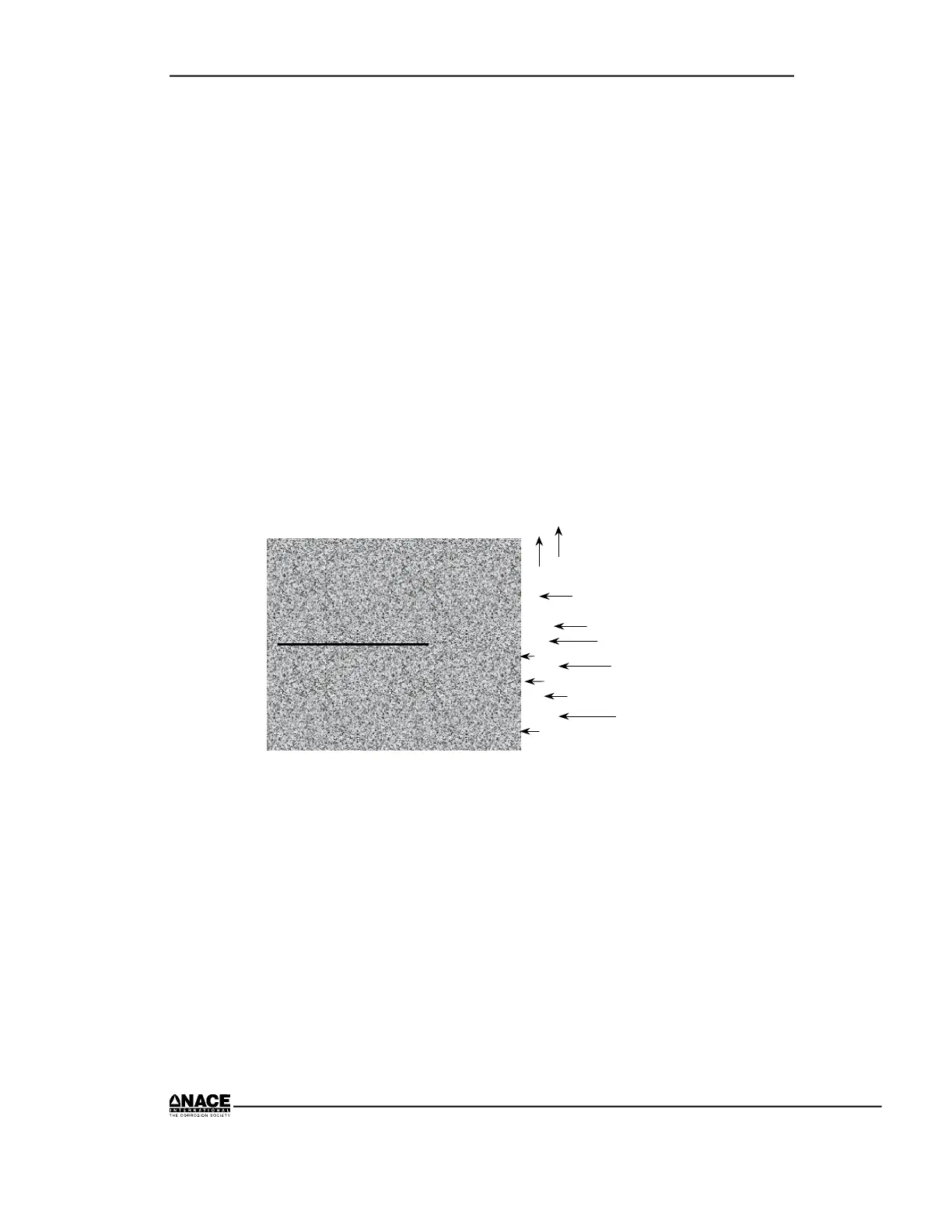
The electrode or metallic site where reduction occurs is called a cathode.
The process appears in Figure 2.6.
H
2
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
e
-
CATHODE
H
0
H
0
H
+
H
+
H
2
H
0
H
0
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
+
H
0
ELECTROLYTE
Figure 2.6 Cathodic Process (half reaction)
 Loading...
Loading...