SINAMICS S120 Cabinet Modules
Engineering Information
SINAMICS Engineering Manual – November 2015
Ó Siemens AG
448/528
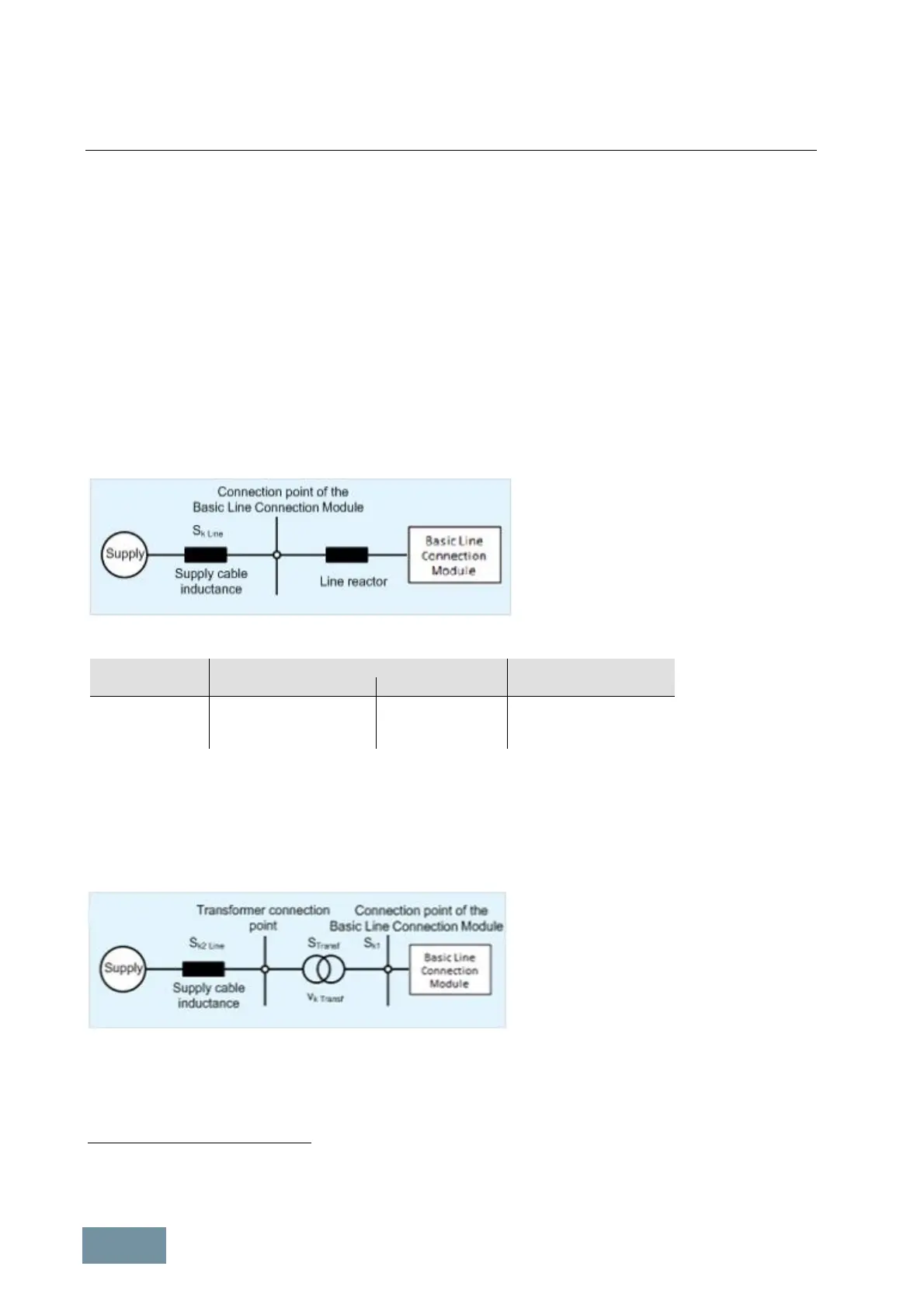
7.3.2.6 Line reactors
Line reactors are used in conjunction with Basic Line Connection Modules (u
k
= 2 %).
A line reactor must be installed whenever
· the rectifiers are connected to a line supply system with high short-circuit power, i.e. with low line supply
inductance,
· more than one rectifier is connected to the same point of common coupling (PCC),
· the rectifiers are operating in parallel to achieve a higher output power.
The line reactor is smoothing the current drawn by the rectifier, thereby reducing harmonic components in the line
current and thus the thermal load on the DC link capacitors of the rectifier. The harmonic effects on the supply are
also reduced, i.e. both the harmonic currents and harmonic voltages in the power supply system are reduced.
Line reactors can be dispensed with only if the supply cable inductance is sufficiently high or the relative short-circuit
power RSC
*)
correspondingly low.
The following applies to Basic Line Connection Modules:
BLCM output Line reactor can be omitted Line reactor is required
kW
for an RSC Order code (option) for an RSC
< 200 ≤ 43 L22 > 43
200 to 500 ≤ 33 L22 > 33
> 500 ≤ 20 L22 > 20
As the configuration of the supply system to which the Basic Line Connection Modules are to be connected is often
not known in practice, i.e. the short-circuit power at the PCC is not known, it is advisable to use a line reactor in
cases of doubt.
A line reactor can only be dispensed with when the RSC value for relative short-circuit power is less than the value
given in the above tables. For example, this applies if the Basic Line Connection Module is connected to the supply
via a transformer with adapted rating and none of the other reasons stated above for using a line reactor are valid.
*)
RSC = Relative Short-Circuit Power according to EN 60146-1-1:
Ratio between the short-circuit power S
K Line
of the supply system and the rated apparent power (fundamental apparent power)
S
converter
of the converter at its point of common coupling

 Loading...
Loading...























