1.2 b: Application
60 YASKAWA ELECTRIC SIEP C710606 10A YASKAWA AC Drive - V1000 PRELIM. Programming Manual
■ I Control
The output of I control is the integral of the deviation. It minimizes the offset between target
and feedback value that typically remains when pure P control is used. The integral time (I-
time) constant determines how fast the offset is eliminated.
■ D Control
D control predicts the deviation signal by multiplying its derivative (slope of the deviation)
with a time constant and adding this to the PID input. This way the D portion of a PID
controller provides a braking action to the controller response and can reduce the tendency
of oscillations and overshoot.
Be aware that D control tends to amplify noise on the deviation signal, which can result in
control instability. D control should therefore only be used when necessary.
■ PID Operation
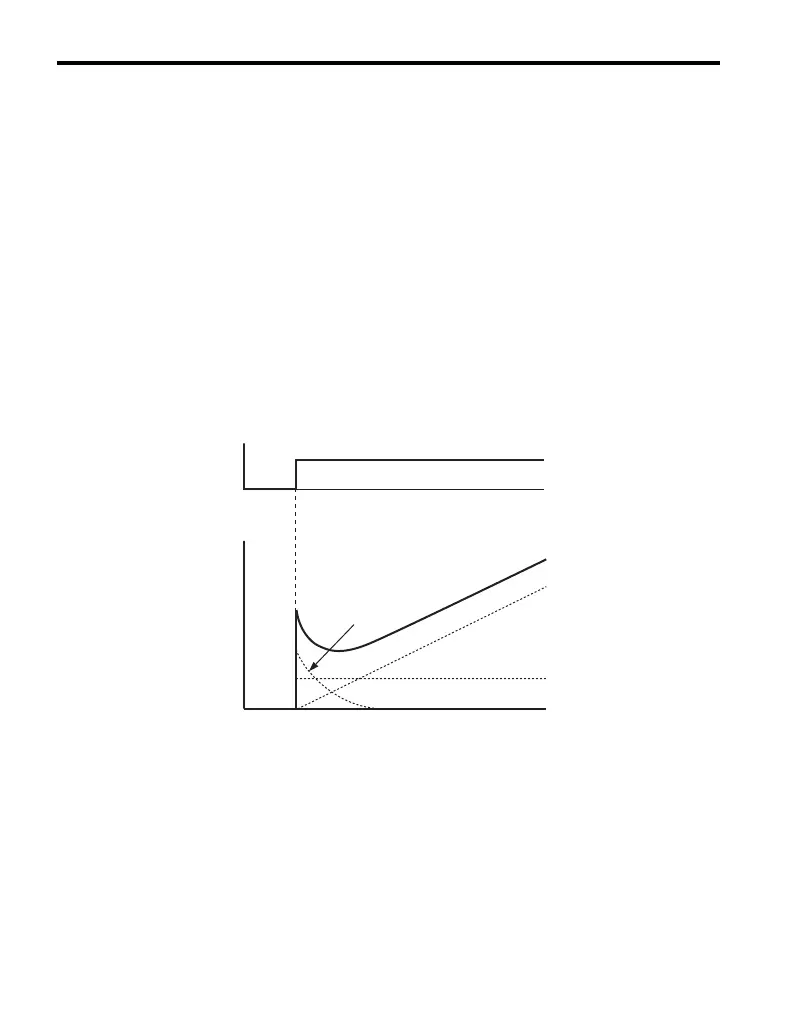
To better demonstrate how PID works, the diagram below shows how the PID output
changes when the PID input (deviation) jumps from 0 to a constant level.
Figure 1.18
Figure 1.18 PID Operation
■ Using PID Control
Applications for PID control are listed in the table below.
PID input
I control
PID Output
D control
Time
PID output
Time
P control

 Loading...
Loading...