4.4.3 NDE bearings, insulated version (option L27)
Relevant, additional bearing currents
When compared to a pure sinusoidal supply, the pulsed output voltage of a frequency converter
results in additional motor bearing currents. The relevant additional bearing currents are:
• Circulating currents
• EDM currents
• Rotor ground currents
Factors that inuence bearing currents
Above a certain magnitude, bearing currents result in localized melting at the bearing rings and
rolling assemblies as well as lubricant wear. This reduces the bearing lifetime. Essential
inuencing factors include:
• Motor speed and associated operating time
• Pulse frequency of the frequency converter
• Grounding relationships between the motor and the connected load
Application for option L27
At speeds 500r/min, the load due to bearing currents increases signicantly. Option L27 is
always required if the motor is operated in the speed range between 0 ... 500 r/min for a longer
period of time. Without option L27, the total operating time in the speed range 0 ... 500 r/min
may be a maximum of 800 h (for an assumed bearing change interval (t
LW
) of the bearings of
20,000 h).
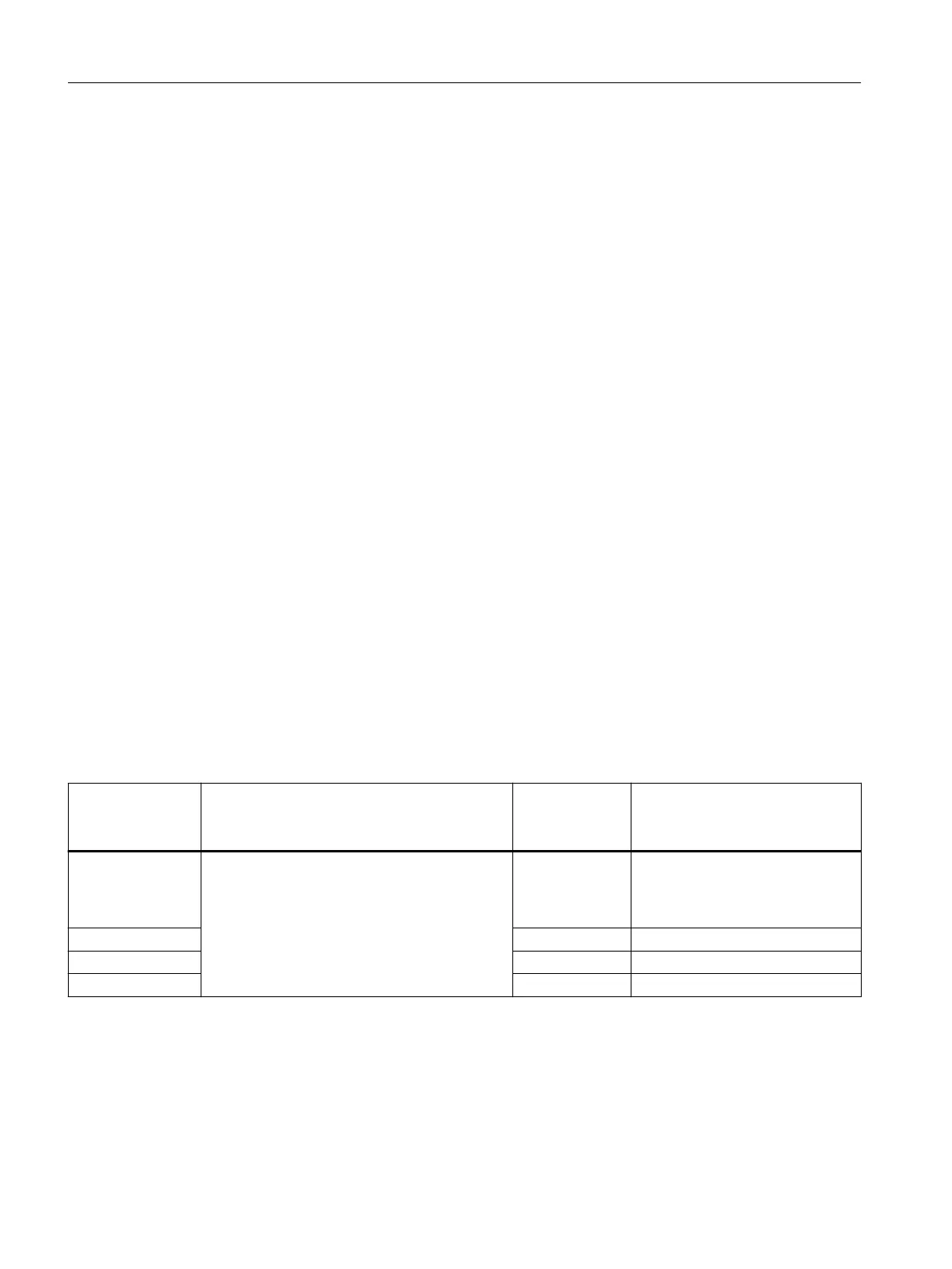
Table 4-20 Measures that are required for operation in the speed range < 500 r/min
Shaft height Bearing change interval (t
LW
) for lifetime
lubrication
h
1)
Options that
are required
Comment
80 - 160
20,000
- Due to the experience from the
eld (in practice) no dangers have
been identied due to bearing cur‐
rents
180 L27 Insulated NDE bearings
225 - Generally insulated NDE bearings
280 - Generally insulated NDE bearings
1) Denition, refer to the table "Recommended bearing change intervals"
Motor grounding
In order to avoid rotor ground currents, the motor frame should be well grounded - e.g. by using
shielded motor cables. The motor cable shield should be connected at both ends through the
largest possible surface area.
Mechanical properties
4.4Types of bearing
1PH8 SIMOTICS M main motors
94 Conguration Manual, 12/2022, A5E51895839A

 Loading...
Loading...














