297
Configuring an automatic IPv4-compatible IPv6
tunnel
Follow these guidelines when you configure an automatic IPv4-compatible IPv6 tunnel:
• You do not need to configure a destination address for an automatic IPv4-compatible IPv6
tunnel. The destination address of the tunnel is embedded in the destination IPv4-compatible
IPv6 address.
• Do not specify the same source addresses for local tunnel interfaces in the same tunnel mode.
To configure an automatic IPv4-compatible IPv6 tunnel:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter automatic
IPv4-compatible IPv6 tunnel
interface view.
interface tunnel
number [
mode
ipv6-ipv4 auto-tunnel
]
N/A
3. Specify an IPv6 address for
the tunnel interface.
See "Configuring basic IPv6
settings."
B
y default, no IPv6 address is
configured for the tunnel interface.
4. Configure a source address
or source interface for the
tunnel interface.
source
{ ip-address |
interface-type interface-number }
By default, no source address or
source interface is configured for
the tunnel interface.
The specified source address or
the primary IP address of the
specified source interface is used
as the source IP address of
tunneled packets.
5. (Optional.) Set the DF bit for
tunneled packets.
tunnel dfbit enable
By default, the DF bit is not set for
tunneled packets.
6. Return to system view.
quit
N/A
Configuration example
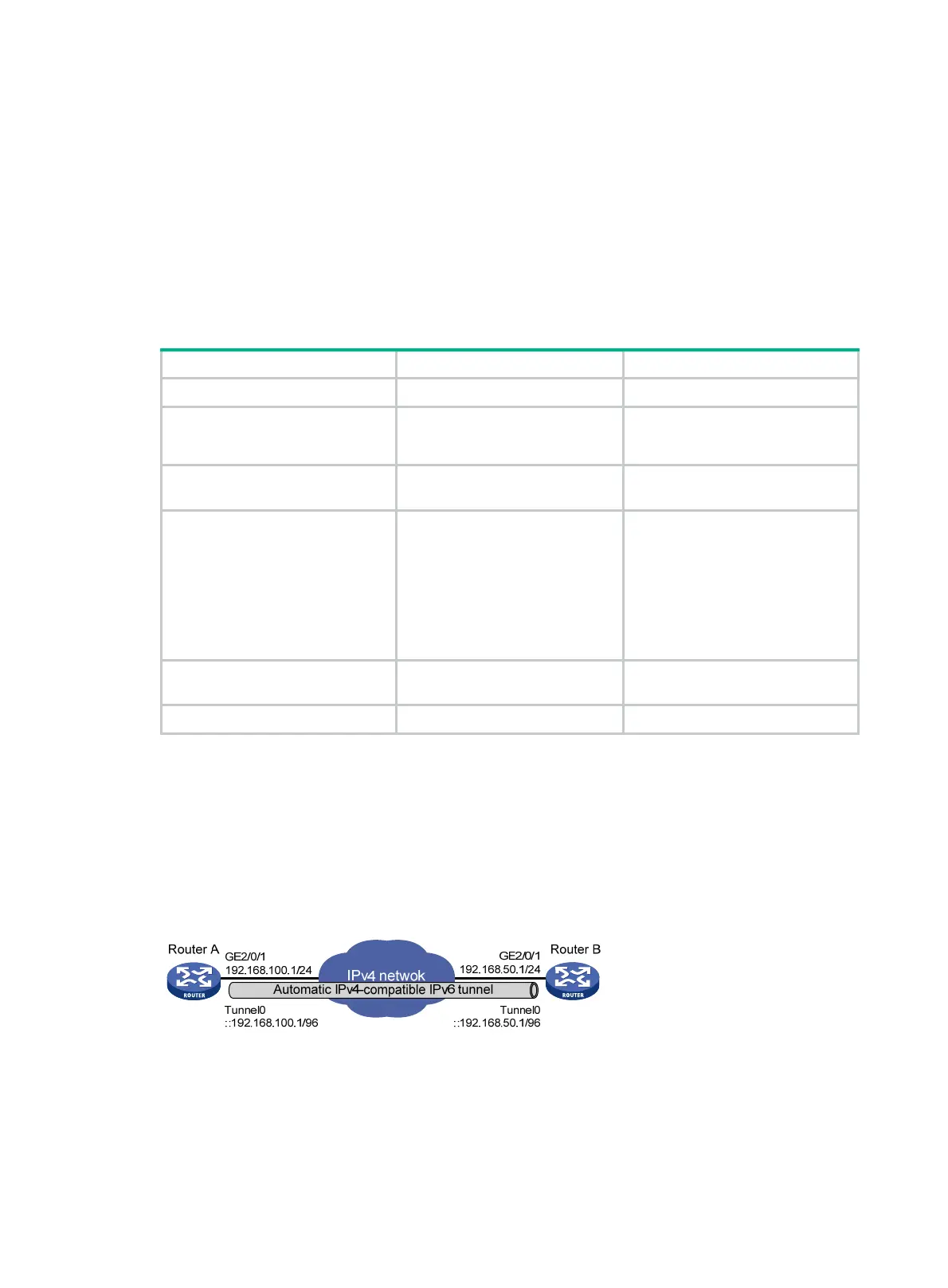
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 123, dual-stack routers Router A and Router B communicate over an IPv4
network. Configure an automatic IPv4-compatible IPv6 tunnel between the two routers to enable
IPv6 communications over the IPv4 network.
Figure 123 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
Make sure Router A and Router B can reach each other through IPv4.
• Configure Router A:
# Specify an IPv4 address for GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
<RouterA> system-view

 Loading...
Loading...