Basic Chemistry and Basic Corrosion Theory 2:8
CP 1 – Cathodic Protection Tester Course Manual
© NACE International, 2000
02/01/05
Electrochemical Circuits
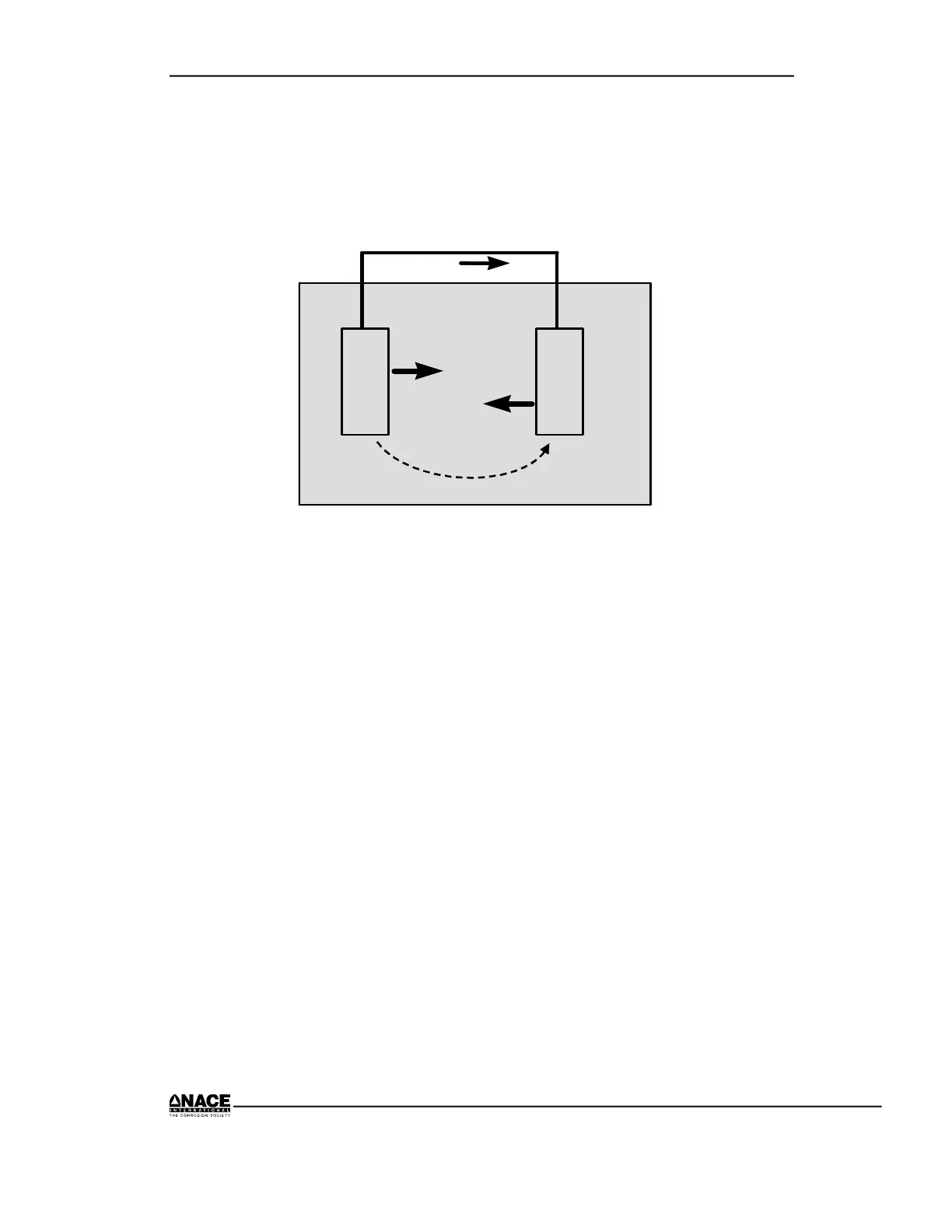
The basic electrochemical corrosion cell is illustrated in Figure 2.7. The
various parts of the basic cell are discussed following the figure.
Α
C
e-
Metallic Path
+ ions
- ions
Electrolytic Path
Conventional Current Flow
Α
C
e-
Metallic Path
+ ions
- ions
Electrolytic Path
Conventional Current Flow
Figure 2.7 Basic Corrosion Cell –
An Electrochemical Circuit
Electrolyte
The electrolyte is an ionized solution capable of conducting electricity.
Ionization
In addition to ions that may be produced in oxidation and reduction
reactions, ions may be present in the electrolyte due to dissociation of
ionized molecules. Cations are positively charged ions and anions are
negatively charged ions). These ions are current-carrying charges.
Therefore, electrolytes with higher ionization have greater conductivity.
 Loading...
Loading...