Getting Started
17
When the IP phones are simply plugged into the network, the DHCP process begins. The
IP phones broadcast DISCOVER messages to request the network information carried in
DHCP options and the DHCP server responds with the specific values in the
corresponding options.
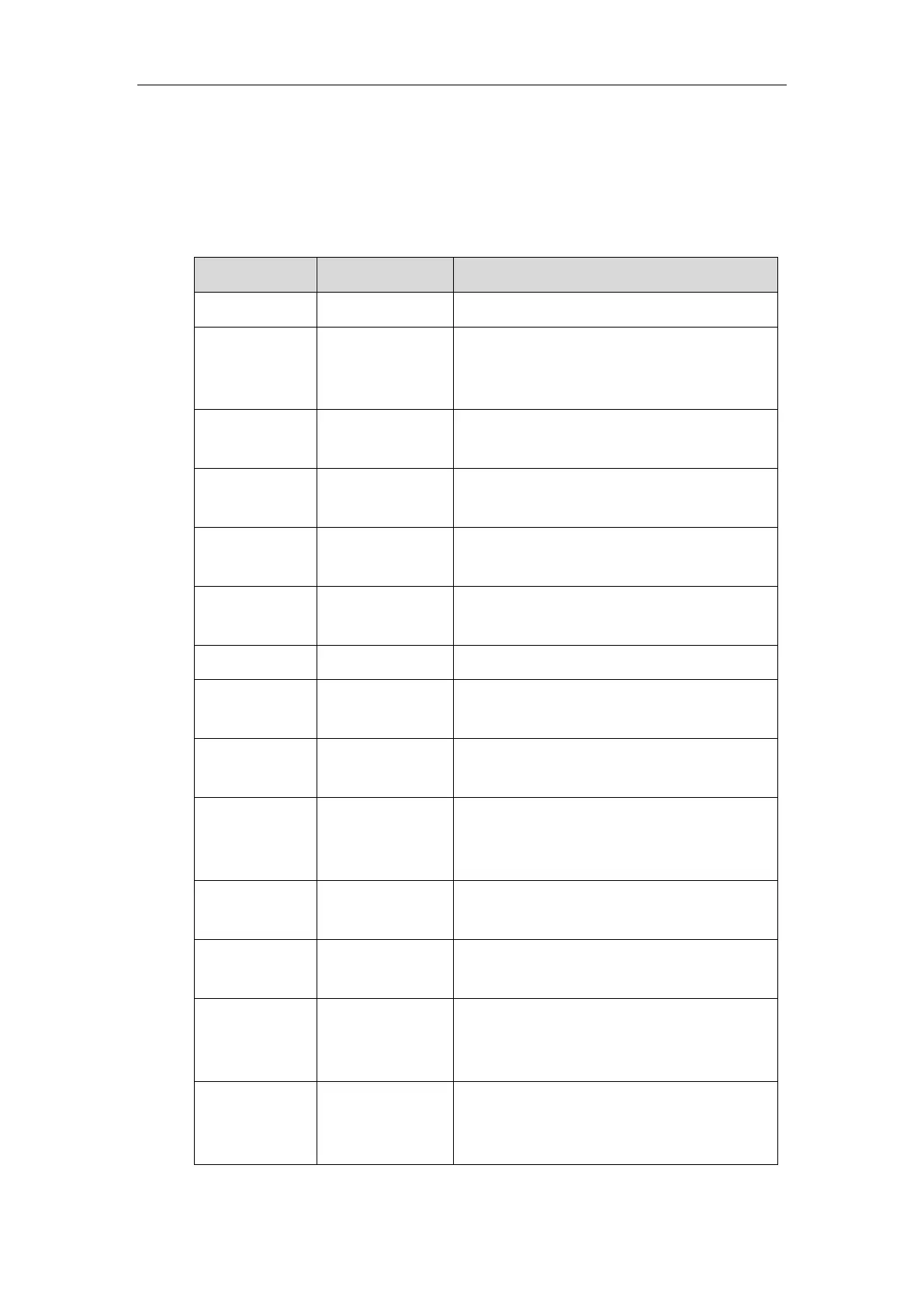
The following table lists the common DHCP options supported by the IP phones.
Specify the client’s subnet mask.
Specify the offset of the client's subnet in
seconds from Coordinated Universal Time
(UTC).
Specify a list of IP address for routers on the
client’s subnet.
Specify a list of time servers available to the
client.
Specify a list of domain name servers
available to the client.
Specify a list of MIT-LCS UDP servers
available to the client.
Specify the name of the client.
Specify the domain name that client should
use when resolving hostnames via DNS.
Specify the broadcast address in use on the
client's subnet.
Network Time
Protocol
Servers
Specify a list of the NTP servers available to
the client by IP address.
Vendor-Specific
Information
Identify the vendor-specific information.
Identify the vendor type.
Identify a TFTP server when the 'sname' field
in the DHCP header has been used for DHCP
options.
Identify a bootfile when the 'file' field in the
DHCP header has been used for DHCP
options.
 Loading...
Loading...






