3.2 I/O Signal Connections
3.2.1 I/O Signal Connector (CN1) Names and Functions
3-5
3
Wiring and Connecting SERVOPACKs
* You can change the allocations. Refer to the following section for details.
6.2.1 Input Signal Allocations on page 6-3
Note: 1. Pin numbers in parentheses ( ) indicate signal grounds.
2. If forward drive prohibition or reverse drive prohibition is used, the SERVOPACK is stopped by software
controls. If the application does not satisfy the safety requirements, add external safety circuits as required.
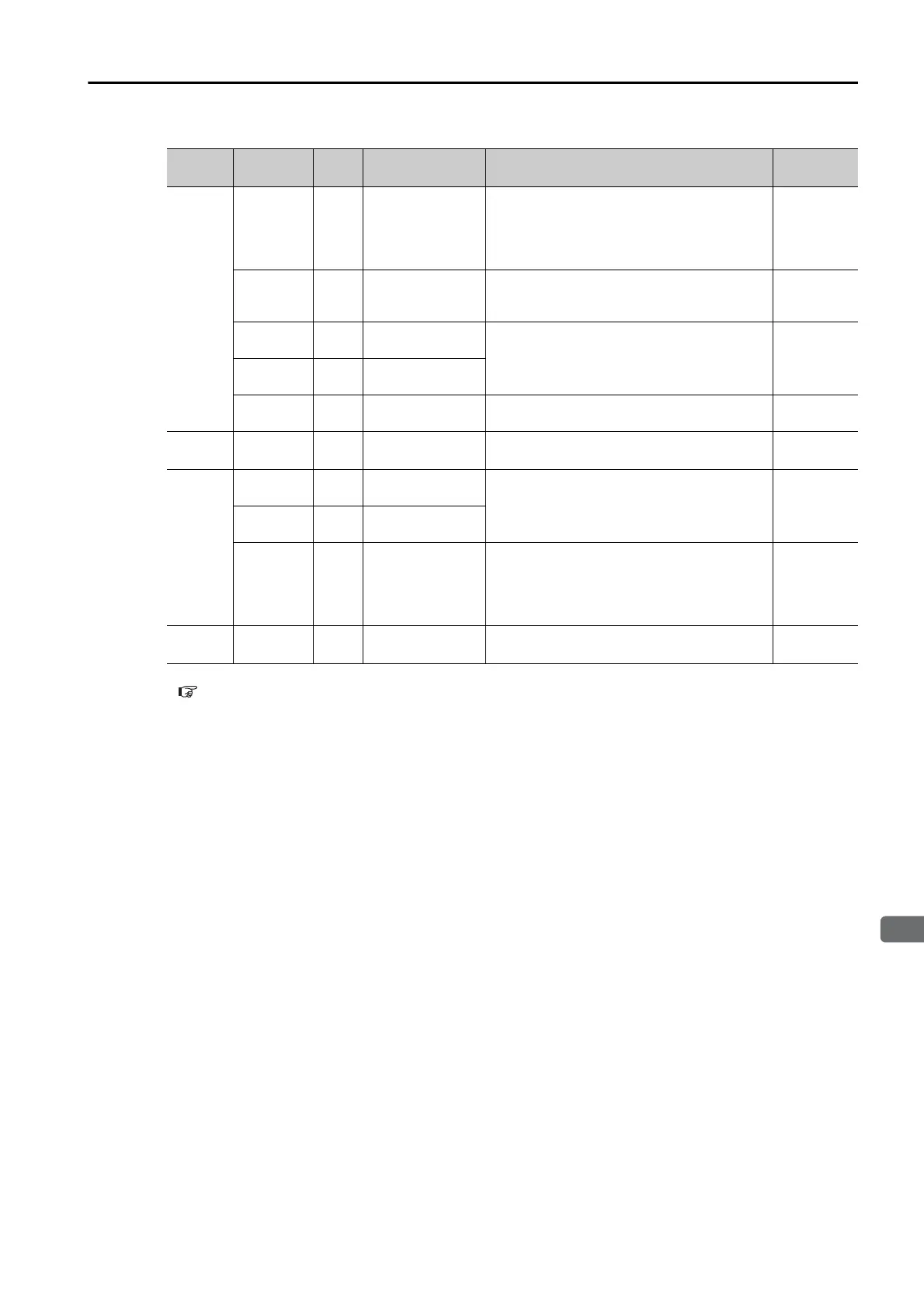
Any
Control
Method
+24VIN 47
Sequence Input
Signal Power
Supply Input
Inputs the sequence input signal power
supply.
Allowable voltage range: 24 VDC ±20%
The 24-VDC power supply is not provided
by Yaskawa.
−
SEN 4 (2)
Absolute Data
Request Input
(SEN)
Inputs the overheat protection signal from a
Linear Servomotor.
−
BAT+ 21
Battery for abso-
lute encoder (+)
These are the pins to connect the absolute
encoder backup battery.
Do not connect these pins if you use the
Encoder Cable with a Battery Case.
−
BAT- 22
Battery for abso-
lute encoder (-)
TH 50
Overheat Protec-
tion Input
Inputs the overheat protection signal from a
Linear Servomotor.
−
Speed
Control
V-REF 5 (6)
Speed Reference
Input
Inputs the speed reference. Maximum input
voltage: ±12 V
−
Position
Control
PULS
/PULS
7
8
Pulse Reference
Input
One of the following input pulse forms is set.
• Sign + pulse train
• CW + CCW pulse trains
• 90° phase-differential pulses
−
SIGN
/SIGN
11
12
Sign of Reference
Input
SI8(DEC)
/SI8(/DEC)
15
14
General-purpose
Sequence Input 8
(Homing
Deceleration
Switch Input)
You can allocate the input signal to use with
a parameter.
The homing speed is changed to the
approach speed or creep speed.
page 6-5
Torq ue
Control
T-REF 9 (10)
Torq u e R ef e r-
ence Input
Inputs the torque reference. Maximum input
voltage: ±12 V
−
Continued from previous page.
Control
Method
Signal
Pin
No.
Name Function
Reference
Page

 Loading...
Loading...











