Intel® Server Board S2600WF Product Family Technical Product Specification
121
B.1. Early POST Memory Initialization MRC Diagnostic Codes
Memory initialization at the beginning of POST includes multiple functions: discovery, channel training,
validation that the DIMM population is acceptable and functional, initialization of the IMC and other
hardware settings, and initialization of applicable RAS configurations.
The MRC progress codes are displayed to the diagnostic LEDs that show the execution point in the MRC
operational path at each step.
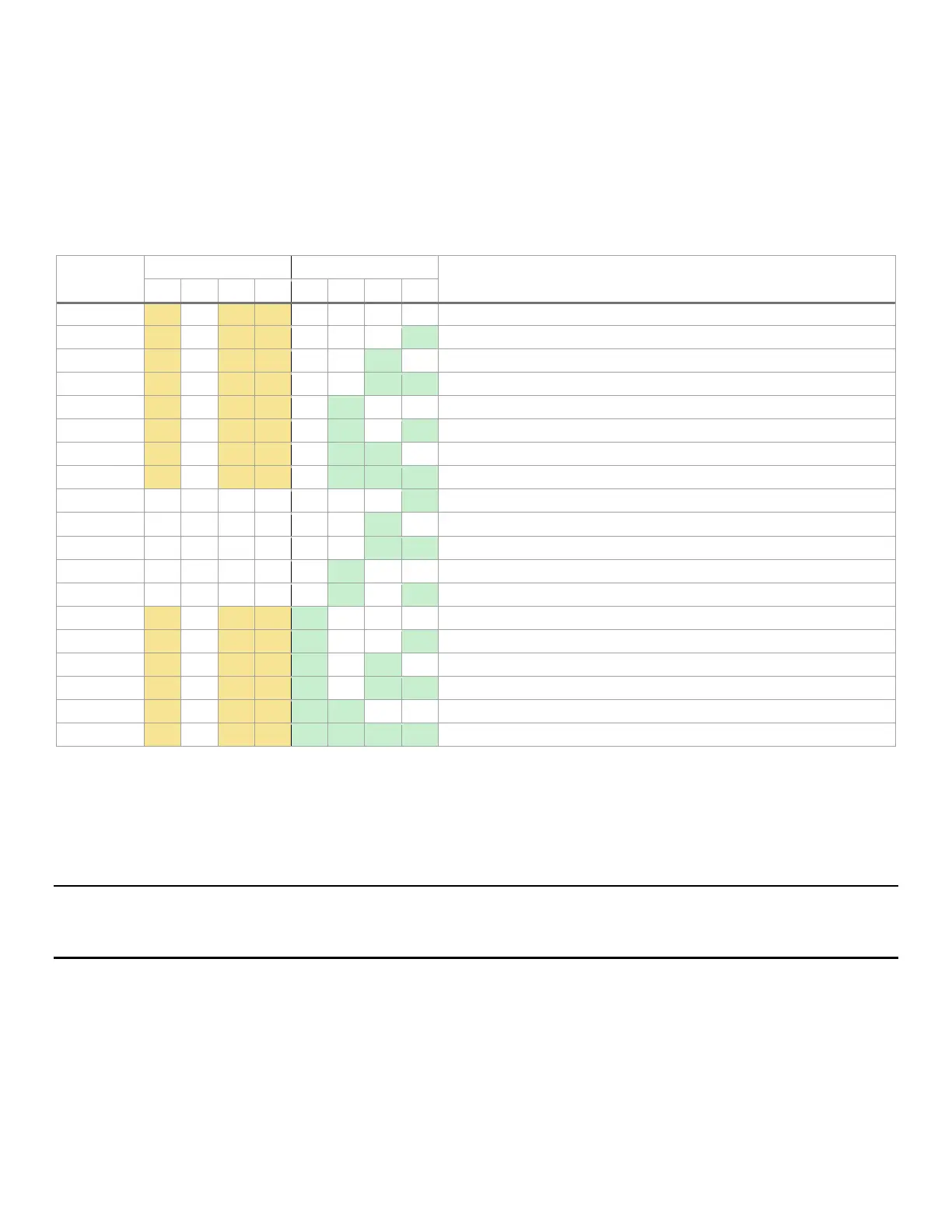
Table 53. MRC progress codes
Post Code
Gather remaining SPD data
Program registers on the memory controller level
Evaluate RAS modes and save rank information
Program registers on the channel level
Perform the JEDEC defined initialization sequence
Train DDR4 ranks – Read DQ/DQS training
Train DDR4 ranks – Receive enable training
Train DDR4 ranks – Write leveling training
Train DDR4 ranks – DDR channel training done
Hardware memory test and init
Execute software memory init
Program memory map and interleaving
Program RAS configuration
Should a major memory initialization error occur, preventing the system from booting with data integrity, a
beep code is generated, the MRC displays a fatal error code on the diagnostic LEDs, and a system halt
command is executed. Fatal MRC error halts do not change the state of the system status LED and they do
not get logged as SEL events. Table 54 lists all MRC fatal errors that are displayed to the diagnostic LEDs.
Note: Fatal MRC errors display POST error codes that may be the same as BIOS POST progress codes
displayed later in the POST process. The fatal MRC codes can be distinguished from the BIOS POST progress
codes by the accompanying memory failure beep code of three long beeps as identified in
Table 57.
 Loading...
Loading...