97
Computing the Cycle Time Section 2-7
Cycle time rate of increase (%) from pulse output ports 2 and 3 = Output fre-
quency (kHz) × 0.1.
Examples:
30 kHz: Approx. 3%
100 kHz: Approx. 10%
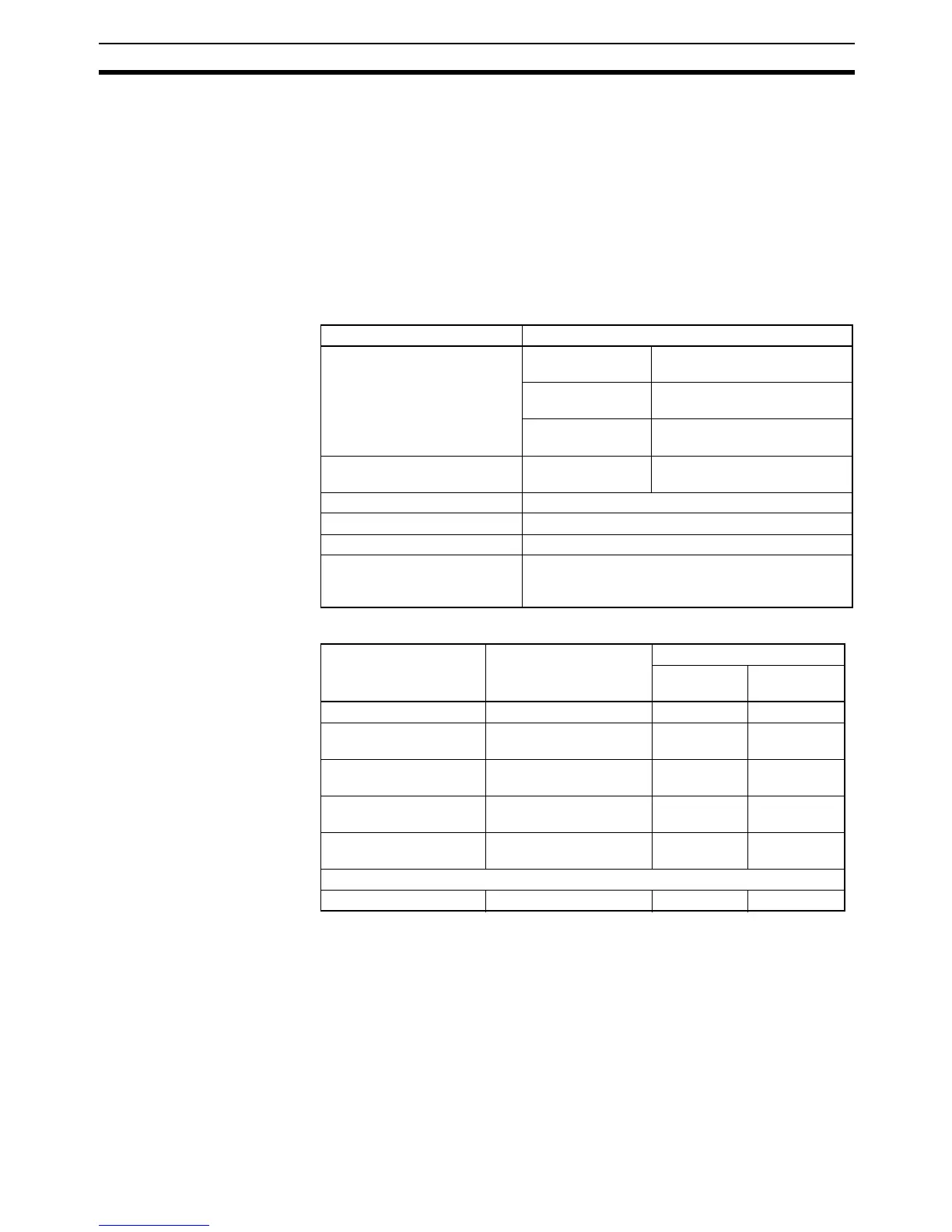
2-7-5 Cycle Time Calculation Example
The following example shows the method used to calculate the cycle time when
CP-series Expansion I/O Units only are connected to a CP1H CPU Unit.
Conditions
Calculation Example
2-7-6 Online Editing Cycle Time Extension
When online editing is executed to change the program from the CX-Program-
mer while the CPU Unit is operating in MONITOR mode, the CPU Unit will
momentarily suspend operation while the program is being changed. The
period of time that the cycle time is extended is determined by the following
conditions.
• Number of steps changed
• Editing operations (insert/delete/overwrite)
• Types of instructions
Item Details
CP1H CPM1A-40EDR
40-pt I/O Unit
2 Units
CPM1A-20EDT
20-pt I/O Unit
2 Units
CPM1A-8EDA
8-pt Output Unit
1 Unit
User program 5 K steps LD instructions: 2.5 Ksteps,
OUT instructions: 2.5 Ksteps
USB port connection Yes and no
Fixed cycle time processing No
Serial port connection No
Peripheral servicing with other
devices (Special I/O Units and
CPU Bus Units)
No
Process name Calculation Processing time
USB port
connected
USB port not
connected
(1) Overseeing --- 0.7 ms 0.7 ms
(2) Program execution 0.1 µs × 2,500 + 0.1 µs ×
2,500
0.5 ms 0.5 ms
(3) Cycle time calculation (Minimum cycle time not
set)
0 ms 0 ms
(4) I/O refreshing 0.39 ms × 2 + 0.18 ms ×
2 + 0.08
1.22 ms 1.22 ms
(5) Peripheral servicing (Only USB port con-
nected
0.1 ms 0 ms
Cycle time (1) + (2) + (3) + (4) + (5) 2.52 ms 2.42 ms

 Loading...
Loading...











