Printed in the Federal Republic of Germany TR-Electronic GmbH 2008, All Rights Reserved
06/27/2017 TR - ECE - BA - DGB - 0073 - 07 Page 99 of 155
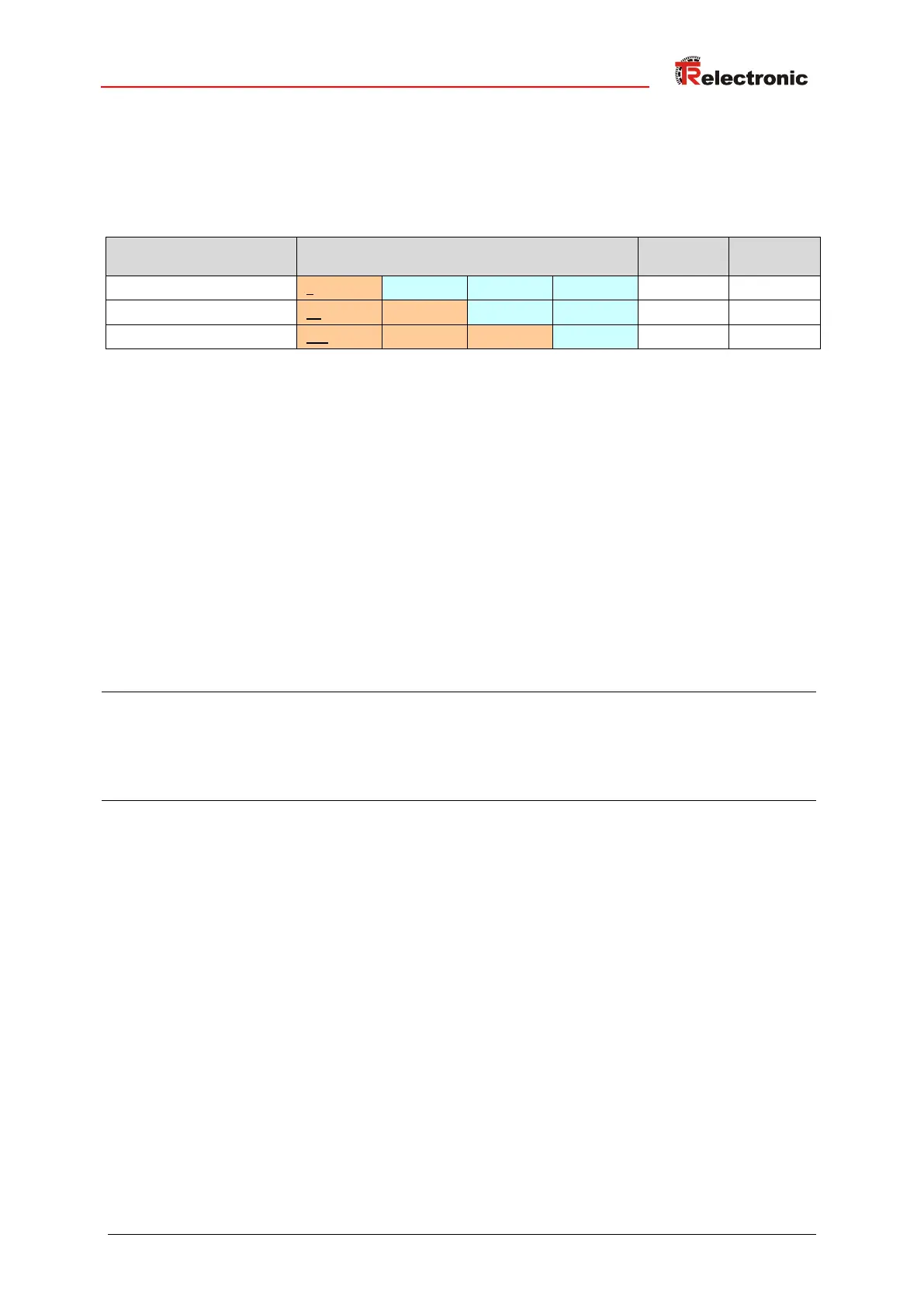
5.3.4 Combination IP-Address and Default Subnet mask
There is a declaration regarding the assignment of IP-address ranges and so-called
“Default Subnet masks”. The first decimal number of the IP-Address (from left)
determines the structure of the Default Subnet mask regarding the number of “1”
values (binary) as follows:
192.0.1.0 - 223.255.254.0
Class A-Net: 1 Byte Net address, 3 Byte Host address
Class B-Net: 2 Byte Net address, 2 Byte Host address
Class C-Net: 3 Byte Net address, 1 Byte Host address
Example Subnet mask
IP-Address = 130.094.122.195,
Net mask = 255.255.255.224
10000010 01011110 01111010 11000011
11111111 11111111 11111111 11100000
10000010 01011110 01111010 11000000
10000010 01011110 01111010 11000011
11111111 11111111 11111111 11100000
(00000000 00000000 00000000 00011111)
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000011
5.3.5 Default Gateway
A default gateway is a node (Router/Gateway) in the EtherNet/IP™ network and
makes possible the access to another network, outside of the EtherNet/IP™ network.
If a Router/Gateway is present in the EtherNet/IP™ network, whose IP address is to
be used.

 Loading...
Loading...







