APPENDIX B — EN 13849 COMPLIANCE, CURTIS 1226 CONTROLLER
Curtis Model 1226 – September 2019
Return to TOC
pg. 88
APPENDIX B — EN 13849 COMPLIANCE,
CURTIS 1226 CONTROLLER
Since January 1, 2012, conformance to the European Machinery Directive has required that the Safety
Related Parts of the Control System (SRPCS) be designed and veried upon the general principles
outlined in EN13849. EN13849 supersedes the EN954 standard and expands upon it by requiring
the determination of the safety Performance Level (PL) as a function of Designated Architecture
plus Mean Time To Dangerous Failure (MTTFd), Common Cause Faults (CCF), and Diagnostic
Coverage (DC). ese gures are used by the OEM to calculate the overall PL for each of the safety
functions of their vehicle or machine.
e OEM must determine the hazards that are applicable to their vehicle design, operation, and
environment. Standards such as EN13849-1 provide guidelines that must be followed in order to
achieve compliance. Some industries have developed further standards (called type-C standards) that
refer to EN13849 and specically outline the path to regulatory compliance. EN1175-1 is a type-C
standard for battery-powered industrial trucks. Following a type-C standard provides a presumption
of conformity to the Machinery Directive.
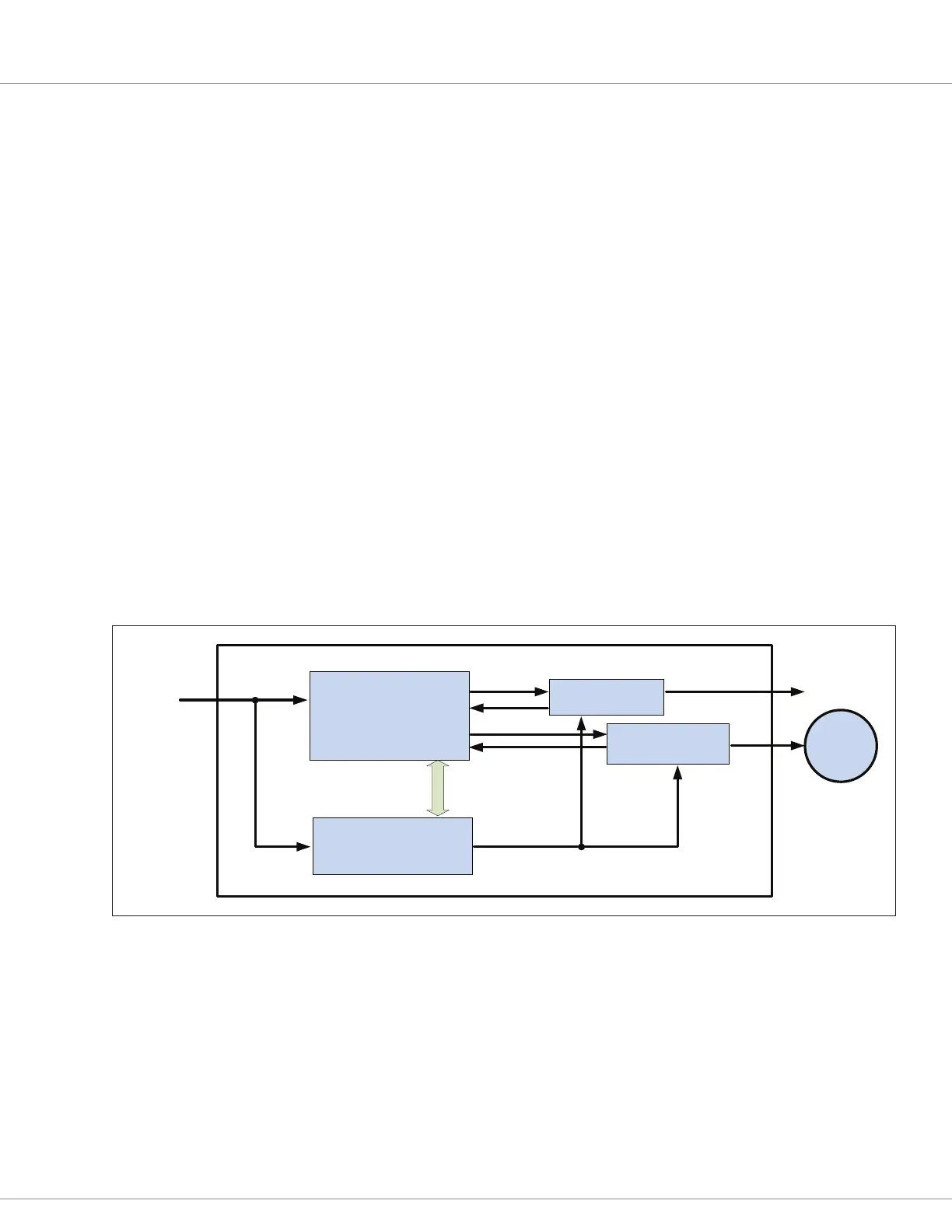
Curtis 1226 controllers comply with these directives using advanced active supervisory techniques;
see the simplied block diagram in Figure 15.
PRIMARY MOTOR
CONTROL
MICROPROCESSOR
SUPERVISOR
MICROPROCESSOR
DRIVERS
POWERBASE
Communicaon
Link
Motor
Outputs
Monitor
Monitor
Shutdown
Inputs
Figure 15
Safety channel block diagram, Curtis 1226 controller
To mitigate the hazards typically found in machine operations, EN13849 requires that safety functions
be dened; these must include all the input, logic, outputs, and power circuits that are involved in
any potentially hazardous operation. Two safety functions are dened for Curtis 1226 controllers:
Uncommanded Powered Motion and Motor Braking Torque.
e Uncommanded Powered Motion safety function provides detection and safe shutdown in the
following circumstances: faulted throttle; improper sequence of forward/reverse switches, throttle,
and interlock; uncommanded movement; or movement at startup. The Motor Braking Torque
safety function provides detection and safe shutdown in the event of the loss of braking torque or
emergency reverse.

 Loading...
Loading...