Configuring DHCP Service Configuration Examples
User Guide 425
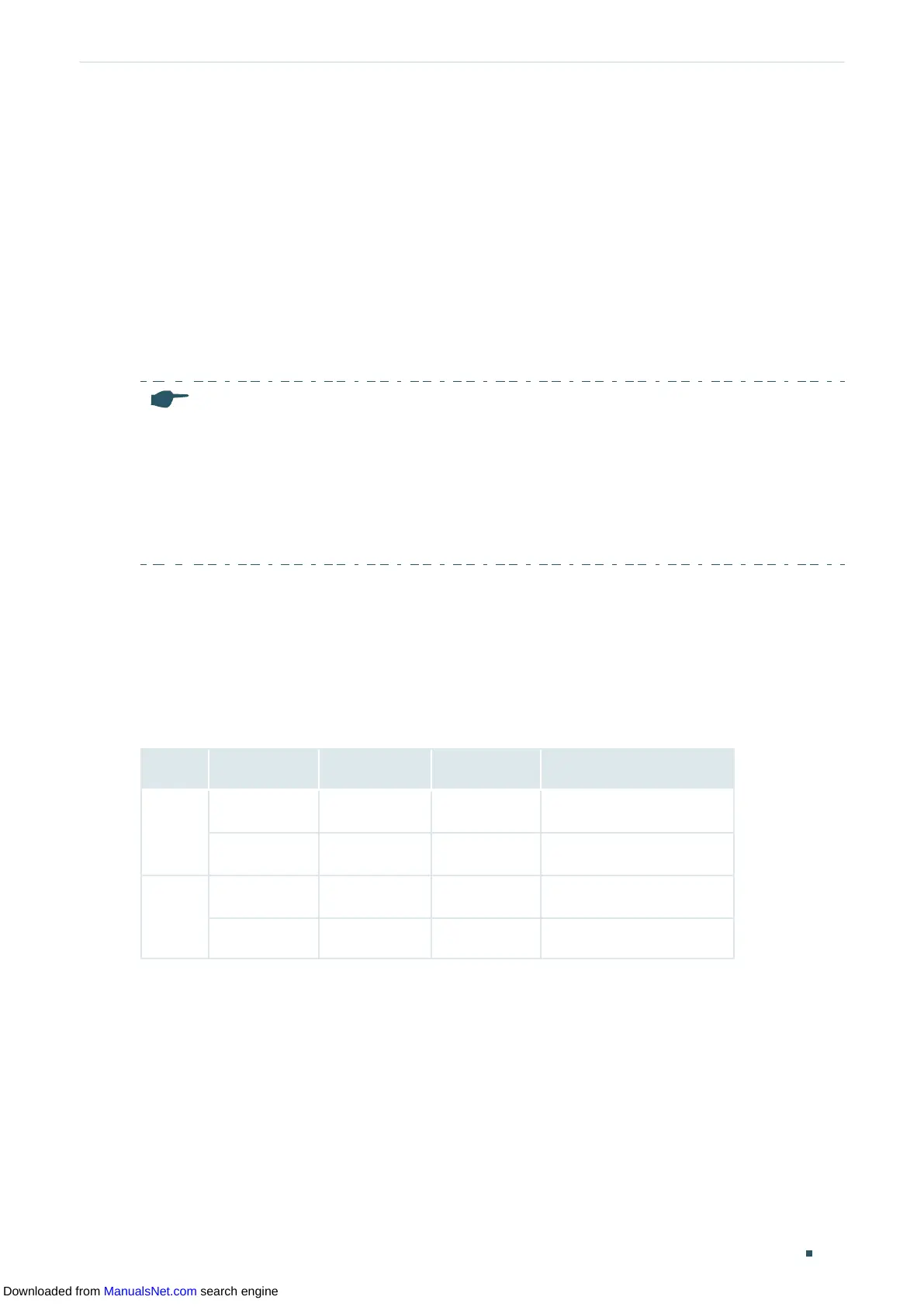
Switch#show ip dhcp relay information interface
Interface Option82 Status Operation Strategy Format Circuit ID ...
--------- ---------------- ------------------ ------- --------- ...
Gi1/0/1 Enable Replace Normal Default:VLAN-PORT ...
Gi1/0/2 Enable Replace Normal Default:VLAN-PORT ...
...
4.2.4 Configuring the DHCP Server
Note:
•
Make sure the DHCP server supports Option82 and more than one DHCP address pool.
•
To make sure the DHCP server can reach the computers, you can create static routes or enable
dynamic routing protocol like RIP on the DHCP server.
•
In this section, we use different notations to distinguish ASCII strings from hexadecimal
numbers. An ASCII string is enclosed with quotation marks, such as “123”, while a hexadecimal
number is divided by colon into parts of two digits, such as 31:32:33.
On the DHCP server, you need to create two DHCP classes to identify the Option 82
payloads of DHCP request packets from Group 1 and Group 2, respectively.
In this example, the DHCP relay agent uses the default circuit ID and remote ID in TLV
format. According to packet formats described in Table 1-1 and Table 1-2, the sub-options
of the two groups are as shown in the following table.
Table 4-1 Sub-options of Group1 and Group 2
Group Sub-option Type (Hex) Length (Hex) Value (Hex)
1
Circuit ID 00 04 00:02:00:01
Remote ID 00 06 00:00:FF:FF:27:12
2
Circuit ID 00 04 00:02:00:02
Remote ID 00 06 00:00:FF:FF:27:12
The configuration file /etc/dhcpd.conf of the Linux ISC DHCP Server is:
ddns-update-style interim;
ignore client-updates;
# Create two classes to match the pattern of Option82 in DHCP request packets from
# Group1 and Group 2, respectively.
# The agent circuit ID inserted by the DHCP relay switch is 6 bytes long in TLV format, one
# byte for Type, one byte for Length, and 4 bytes for Value. Therefore, the offset is 2 and the
length is 4.
Downloaded from ManualsNet.com search engine

 Loading...
Loading...











