688 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-RM003N-EN-P - October 2011
Appendix C Structured Text Programming
Description: The syntax is described in the table.
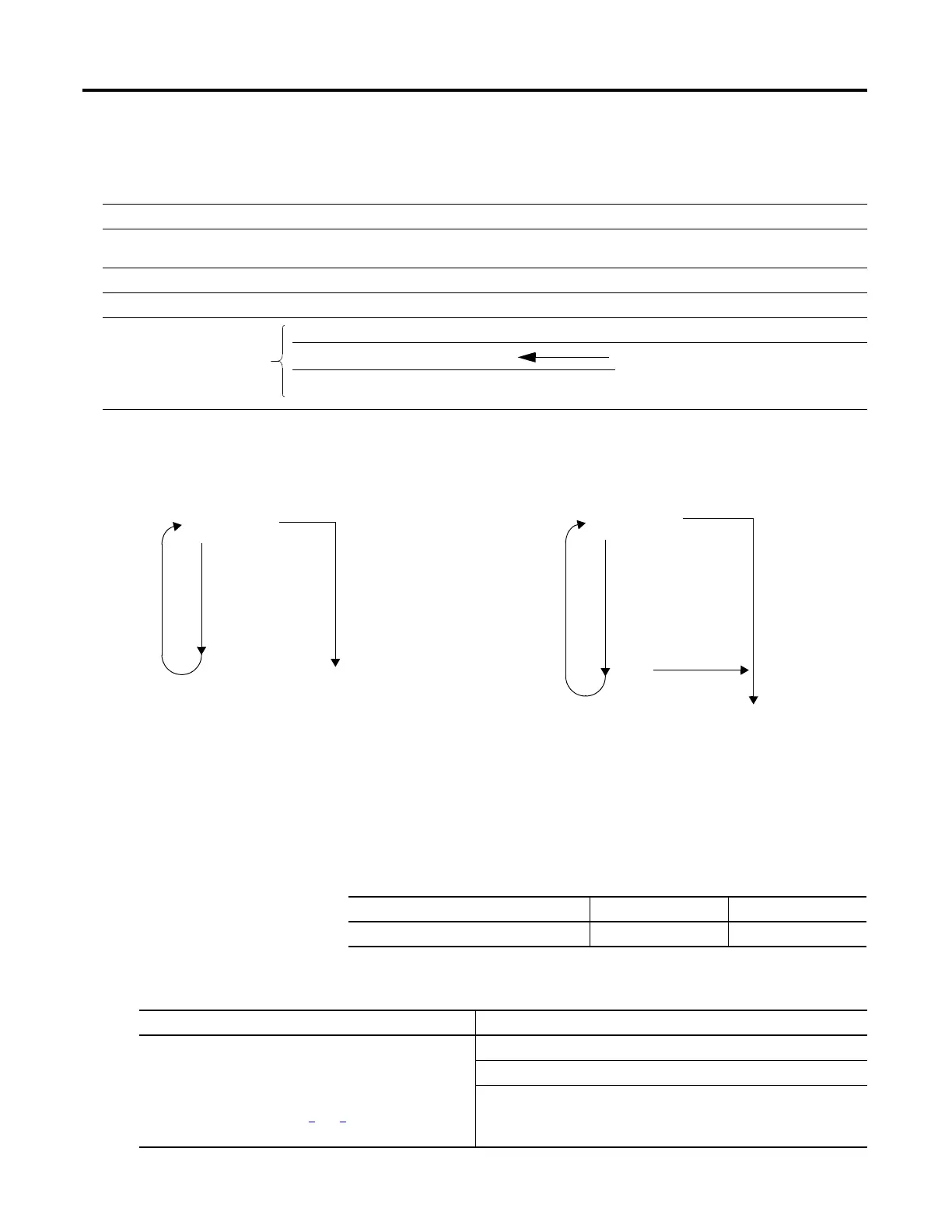
The following diagrams show how a FOR...DO loop executes and how an EXIT
statement leaves the loop early.
Arithmetic Status Flags: Not affected
Fault Conditions:
Example 1:
FOR count := initial_value
TO final_value
Optional { BY increment If you don’t specify an increment, the loop
increments by 1.
DO
<statement>;
Optional IF bool_expression THEN
EXIT; If there are conditions when you want to exit
the loop early, use other statements, such as an
IF...THEN construct, to condition an EXIT
statement.
END_IF;
END_FOR;
Statement 1
Statement2
Statement 3
Statement 4
…
Done x Number
Of Times?
No
Yes
Rest Of The Routine
Statement 1
Statement 2
Statement 3
Statement 4
…
Exit ?
Done x Number
Of Times?
No
Yes
Rest Of The Routine
Yes
No
The FOR…DO loop executes a specific number of
times.
To stop the loop before the count reaches the last value, use
an EXIT statement.
A major fault will occur if Fault type Fault code
The construct loops too long. 6 1
If you want this Enter this structured text
Clear bits 0…31 in an array of BOOLs:
1. Initialize the subscript tag to 0.
2. Clear array[ subscript ] . For example, when
subscript = 5, clear array[5].
3. Add 1 to subscript.
4. If subscript is ≤ to 31, repeat 2
and 3.
Otherwise, stop.
For subscript:=0 to 31 by 1 do
array[subscript] := 0;
End_for;

 Loading...
Loading...











