Applied Instructions
84
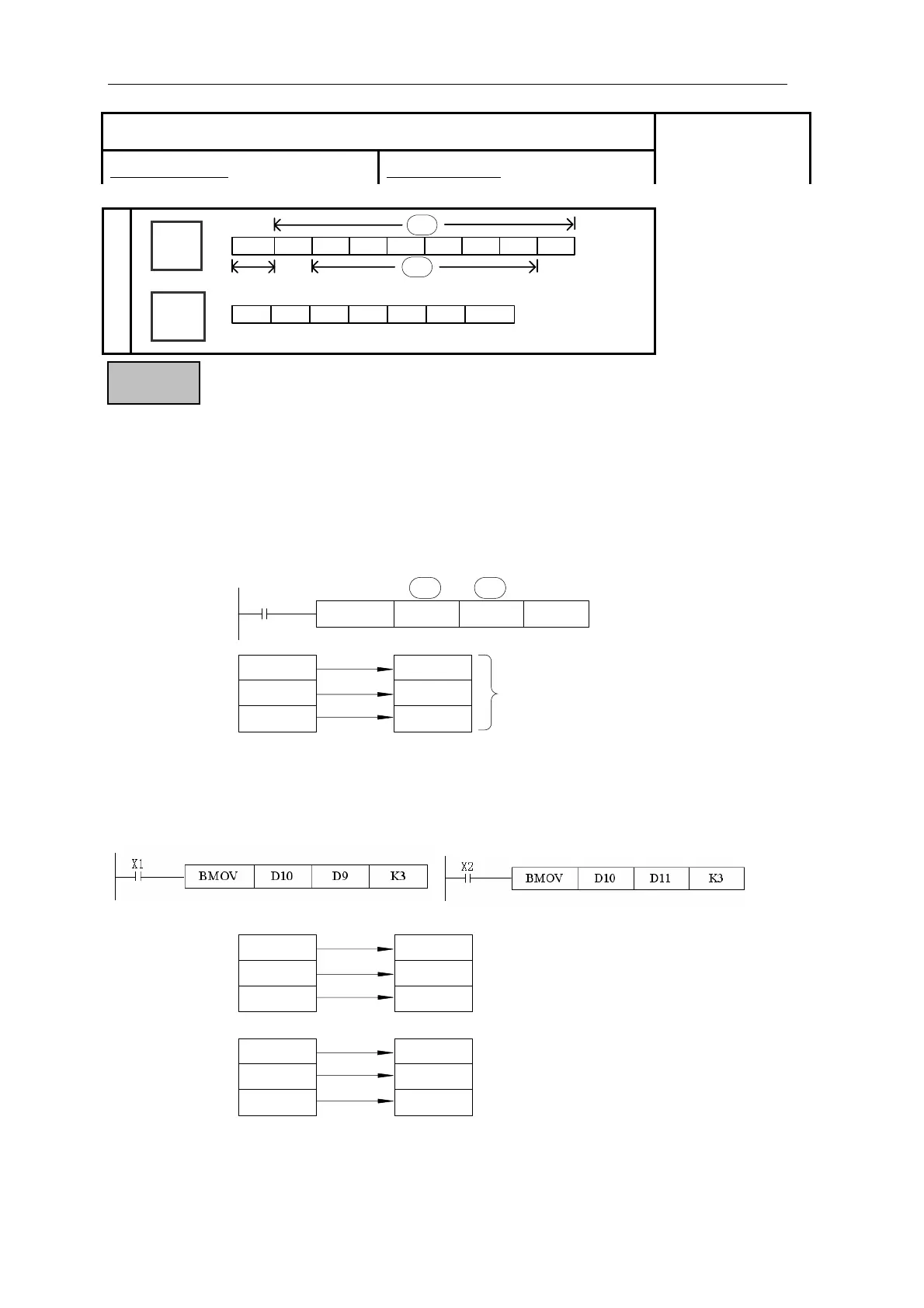
z A quantity of consecutively occurring data elements can be copied to a new destination. The
source data is identified as a device head address(S) and a quantity of consecutive data elements
(n). This is moved to the destination device (D) for the same number of elements (n). (If the
quantity of source device (n) exceeds the actual number of available source devices, then only
those devices which fall in the available range will be used. If the number of source devices
exceeds the available space at the destination location, then only the available destination devices
will be written to.)
BMOV D5 D10 K3
X0
n
S· D·
D5
D6
D7
D10
D11
D12
n=3
z The BMOV instruction has a built in automatic feature to prevent overwriting errors from
occurring when the source (S-n) and destination (D-n) data ranges coincide. This is clearly
identified in the following diagram:
z (NOTE: The numbered arrows indicate the order in which the BMOV is processed).
D10
D11
D12
D9
D10
D11
D10
D11
D12
D11
D12
D13
①
②
③
③
②
①
Function
[BMOV]
16 bits instruction:BMOV 32bits instruction:-
Suitable Models:
XC1、XC3、XC5
Suitable Device
S·
Word
Device
n
D
FD
DM
DX
DY
DS
TD
CD
K/H
D·
Bit
Device
X
Y
M
S
T
C
Dn.m

 Loading...
Loading...