299
• Automatic tunnels do not support dynamic routing. You must configure a static route destined
for the destination IPv6 network if the destination IPv6 network is not in the same subnet as the
IPv6 address of the tunnel interface. You can specify the local tunnel interface as the egress
interface of the route or specify the IPv6 address of the peer tunnel interface as the next hop of
the route. For more information about route configuration, see Layer 3—IP Routing
Configuration Guide.
To configure a 6to4 tunnel:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter 6to4 tunnel
interface view.
interface tunnel
number [
mode
ipv6-ipv4 6to4
]
N/A
3. Specify an IPv6 address
for the tunnel interface.
See "Configuring basic IPv6
settings."
By default, no IPv6 address is
configured for the tunnel interface.
4. Configure a source
address or source
interface for the tunnel
interface.
source
{ ip-address | interface-type
interface-number }
By default, no source address or
source interface is configured for
the tunnel interface.
The specified source address or
the primary IP address of the
specified source interface is used
as the source IP address of
tunneled packets.
5. (Optional.) Set the DF bit
for tunneled packets.
tunnel dfbit enable
By default, the DF bit is not set for
tunneled packets.
6. Return to system view.
quit
N/A
7. (Optional.) Enable
dropping IPv6 packets
that use IPv4-compatible
IPv6 addresses.
tunnel discard
ipv4-compatible-packet
By default, IPv6 packets that use
IPv4-compatible IPv6 packets are
not dropped.
6to4 tunnel configuration example
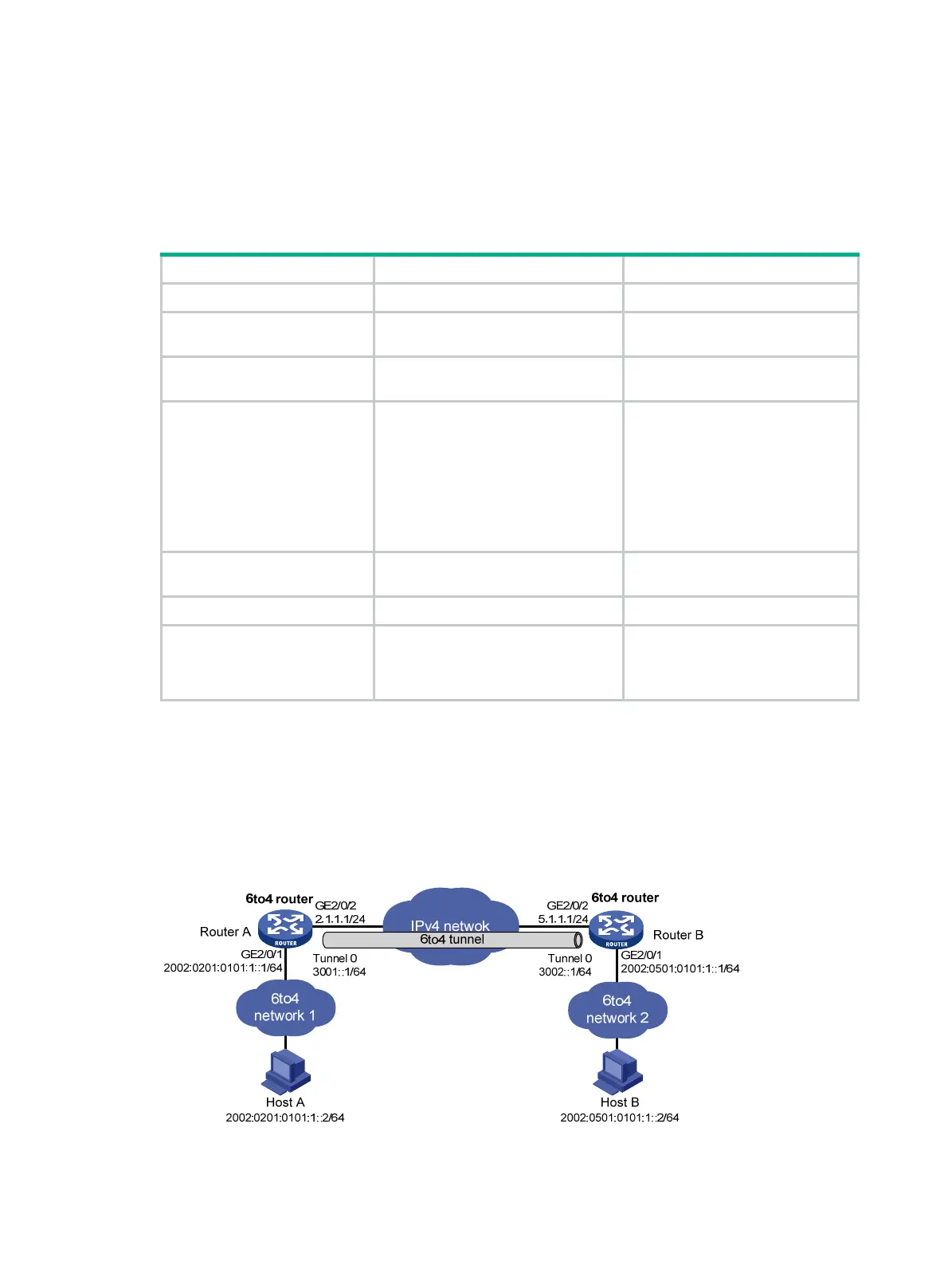
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 124, configure a 6to4 tunnel between 6to4 routers Router A and Router B so
Host A and Host B can reach each other over the IPv4 network.
Figure 124 Network diagram
 Loading...
Loading...