Manual 37278B GCP-30 Series - Genset Control
Page 34/174 © Woodward
PID-controller PI-controller
K
PR
= 0.6 × K
Pcrit
K
PR
= 0.45 × K
Pcrit
T
n
= 0.5 × T
crit
T
n
= 0.83 × T
crit
T
V
= 0.125 × T
crit
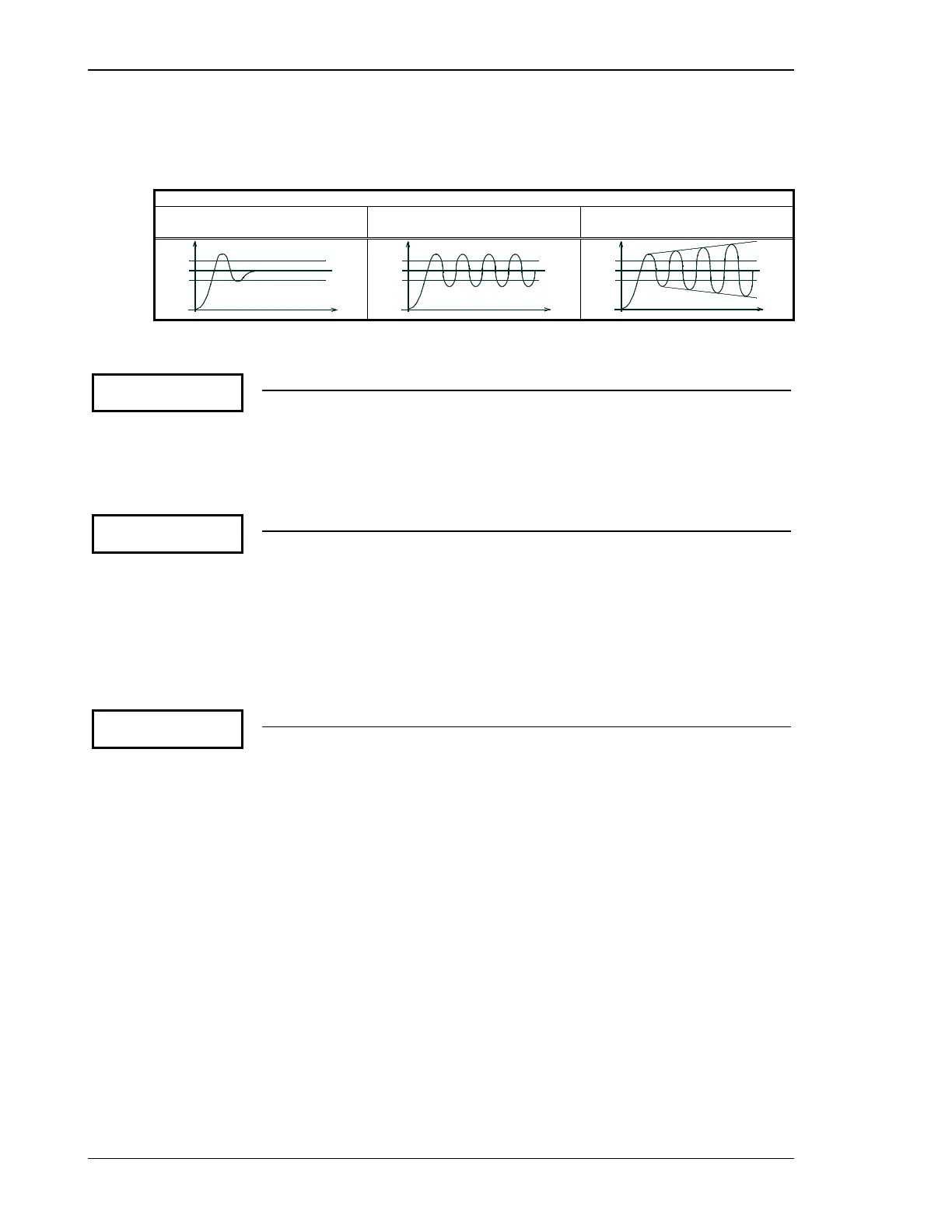
Step response
Controller setting
Optimal (xm ≤ 10 %)
Controller setting
Tcrit
Controller setting
Incorrect
0
1
x
0
t/s
0
0
1
x
t/s
0
1
x
0
t/s
Figure 3-3: Step responds - governor configuration
P-gain
Kpr = 000
P-gain (K
PR
) Proportional-action coefficient 1 to 240
The proportional-action coefficient K
PR
indicates the closed-loop control system
gain. By increasing the gain, the response is increased to permit larger corrections
to the variable to be controlled. The farther out of tolerance the process is the larger
the response action is to return the process to the tolerance band. If the gain is con-
figured too high, the result is excessive overshoot/undershoot of the desired value.
Reset time
Tn = 00.0s
Reset time (T
n
) 0.2 to 60.0 s
The reset time T
n
represents the I-component of the PID controller. The reset time
corrects for any offset (between set point and process variable) automatically over
time by shifting the proportioning band. Reset automatically changes the output re-
quirements until the process variable and the set point are the same. This parameter
permits the user to adjust how quickly the reset attempts to correct for any offset.
The reset time constant must be greater than the derivative time constant. If the re-
set time constant is too small, the engine will continually oscillate. If the reset time
constant is too large, the engine will take to long to settle at a steady state.
Derivative time
Tv=0.00s
Derivative-action time (T
V
) 0.00 to 6.00 s
The derivative-action time T
V
represents the D-component of the PID controller.
By increasing this parameter, the stability of the system is increased. The controller
will attempt to slow down the action of the actuator in an attempt to prevent exces-
sive overshoot or undershoot. Essentially this is the brake for the process. This por-
tion of the PID loop operates anywhere within the range of the process unlike reset.

 Loading...
Loading...











