Installation and Operation
Targets Status Protocol - IF3 Interface
DV16401.03 Issue 04 May 2021 BD406/PBD406 75
Communication Description
Packet Description
• All bytes have 8-bit data.
• Bits are numerated from 0 (bit 0 is least significant bit - LSB).
• Bytes are numerated from 0.
• Byte 0 is the first byte in the sequence.
• The smallest information interchanged through a physical channel is a byte.
• Bytes are grouped into blocks called packet.
• A packet can carry single frame from the transmission protocol.
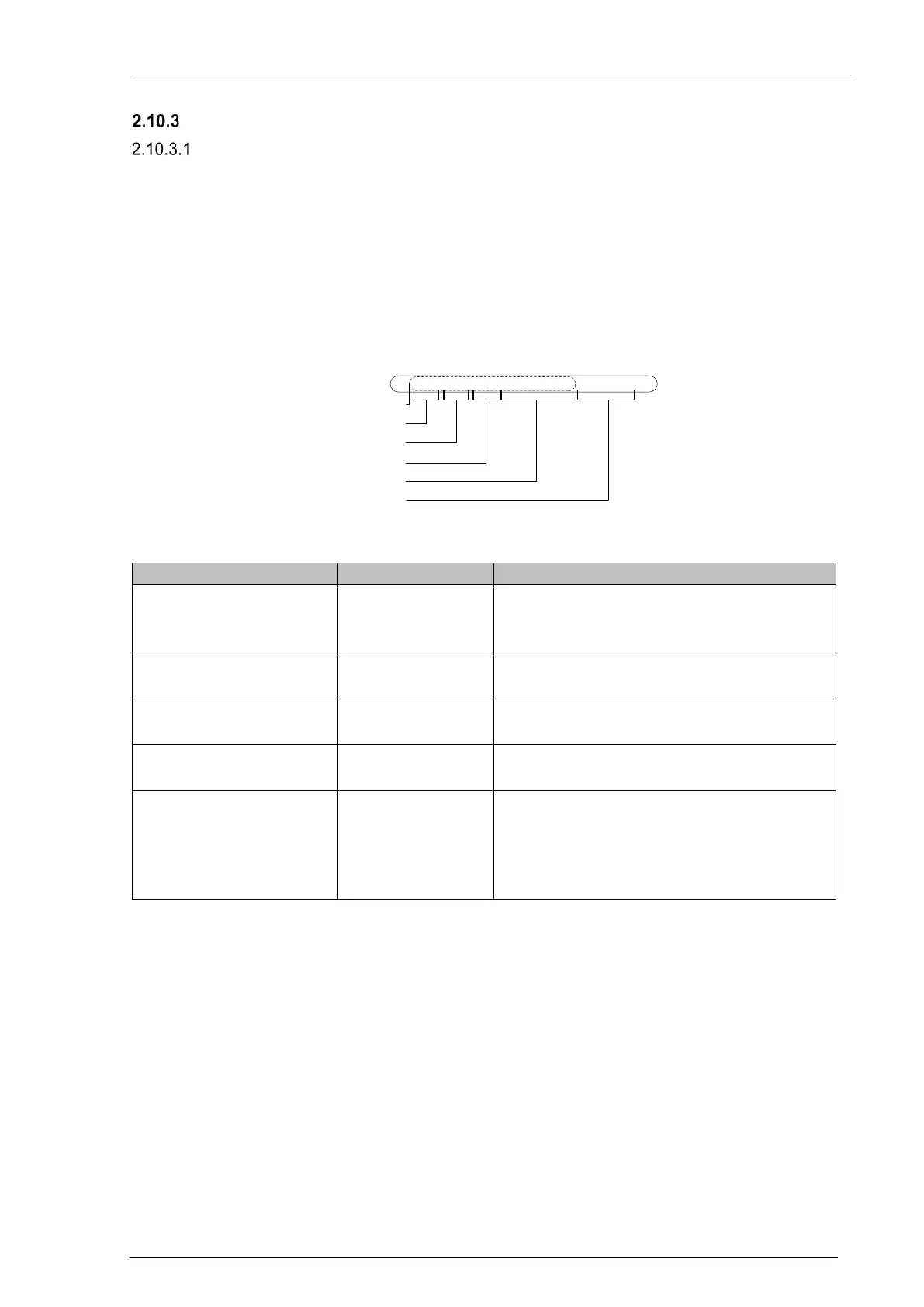
Structure of a packet:
Packet Header
Protocol ID
Frame Length
Frame
Packet CRC
0xA5 0x1C 0x45 0xXX … 0xZZ 0xAA 0xBB
Packet
CRC protected
Figure 32: Target Status Protocol - Packet Description
First byte of the packet.
Packet always begins with packet header.
Always equal to: 0xA5.
Always equal to: 0x1C
Frame field length in bytes.
Permitted value: 0x00..0xFF
Permitted value for each byte: 0x00..0xFF
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) see "Packet
CRC Definition" page 80.
The packet CRC is transmitted with MSB first.
It is used for packet integrity protection.
Permitted value for each byte: 0x00..0xFF
Table 2: Target Status Protocol - Packet Description

 Loading...
Loading...