Fundamental Principles and System Description
Engineering Information
SINAMICS Engineering Manual – November 2015
Ó Siemens AG
146/528
1.9.4.2 Summary of bearing current types and counter-measures
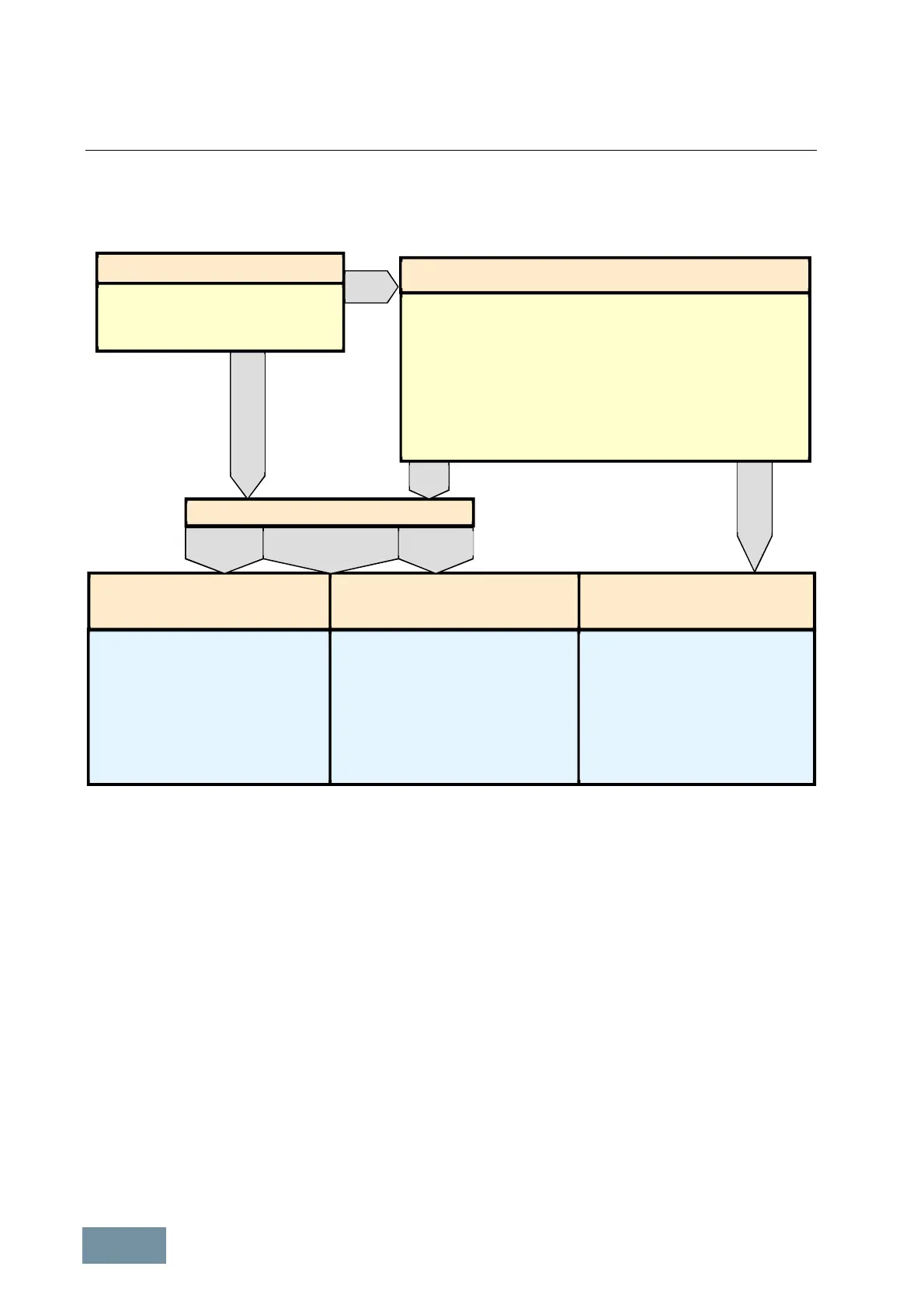
The following overview shows the different types of bearing currents depending on the shaft height and the grounding
conditions of stator and rotor.
Dominant bearing current types dependent on the shaft height and the grounding conditions of stator and rotor
If the rotor is well grounded via a conductive coupling and a well-grounded driven machine or load but the stator is
poorly grounded due to unsatisfactory installation, the rotor grounding currents become dominant which, in turn, can
quickly damage the bearings of the motor and driven machine or load. These situations must be avoided absolutely
by ensuring that the stator is properly grounded in an EMC-compliant installation and/or by means of an insulating
coupling.
If, by means of a well grounded stator with an EMC-compliant installation and/or an insolating coupling, the
occurrence of rotor shaft currents is prevented, EDM currents are dominant in smaller motors with shaft heights of up
to 100. Circular currents play a secondary role here. So the resulting bearing currents are on a low-risk level for the
bearings and no further measures usually need to be taken. As the shaft height increases, the EDM currents change
slightly, while the circular currents continually increase. From shaft heights of 225 the circular currents become
dominant and critical for the bearings. Therefore, from shaft heights of 225, the use of an isolated bearing on the
NDE of the motor is very highly recommended. This applies in particular if the motor is operated frequently or
continuously
· at low speeds below approximately 800 – 1000 rpm, or is required to operate
· at speeds that change very quickly,
because an even, stable lubricating film cannot develop in the bearing under these operating conditions.
Basically a dv/dt filter or a sinusoidal filter can also be used at the output of the converter, as alternative to an isolated
bearing in the motor.
The measures to be implemented on the motor in order to prevent bearing current damage are illustrated graphically
below.
Rotor grounding
Stator grounding
Rotor shaft currents
Counter measure:
EDM currents
Counter measure:
Circular currents
Counter measure:
no
EDM currents without superimposed
circular and rotor shaft currents have a
tolerable magnitude. Therefore, usually
no measures are required.
§ Isolated bearing on the NDE of the
motor (NDE = Non-Drive End)
or, alternatively
§ dv/dt filter or sinusoidal filter at the
output of the converter / inverter
(dv/dt phase to ground < 0.5 kV/ms)
Good rotor grounding achieved through
conductive coupling to the well-grounded
driven machine?
Good stator grounding through
• shielded, symmetrical motor cable?
and
• shield connected on both sides and with a large surface area?
and
• HF potential bonding between motor housing and driven machine?
From shaft heights of ≥ 225 also recommended:
HF potential bonding between motor terminal box and housing?
yes
• shielded, symmetrical motor cable
shield (connected on both sides)
• HF potential bonding between motor
housing and driven machine
From shaft heights ≥225 recommended
• HF potential bonding between motor
terminal box and motor housing

 Loading...
Loading...























