144
Inbound interface: GigabitEthernet2/0/2
State: ICMP_REPLY
Application: INVALID
Start time: 2012-08-15 14:53:29 TTL: 12s
Initiator->Responder: 1 packets 84 bytes
Responder->Initiator: 1 packets 84 bytes
Total sessions found: 1
Outbound bidirectional NAT configuration example
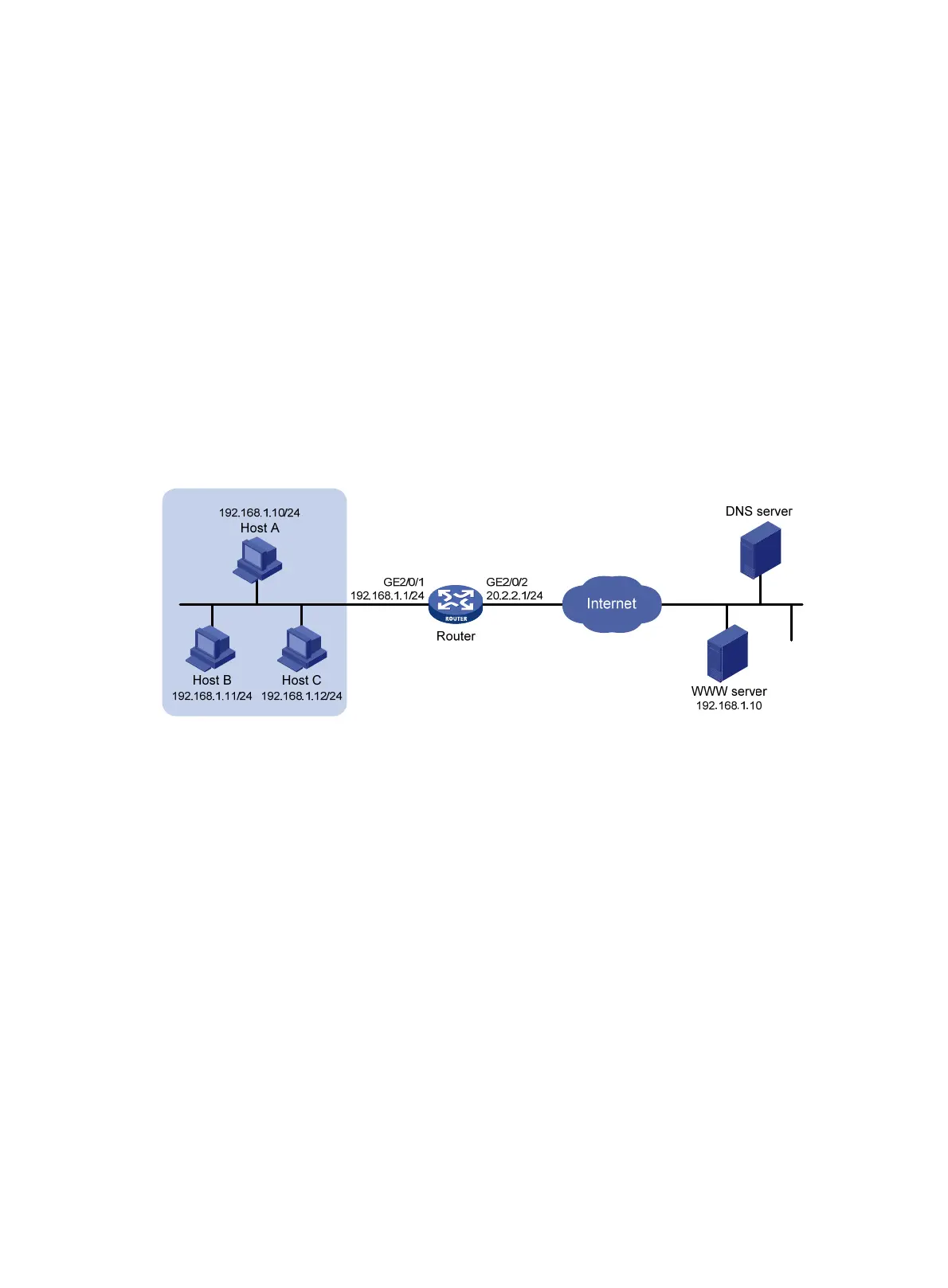
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 65, the private network where the Web server resides overlaps with the company
private network 192.168.1.0/24. The company has two public IP addresses 202.38.1.2 and
202.38.1.3. Configure NAT to allow internal users to access the external Web server by using the
server's domain name.
Figure 65 Network diagram
Requirements analysis
To meet the network requirements, you must perform the following tasks:
• Configure inbound dynamic NAT with ALG to make sure the internal host reaches the Web
server instead of another internal host. NAT with ALG can translate the Web server's IP address
in the DNS reply payload to a dynamically assigned public address.
• Configure outbound dynamic NAT to translate the source IP address of packets from an internal
host to a dynamically assigned public address.
• Add a static route to the public IP address of the external Web server.
Configuration procedure
# Specify IP addresses for the interfaces on the router. (Details not shown.)
# Enable NAT with ALG and DNS.
<Router> system-view
[Router] nat alg dns
# Configure ACL 2000, and create a rule to permit packets only from subnet 192.168.1.0/24 to pass
through.
[Router] acl basic 2000
[Router-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
[Router-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] quit
 Loading...
Loading...