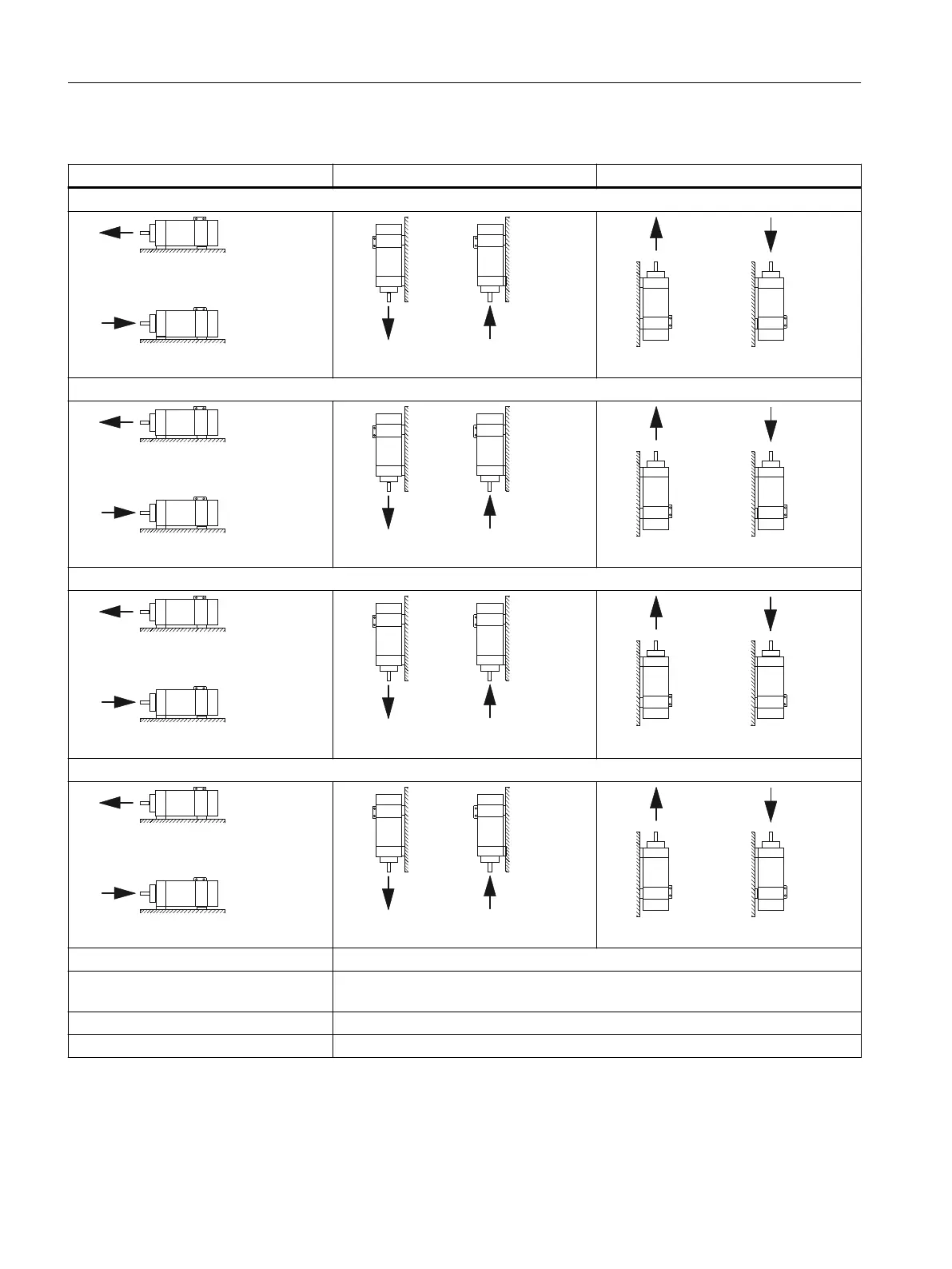
Table 4-23 Calculating the permissible axial force
Horizontal arrangement Shaft end facing downwards Shaft end facing upwards
SH 80-SH160 with bearing version Standard with locating bearing, Performance, High Performance, Advanced Lifetime
)
$=
)
$=
)
$
)
&
)
$=
)
$=
)
&
)
$
)
$=
)
/
)
$=
)
$
)
/
)
&
)
$=
)
$=
)
&
)
$
)
$=
)
&
)
$=
)
$
)
/
)
&
)
/
)
$
)
$=
)
$=
SH 80-SH160 with bearing version Standard
)
$=
)
$=
)
$
)
&
)
$=
)
$=
)
&
)
$=
)
/
)
$=
)
$
)
/
)
&
)
$=
)
$=
)
&
)
$=
)
&
)
$=
)
$
)
/
)
&
)
/
)
$=
)
$=
SH 180andSH225
)
$=
)
$
)
&
)
$=
)
$=
)
$=
)
$
)
&
)
$=
)
$
)
$=
)
$
)
&
)
/
)
$=
)
$=
)
&
)
/
)
$=
)
$
)
$=
)
$
)
&
)
/
)
/
)
&
)
$=
)
$=
SH 280
)
$=
)
$=
)
$
)
&
)
$=
)
$=
)
&
)
$
)
$=
)
/
)
$=
)
$
)
/
)
&
)
$=
)
$=
)
&
)
$
)
$=
)
&
)
$=
)
$
)
/
)
&
)
/
)
$
)
$=
)
$=
F
AZ
Permissible axial force in operation
F
A
Permissible axial force as a function of the average operating speed nm in each case,
ignoring the preloading force and the force due to the weight of the rotor
F
C
Pre-loading force
F
L
Force due to weight of rotor
Mechanical properties
4.7Radial and axial forces
1PH8 SIMOTICS M main motors
114 Conguration Manual, 12/2022, A5E51895839A

 Loading...
Loading...














