Fundamental Principles and System Description
Engineering Information
SINAMICS Engineering Manual – November 2015
Ó Siemens AG
72/528
1.4 Harmonic effects on the supply system
1.4.1 General
The analysis presented in this section refers exclusively to low-frequency harmonic effects in the frequency range up
to 9 kHz. It does not take into account high-frequency harmonic effects as they relate to EMC (Electromagnetic
Compatibility) or radio frequency interference suppression. These high-frequency harmonic effects in the frequency
range from 150 kHz to 30 MHz are dealt with in the section "Line filters".
If electrical loads with non-linear characteristics are connected to a supply system with a sinusoidal voltage source
(generator, transformer), non-sinusoidal currents flow, which distort the voltage at the PCC (point of common
coupling). This influence on the line voltage caused by connecting non-linear loads is referred to as "harmonic effects
on the supply system" or "supply system perturbation".
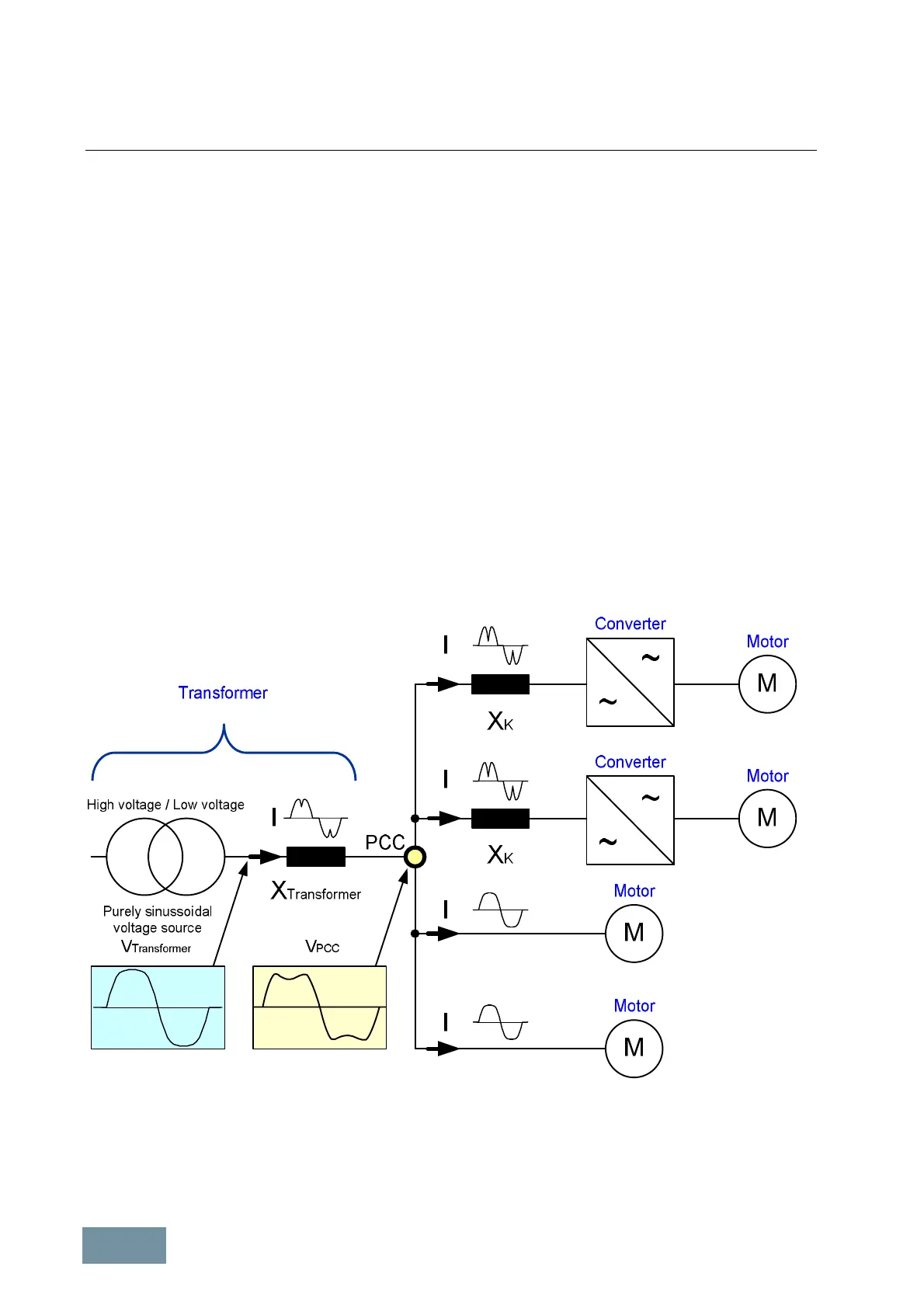
The following diagram illustrates the correlation using the example of a low-voltage system which is supplied via a
transformer representing a purely sinusoidal voltage source and the internal resistance X
Transformer
. Loads with
various characteristics are connected to the PCC. The motors have a linear current-voltage characteristic and when
fed with purely sinusoidal voltage the currents drawn from the supply system are also purely sinusoidal. The
converters have a non-linear current-voltage characteristic because of the non-linear components in the rectifier
circuits (thyristors, diodes). Therefore the currents drawn from the supply system are non-sinusoidal in spite of the
supply with purely sinusoidal voltage. These non-sinusoidal currents, which are produced by the converters with non-
linear characteristic, cause non-sinusoidal voltage drops across the internal resistance of the transformer X
Transformer
and therefore distort the voltage at the PCC.
Low-voltage system supplied via a transformer representing a purely sinusoidal voltage source
The non-sinusoidal quantities at the PCC (voltages and currents) can be divided into sinusoidal components, the
fundamental frequency component and the harmonic components. The higher the harmonic components of a
quantity are, the larger are the distortions of this quantity, i.e. the larger the deviations of this quantity from the
sinusoidal fundamental frequency.

 Loading...
Loading...























