Applied Instructions
《16 bits operation》
MUL D0 D2 D4
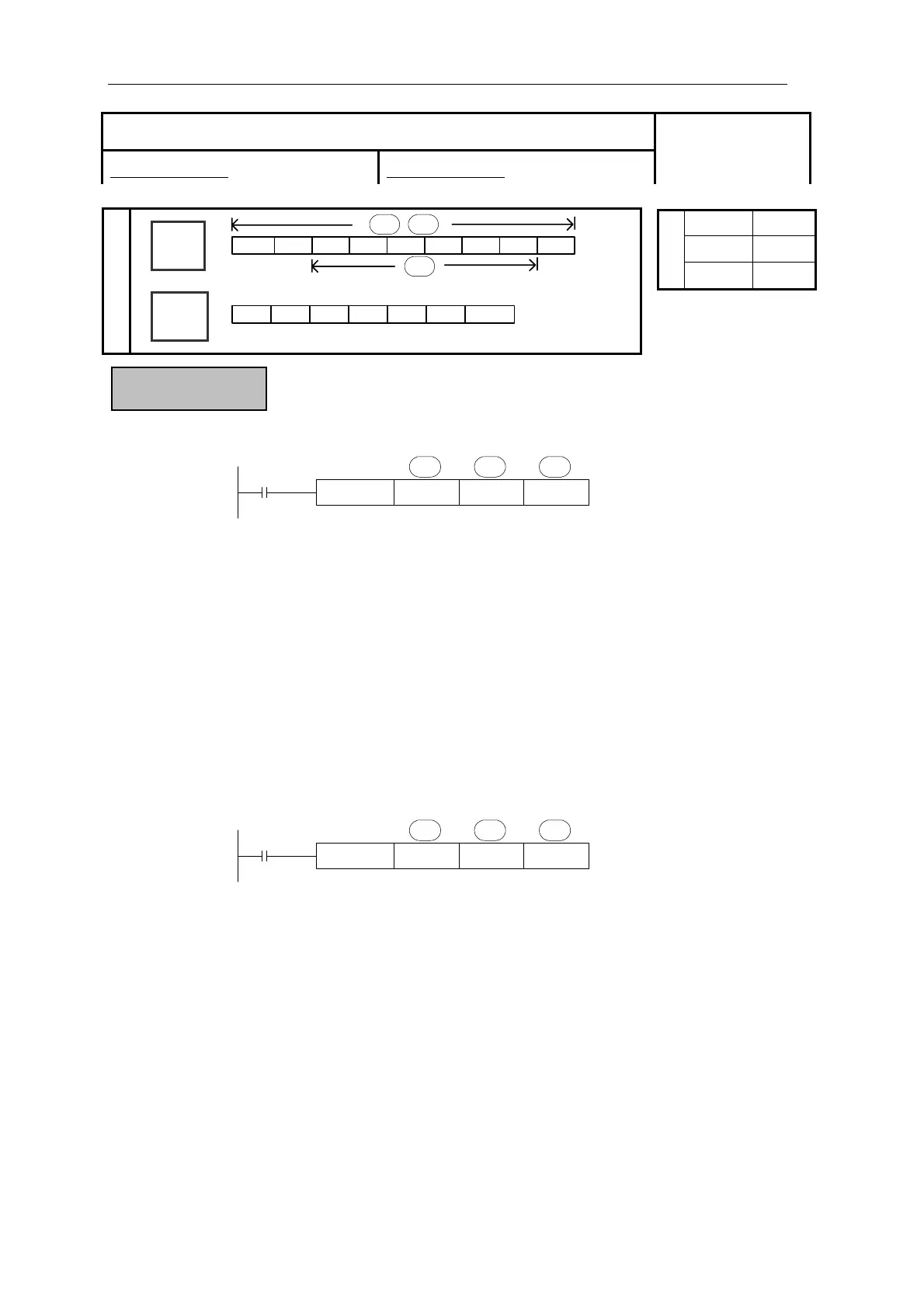
X0
S1· S2· D·
《32 bits operation》
X1
DMUL D0 D2 D4
S1· S2· D·
Function & action
BIN BIN BIN
(D0)
× (D2) → (D5, D4)
16 bits 16 bits
→ 32 bits
BIN BIN BIN
(D1,D0) × (D3,D2) → (D7,D6,D5,D4)
32 bits 32 bits
→ 64 bits
z The content of the two source devices are multiplied together and the result is stored at
the destination device in the format of 32 bits. As in the upward chart: when (D0)=8、
(D2)=9, (D5, D4) =72.
z The result’s highest bit is the symbol bit: positive (0)、negative (1).
z When be bit unit, it can carry on the bit appointment of K1~K8. When appoint K4, only
the result’s low 16 bits can be obtained.
s
z In 32 bits operation, when use bit device as the destination address, only low 32 bits
result can be obtained. The high 32 bits result can not be obtained, so please operate
again after transfer one time to the word device
z Even use word device, 64 bits results can’t be monitored at once.
z In this situation, float point data operation is recommended.
[MUL]
16 bits instruction:MUL 32 bits instruction:DMUL
Suitable Models:
XC1、XC3、XC5
Zero M8020
Borrow M8021
Flag
Carry M8022
Word
Device
Bit
Device
X
Y
M
S
T
C
Dn.m
D
FD
DM
DX
DY
DS
TD
CD
K/H
S1·
S2·
D·
93
 Loading...
Loading...