Drive Dimensioning
Engineering Information
SINAMICS Engineering Manual – November 2015
Ó Siemens AG
512/528
In the field-weakening range, the motor current I
Mot
can be calculated with acceptable accuracy for typical
asynchronous motors for any field-weakening point according to the following formula:
2
22
2
2
ratedAct
ratedrated
rated
Mot
I
M
M
f
f
I
f
f
I
-
×
÷
÷
ø
ö
ç
ç
è
æ
×
÷
÷
ø
ö
ç
ç
è
æ
+×
÷
÷
ø
ö
ç
ç
è
æ
=
m
.
Key to formula:
· f Motor frequency at the field-weakening point under consideration
· f
rated
Rated frequency of motor
· I
μ
Magnetization current (no-load current) of motor. This is calculated from the rated current
I
Mot-rated
of the motor and the rated power factor cosφ
Mot-rated
of the motor as follows
ratedMotratedMot
II
--
-=
j
m
cos1
.
· M Motor torque at the field-weakening point under consideration
· M
rated
Rated motor torque
· I
Act-rated
Rated active current of motor. This is calculated from the rated current I
Mot-rated
of the
motor and the magnetization current I
μ
of the motor as follows
22
m
III
ratedMotratedAct
-=
--
.
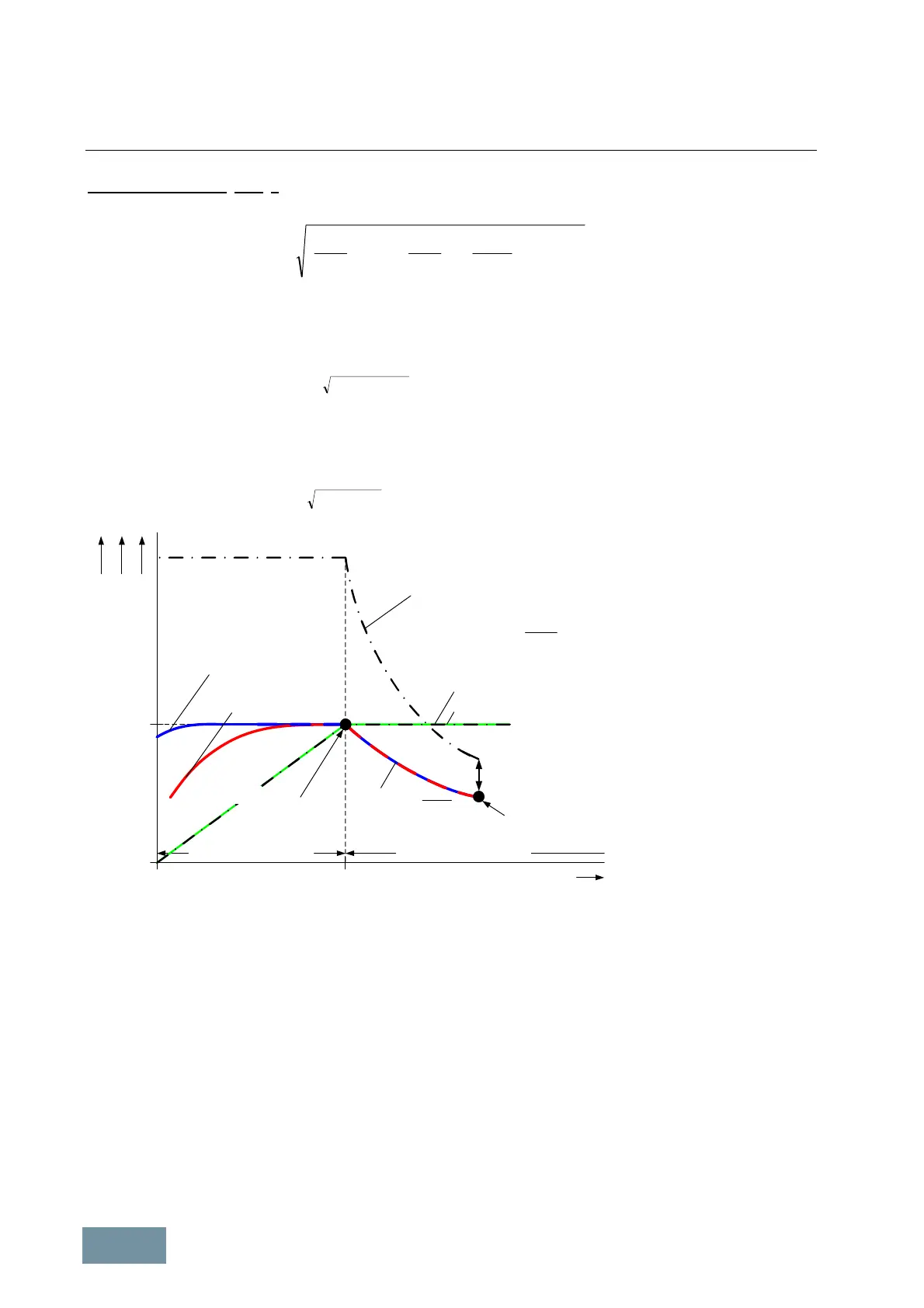
Constant flux range
Torque limit curve
for self-cooled motors
P
P rated
f
f
rated
n
n
rated
or
0
Nominal
Operating point
Torque limit curve
for forced-cooled motors
0
Stall torque in converter-fed operation
in the field-weakening range
k
f
f
rated
( )
2
M
M
rated
Power P
Difference ≥ 30%
Field-weakening range
Operating point in the
field-weakening range
=
f
f
rated
M
Stall torque in line operation
k
M
k-reduced
= M
•
M
rated •
=M Mrated
M = f(n)
P = f(n)
=P P
rated
M
or
V
V
rated
V = f(n)
or
Voltage V
or
=V V
rated
or
Typical characteristic of thermally permissible torques in continuous operation of Siemens asynchronous
motors as a function of speed when motor is utilized according to temperature class 155 (F)
10.4 Permissible motor-converter combinations
Rated motor current higher than the rated current of the converter or Motor Module
If the motor used has a higher rated current than the rated current of the converter or Motor Module, the following
must be noted.
The motor cannot be operated according to its ratings, but only under partial load. The higher the rated current of the
motor as compared to the rated current of the converter, the lower the possible partial load. Another factor to
consider is that the power factor cosφ of the motor becomes increasingly poor as the load on the motor decreases. In
a borderline situation, the motor can only be operated on its magnetizing current which means that it cannot be
loaded at all. This borderline situation is encountered with typical asynchronous motors in the power range of about
100 kW if the ratio between motor rated current and converter rated current reaches approximately 3:1.

 Loading...
Loading...























