USER MANUAL | ICOS | INSTRUCTIONS | UM/ICOS-EN REV. B.2
Appendix A: About Gas Analyzers and
Laser Absorption Spectroscopy
Conventional Laser Absorption Spectroscopy
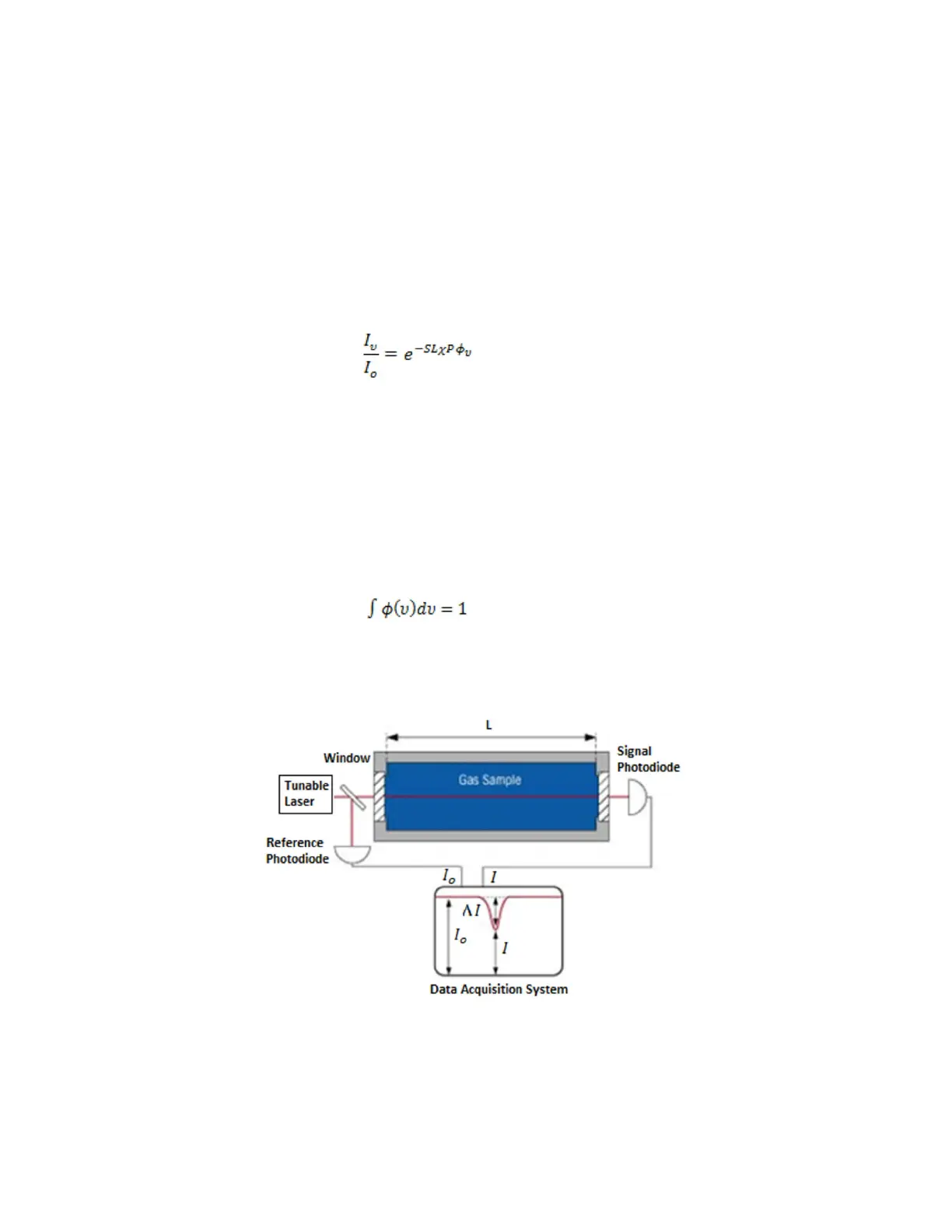
For gas measurements based on conventional laser-absorption spectroscopy (Figure 56), a
laser beam is directed through a sample, and the mixing ratio (or mole fraction) of a gas is
determined from the measured absorption using Beer’s Law, which may be expressed:
Where:
I
v
is the transmitted intensity through the sample at frequency
I
o
is the (reference) laser intensity prior to entering the cell
S is the absorption line strength of the probed transition
L is the optical path length of the laser beam through the sample
is the mole fraction
P is the gas pressure
Φ
v
is the line-shape function of the transition at frequency
In this case,
If the laser line width is much narrower than the width of the absorption feature, high-
resolution absorption spectra may be recorded by tuning the laser wavelength over the
probed feature.
Figure 56: Typical Laser Absorption Spectroscopy Setup

 Loading...
Loading...