8-39
8 Pulse Outputs
CJ2M CPU Unit Pulse I/O Module User’s Manual
8-5 Defining the Origin
8
8-5-1 Origin Searches
8-5 Defining the Origin
The CJ2 CPU Units have two methods that can be used to define the origin position.
• Origin searches
The ORG(889) instruction outputs pulses to turn the motor according to the pattern specified in the
origin search parameters. As the motor turns, the origin search function defines the origin from the
following three position input signals.
• Origin input signal
• Origin proximity input signal
• CW limit input signal and CCW limit input signal
• Changing the present value of the pulse output
When setting the current position as the origin, execute INI(880) to reset the pulse output PV to 0.
When the ORG(889) instruction executes an origin search, it outputs pulses to actually move the motor
and defines the origin position using the input signals that indicate the origin proximity and origin posi-
tions. The input signals that indicate the origin position can be received from the servomotor's built-in
phase-Z signal or external sensors, such as photoelectric sensors, proximity sensors, or limit switches.
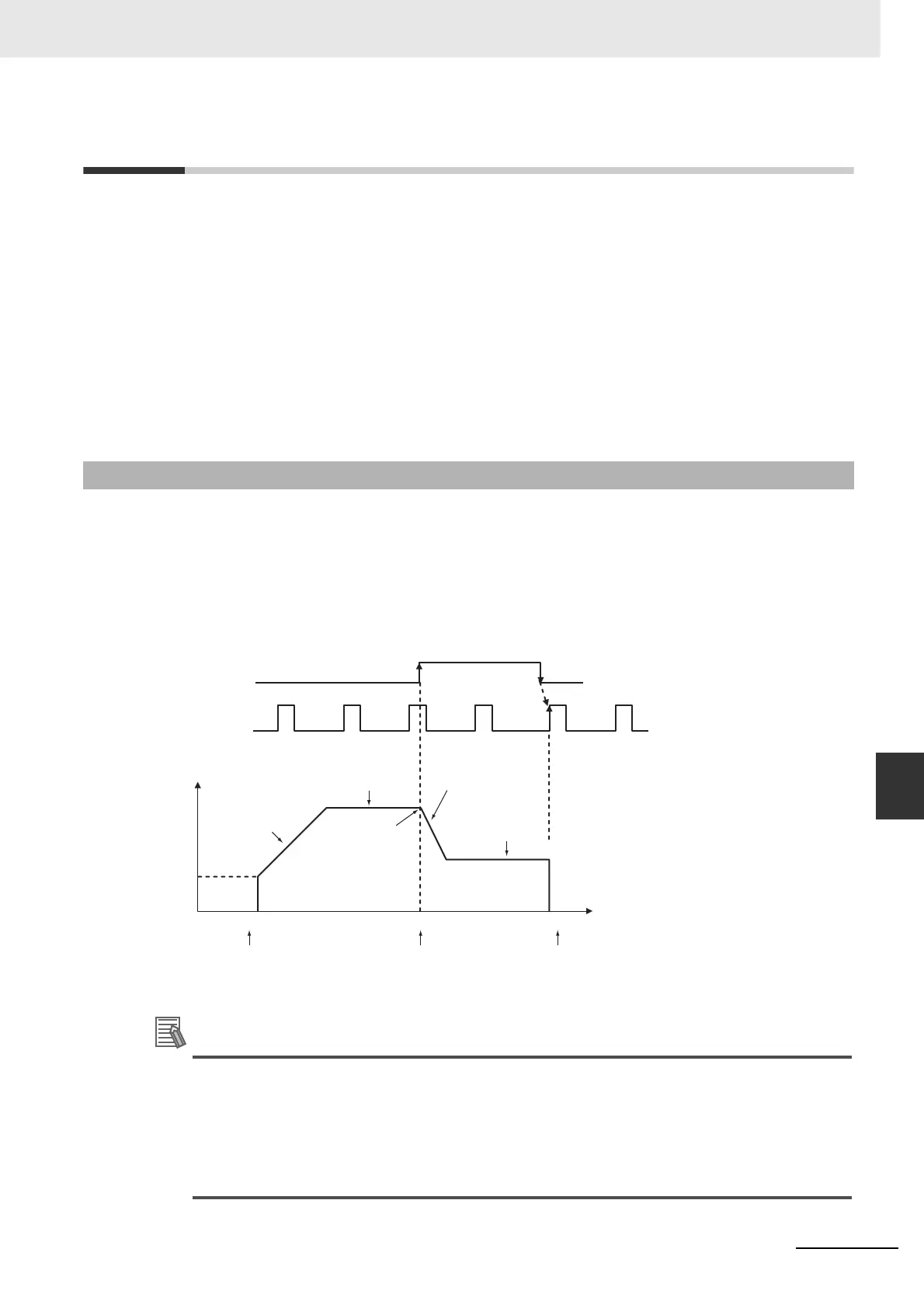
In the following example, the motor is started at a specified speed, accelerated to the origin search high
speed, and run at that speed until the origin proximity position is detected. After the origin proximity
input is detected, the motor is decelerated to the origin search low speed and run at that speed until the
origin position is detected. The motor is stopped at the origin position.
Additional Information
The motor can be moved even if the origin position has not been defined, but positioning opera-
tions will be limited as follows:
• Origin return: Cannot be used.
• Positioning with absolute pulse specification: Cannot be used.
• Positioning with relative pulse specification: Outputs the specified number of pulses after set-
ting the present position to 0.
8-5-1 Origin Searches
1
0
1
0
Origin
proximity
input signal
Origin input
signal
Pulse frequency
Origin search
acceleration
rate
Origin search high
speed
Deceleration
timing
Origin search
deceleration rate
Origin search
proximity speed
Origin
search
starting
speed
Start
Execution of ORG
Decelerate from high to
low speed
Specified by the origin
proximity input signal
Stopped
Specified by the origin
input signal.
Time
(Example for origin detection when proximity signal turns OFF
(described later))

 Loading...
Loading...











