7914FDE.fm Draft Document for Review March 28, 2011 12:24 pm
452 IBM System Storage DS3500: Introduction and Implementation Guide
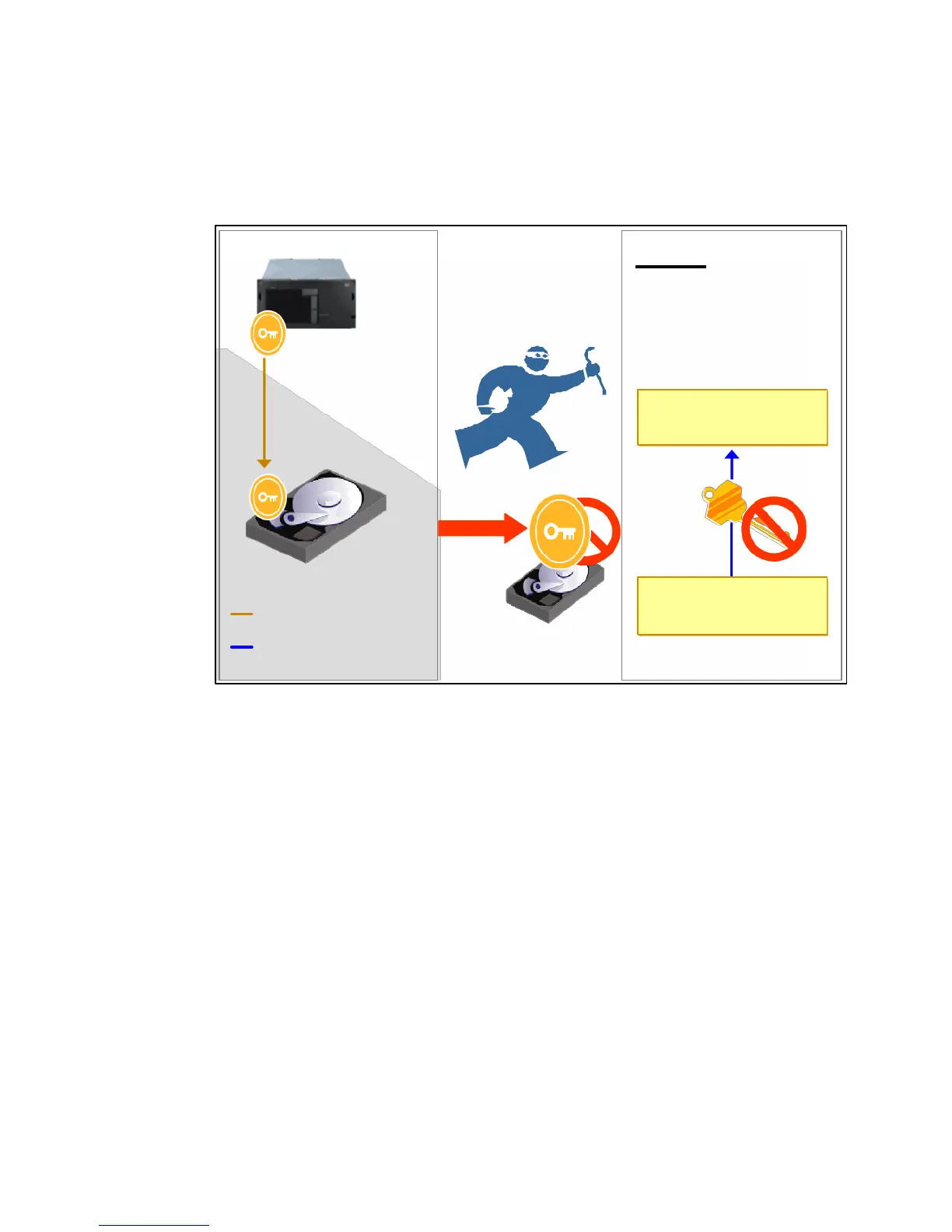
With this relationship, the correct keys, and authentication, the FDE drive will encrypt data
written and decrypt data read from it. But if the disk is removed and data on the disk is
attempted to be read, as shown in Figure 15-2, the user will not have the appropriate
authorizations, as data cannot be read from or written to the drive without authenticating with
the DS3500 Disk Encryption Manager, which will unlock the drive.
Figure 15-2 Unauthorized access to the drive results in the data remaining encrypted
15.2 Disk Security components
There are a number of new components to this new feature that are detailed in this section.
All of these features are managed by the Storage Manager (V10.70.x and higher).
15.2.1 DS3500 Disk Encryption Manager
The Disk Encryption Manager on the DS3500 system maintains and controls the key linkage
and communications with FDE drives. It will be included with the firmware and Storage
Manager. It:
Provides all the management tools necessary to quickly and simply enable and secure
FDE drives.
Establishes and manages a single authorization scheme for all the FDE drives in a
DS3500 storage subsystem.
– Places FDE drives in a secured state.
– Defines secure arrays.
– Supports the decommissioning or re-purposing of drives with Instant Secure Erase.
IBM DS3500 Disk Encryption
Manager
Self-encrypting Drive
Reading from the Drive
Decryption Process
Data Flow
Authorization Flow
Data on Drive
Data
Encrypt ion
Key
Data cannot be read if
authorization fails
%$#@ßde??ff???s?d%
$#@j&&6544IY899#@&$

 Loading...
Loading...











