230
Task Command
IRF mode).
Clear IPv6 and ICMPv6 packet statistics (distributed
devices in IRF mode).
reset ipv6 statistics
[
chassis
chassis-number
slot
slot-number ]
Clear IPv6 TCP traffic statistics.
reset tcp statistics
Clear IPv6 UDP traffic statistics.
reset udp statistics
IPv6 configuration examples
Basic IPv6 configuration example
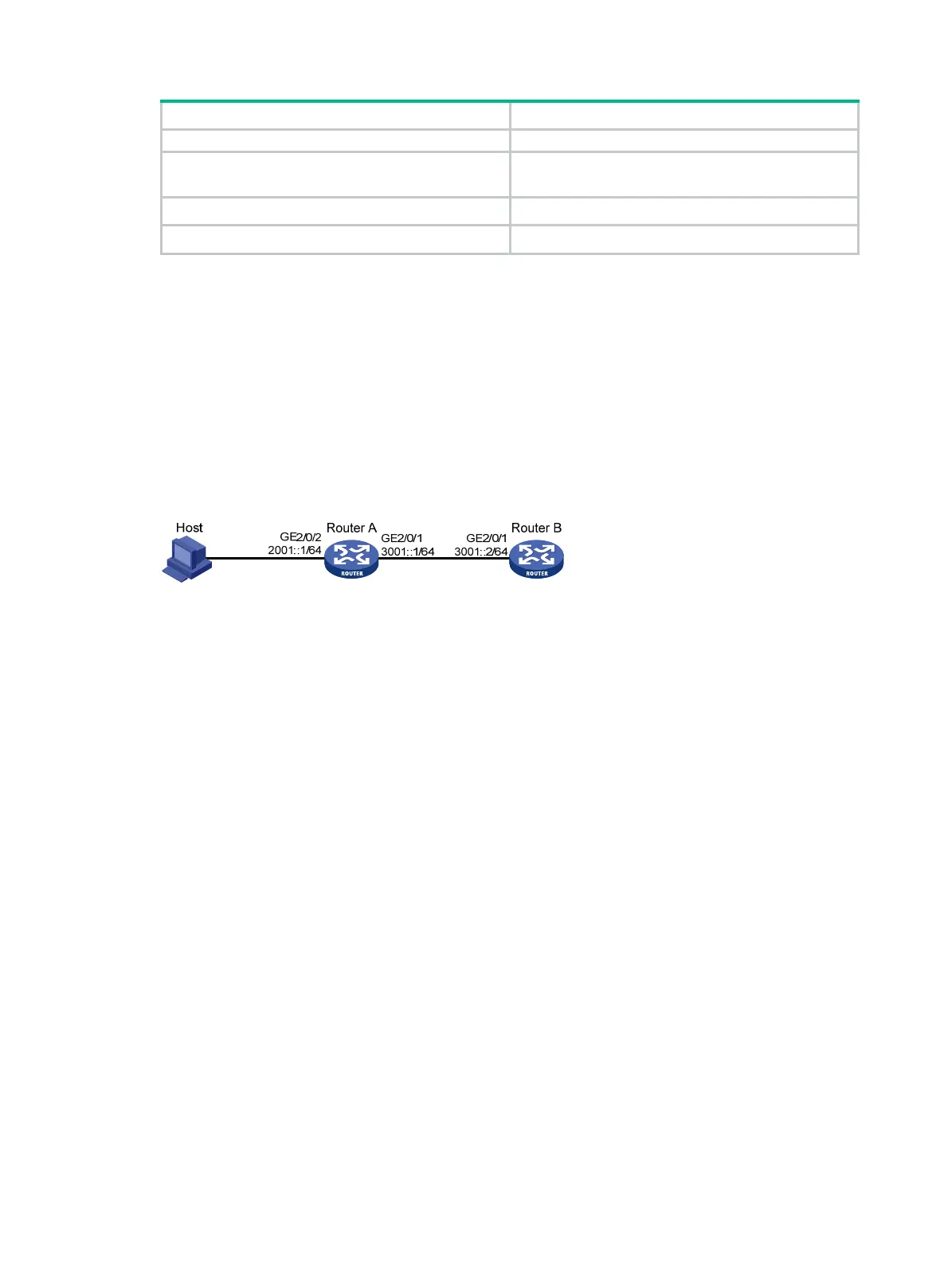
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 90, configure IPv6 addresses for the routers and verify that they can reach each
other. Configure a route to the host on Router B. Enable IPv6 for the host to automatically obtain an
IPv6 address through IPv6 ND. The host has a route to Router B.
Figure 90 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure Router A:
# Configure a global unicast address for interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ipv6 address 3001::1/64
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Configure a global unicast address for interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/2 and enable it to
advertise RA messages (an interface does not advertises RA messages by default).
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/2
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] ipv6 address 2001::1/64
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] undo ipv6 nd ra halt
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] quit
2. Configure Router B:
# Configure a global unicast address for interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ipv6 address 3001::2/64
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Configure an IPv6 static route to the host.
[RouterB] ipv6 route-static 2001:: 64 3001::1
3. Configure the host:
Enable IPv6 on the host to automatically obtain an IPv6 address through IPv6 ND.
# Display neighbor information for GigabitEthernet 2/0/2 on Router A.

 Loading...
Loading...