Fundamental Principles and System Description
Engineering Information
SINAMICS Engineering Manual – November 2015
Ó Siemens AG
31/528
1.1.4.4 A comparison of the key features of open-loop and closed-loop control modes
The following table shows an overview of the key features of the three open-loop and closed-loop control modes.
Main features V/f control Vector control Servo control
Drive characteristic Simple control Precise torque controller Precise position controller
Control model - Dimensioned for accuracy
Dimensioned for dynamic
response
Main applications
Drives with low requirements of
dynamic response and accuracy.
Highly synchronized multi-motor
drives, e.g. on textile machines
with SIEMOSYN motors
Speed-controlled drives with
extremely high torque accuracy.
For universal application in
general machine engineering.
Ideal for operation of motors
without encoder.
Drives with highly dynamic
motion control.
For use on machine tools and
clocked production machines.
Dynamic response
- without encoder
- with encoder
Low
-
Medium
High
Medium
Very high
Torque accuracy
- without encoder
- with encoder
-
-
High
Very high
-
Medium
Key features of different open-loop and closed-loop control modes on SINAMICS converters
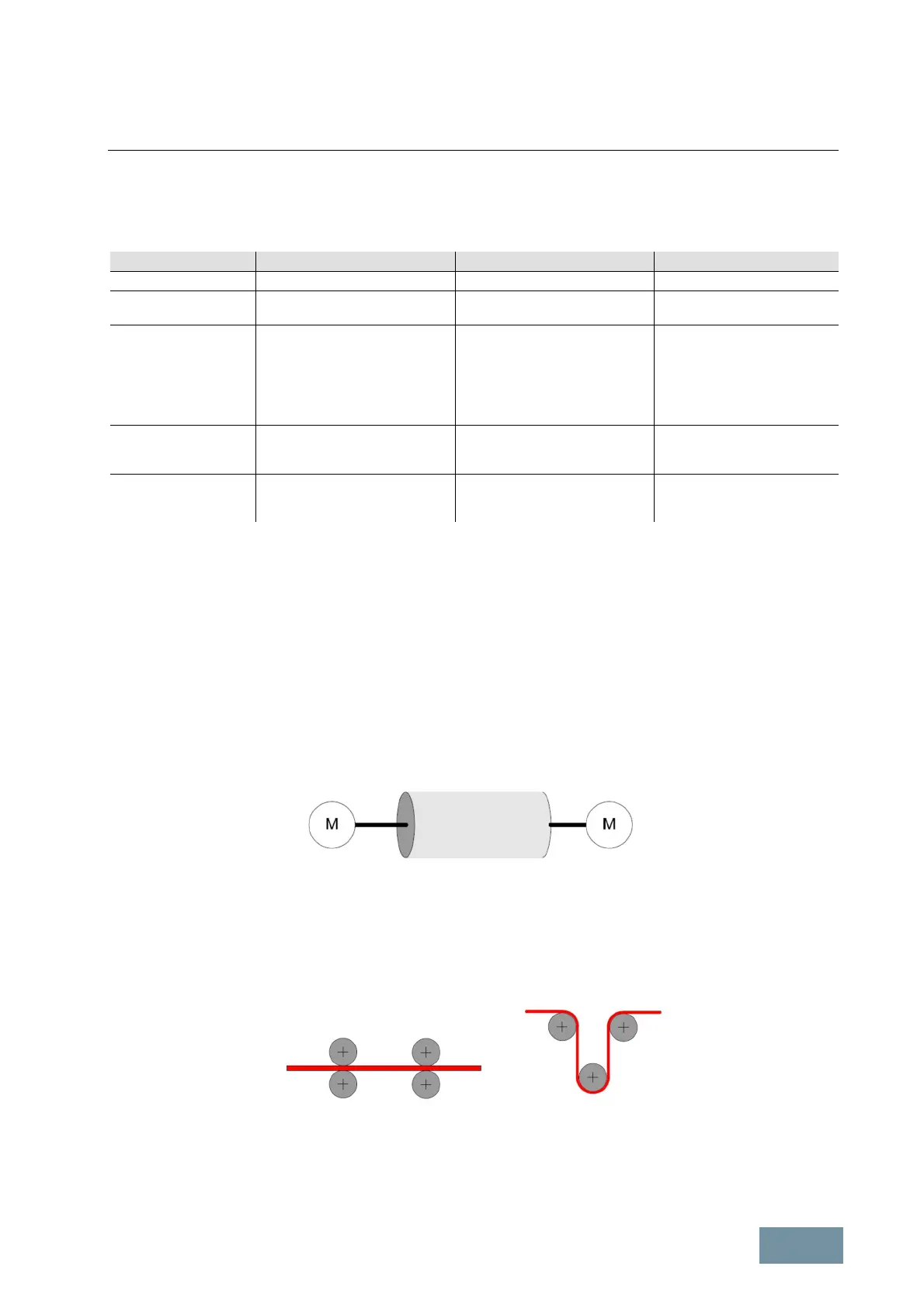
1.1.4.5 Load balance on mechanically coupled drives
General
For many applications mechanically coupled drives are used. In this case, the mechanical coupling can be rigid, as it
is for example with a roller that is driven by two identical motors, or flexible as in the example of a conveyor belt for
material handling which is driven by a mechanical grouping of multiple motors. Both types of coupling require load
balance in order to distribute the entire mechanical load in a controlled manner and in defined proportions among the
individual drives.
With a rigid coupling, the motors are rigidly coupled with one another by the mechanical system, for example, with
rollers and gears.
As a result of the rigid coupling, it is essential that all motors operate at an identical speed. Since identical motors are
normally used in couplings of this kind, the torques generated by the motors should also be identical. This can be
ensured only by providing a load balance between the drive systems. An uneven load distribution between the
motors can otherwise develop. In the worst-case scenario, the load might be braked continuously by one motor but
constantly accelerated by the other.
Flexibly coupled motors are intercoupled only by means of a material conveyor which generally exhibits a certain
elasticity.
But there are also limits to this elasticity. If one motor applies a stronger pulling force to the material than applied by
the other motor, the material tension and thus also the mechanical tension can alter significantly. This can have an
effect on the entire process and even damage the material or other equipment. This is why load balance is also
required for flexibly coupled motors.

 Loading...
Loading...























