7.5 Localizing a signal source (Outdoor)
Narda IDA-3106 139
7.5 Localizing a signal source (Outdoor)
This section describes the typical procedure for localizing a signal source
outdoors. You can find detailed information about individual functions such
as Average Position and Distance under The Map menu on page 143. You
can find a description of how to localize a signal source indoors under
Finding the location of a signal scource (Indoor) on page 154.
You can determine the location of a signal source in two ways:
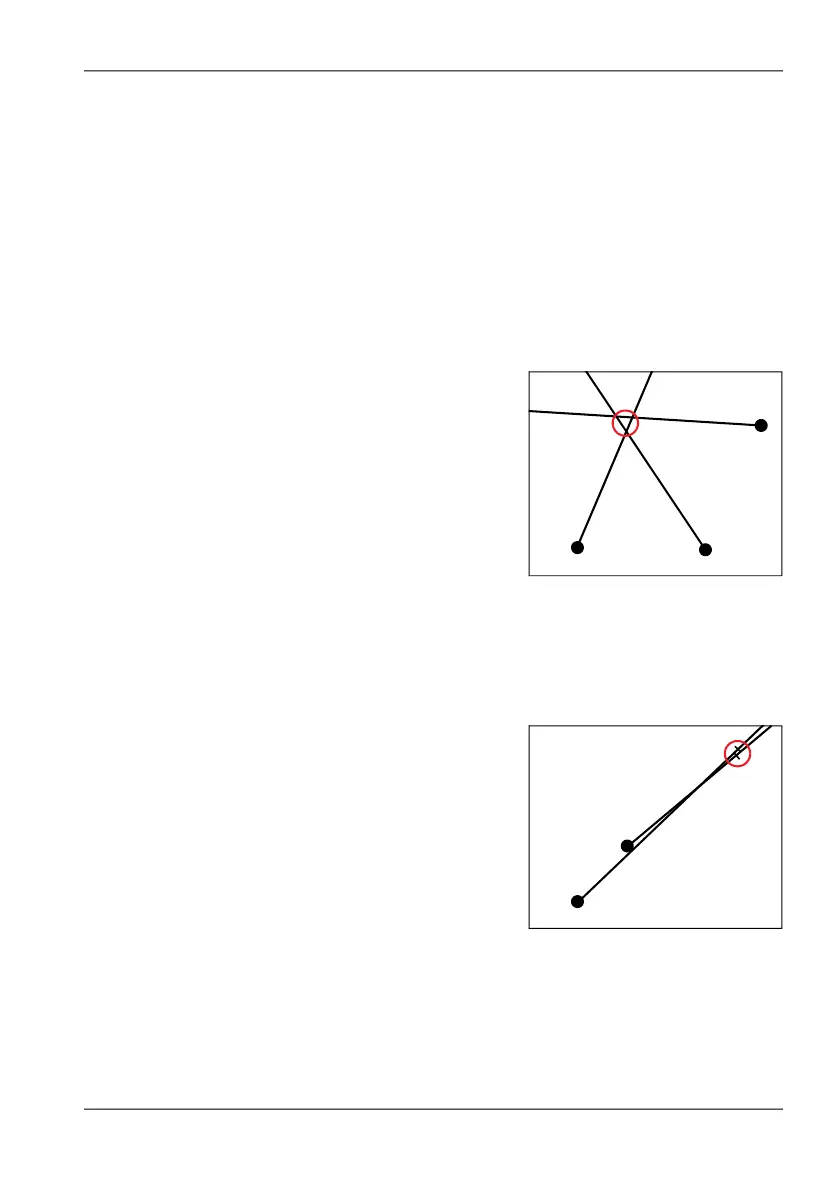
By triangulation
If you take bearings on a signal source
from several different locations, the
bearing lines will intersect within a small
area. The signal source is in this area. It
does not matter whether you have
determined the bearings from
Manual Bearing or Horizontal Scan. You
can determine the location on the basis of
the bearings using the Average Position
function in the Map menu.
NOTE: Triangulation is invalid if the bearings do not intercept or the angle between
the bearings is too acute. Choosing a different location may help you to get
a valid result.
From the distance
It can be time-consuming and require
travel over long distances to take
bearings on a signal source from different
locations. As an alternative, the power
level of the signal source can be
measured in the direction of the source
from two points far enough apart so that
the location can be determined from the
direction and the difference in signal
levels. The Distance function in the Map
menu is provided for this purpose. This method does require that the source
signal level is constant and that reflections are small (this is critical in street
canyons, for example).
A
B
C
A
B
 Loading...
Loading...