1.5 MODBUS-RTU PROTOCOL
The Modbus-RTU protocol has been implemented to be as compatible as possible with the original published
Modicon Modbus-RTU standard.
Note: The Modbus protocol allows parameter register access only as defined by the explicit mapping in
this manual. To send the ASCII commands (R000, T`A, MAM, MRS, etc.) that are handled by the other
three protocols, the Modbus Extended Services registers must be used.
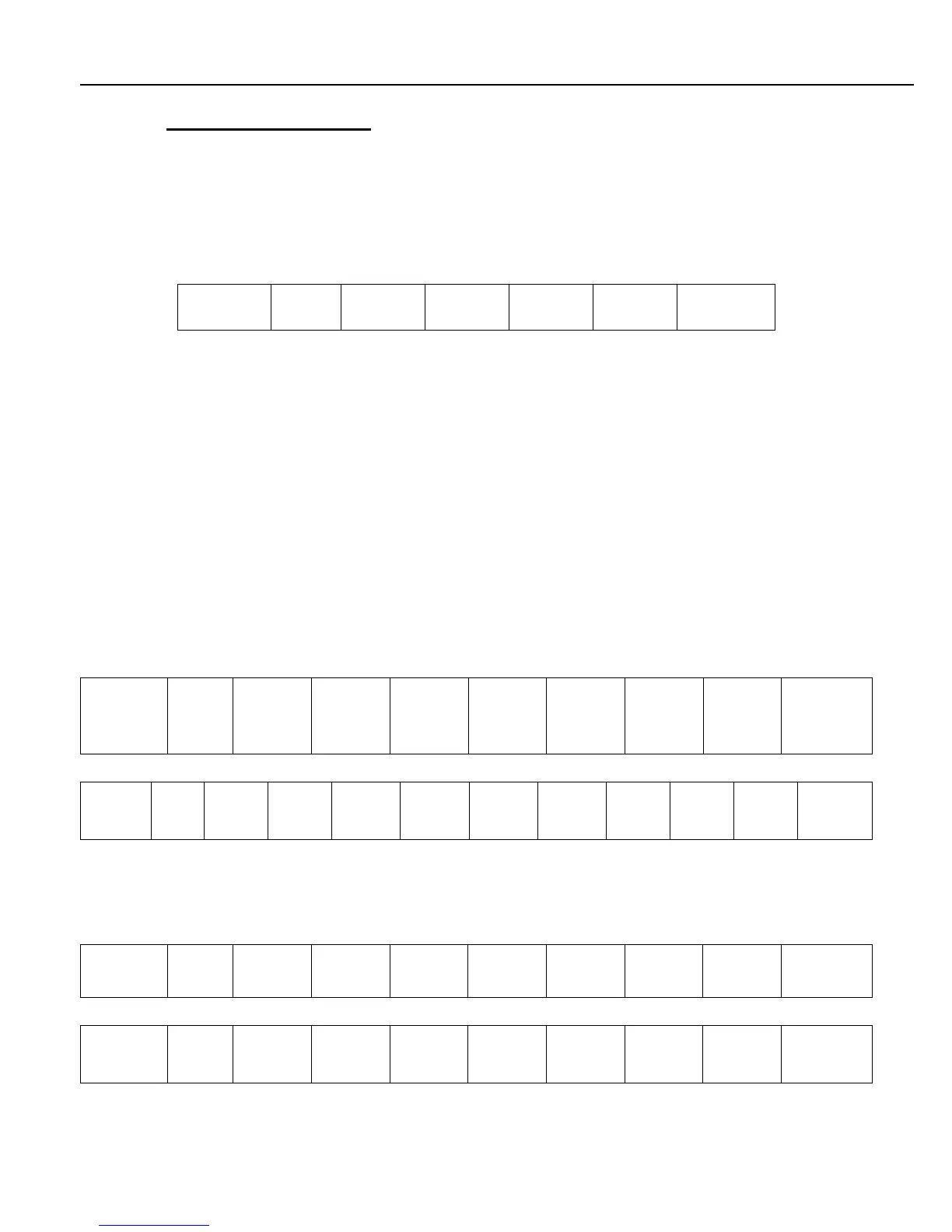
Using the Modbus protocol, MultiLoad accepts data in the following format:
Modbus-RTU protocol messages are framed by a quiet time of three and one-half characters.
ADR is binary character of the address of the MultiLoad. Typically 0x01.
Fn is the Modbus function. Functions implemented are as follows.
The formal specification of Modbus lists the starting Holding Register address as 40001. The Modbus
Holding Register functions (Fn 3, 6 and 16) all have an implied 4XXXX reference. Referencing Holding
Register 40001 is addressed as register 0000 in the register address field in the message for fn 3, 6, and
16.
Since Modbus addressing has been implemented in various ways over the years, to avoid confusion in
this manual, the Modbus Holding Register addresses listed are the value in the register address field in
the message. If it is necessary to know the formal Modbus Holding Register address, simply add 40001
to the register addresses listed in the manual.
1.5.1 READ HOLDING REGISTERS (FN=3)
Note: Both Modbus registers MUST be read at the same time when reading 32-bit values.
Tx:
 Loading...
Loading...