RP0193-2001
6 NACE International
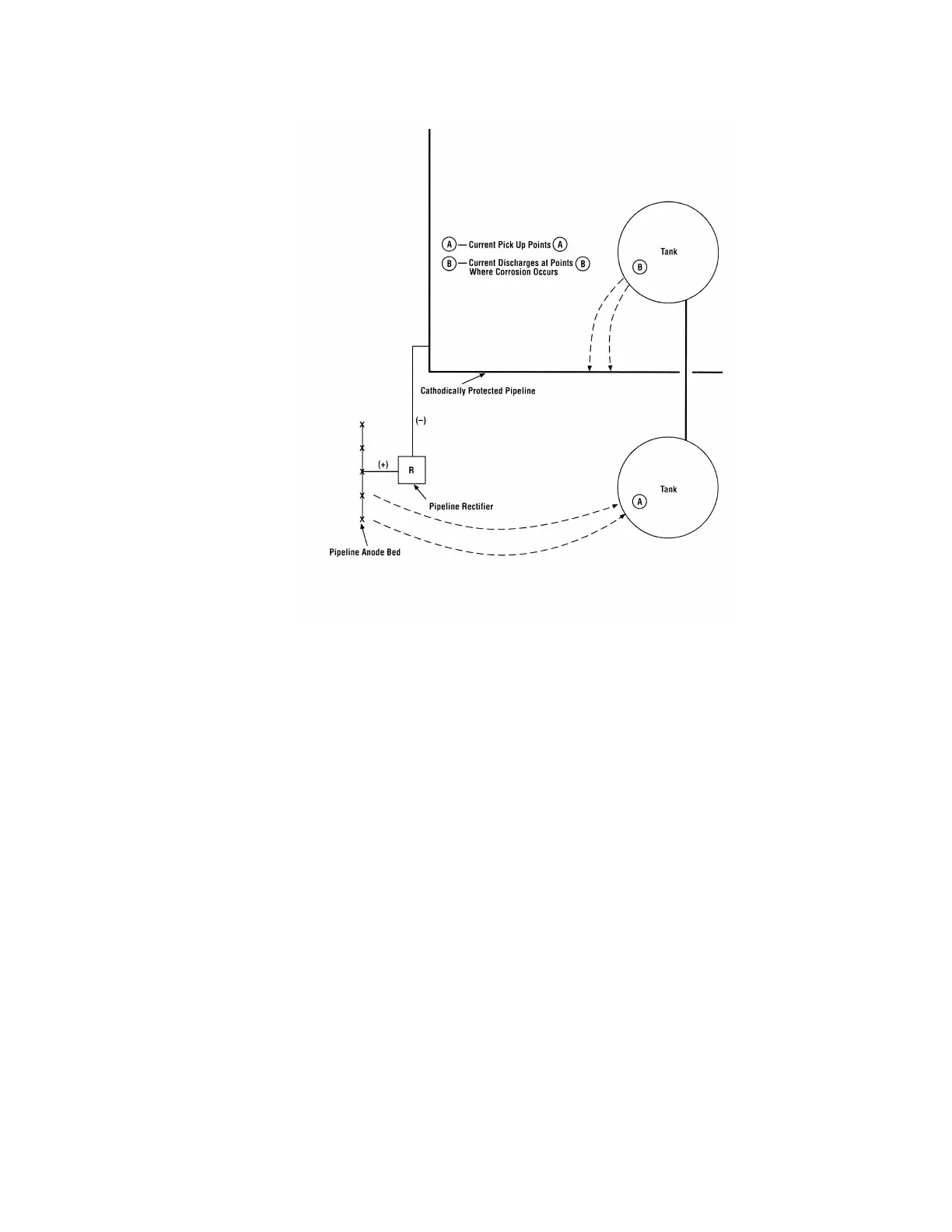
Figure 3: Stray Current Corrosion
4.2.3 Potential measurements on storage tanks shall
be made with the reference electrode located as close
as possible to the tank bottom. On most tanks,
measurements should be taken at the perimeter, near
the center of the tank bottom, and at various points in
between. Consideration must be given to voltage
drops other than those across the structure-to-
electrolyte boundary, the presence of dissimilar metals,
and the influence of other structures. These factors
may interfere with valid interpretation of potential
measurements. Also, measurements made with a
reference electrode located on asphalt pavement or a
concrete slab or outside the concrete wall may be in
error.
4.3 Criteria for Corrosion Control of Carbon Steel Tank
Bottoms
4.3.1 Corrosion control can be achieved at various
levels of cathodic polarization depending on
environmental conditions. However, in the absence of
specific data that demonstrate that cathodic protection
has been achieved, one or more of the following must
apply to the system:
4.3.1.1 A negative (cathodic) potential of at
least 850 mV with the cathodic protection current
applied. This potential shall be measured with
respect to a saturated copper/copper sulfate
reference electrode (CSE) contacting the
electrolyte. Consideration must be given to
voltage drops other than those across the
structure-to-electrolyte boundary for valid
interpretation of this voltage measurement.
4.3.1.1.1 Consideration is understood to
mean the application of sound engineering
practice in determining the significance of
voltage drops by methods such as:
(a) Measuring or calculating the voltage
drop(s),
(b) Reviewing the historical performance of
the cathodic protection system,
(c) Evaluating the physical and electrical
characteristics of the tank bottom and its
environment, and
(d) Determining whether or not there is
physical evidence of corrosion.
4.3.1.2 A negative polarized potential of at least
850 mV relative to a CSE.
4.3.1.3 A minimum of 100 mV of cathodic
polarization between the carbon steel surface of
the tank bottom and a stable reference electrode
 Loading...
Loading...