128
CFW-08 OPTIONS AND ACCESSORIES
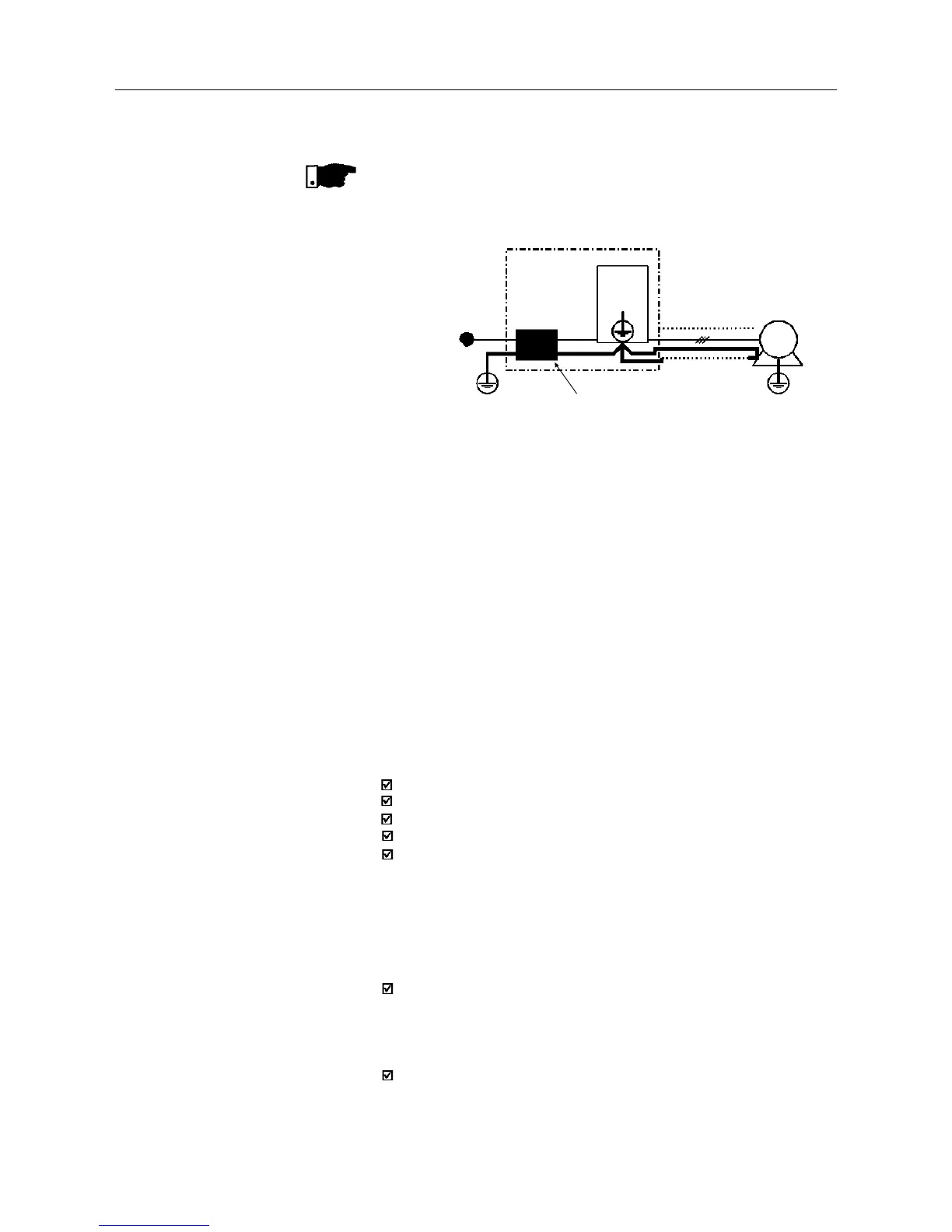
Power
Supply
Ground
Filter
CFW-08
Driving Panel
Conduit or
Shielded Cable
Motor
Motor Ground
(frame)
PE
PE
Figure 8.20 - Connection of the external RFI filter - Class B
8.16 LINE REACTOR
Due to the input circuit characteristic, common to the most inverters
available on the market, consisting of a diode rectifier and a capacitor
bank, the input current (drained from the power supply line) of inverters is
a non sinusoidal waveform and contains harmonics of the fundamental
frequency (frequency of the power supply - 60 or 50Hz).
These harmonic currents circulate through the power supply line and
cause harmonic voltage drops which distort the power supply voltage of
the inverter and other loads connected to this line. These harmonic currents
and voltage distortions may increase the electrical losses in the
installation, overheating the components (cables, transformers, capacitor
banks, motors, etc.), as well as lowering the power factor.
The harmonic input currents depend on the impedance values that are
present in the rectifier input/output circuit.
The installation of a line reactor reduces the harmonic content of the
input current, providing the following advantages:
increasing the input power factor;
reduction of the RMS input current;
reduction of the power supply voltage distortion;
increasing the life of the DC link capacitors.
reduction of the overvoltage transients that may occur in the power
supply line.
8.16.1 Application Criteria
In a general manner, the CFW-08 series inverters can be connected
directly to the power supply line without line reactors. But in this case,
ensure the following:
To ensure the inverter expected life, a minimum line impedance
that introduces a voltage drop as shown in table 8.3, as a function of
the motor load, is recommended. If the line impedance (transformers
+ wirings) is lower than these values, it is recommended to use line
reactor(s).
When it is necessary to add a line reactor to the system, it is
recommended to size it considering a 2 to 4% voltage drop (for
nominal output current). This pratice is results in a compromise between
motor voltage drop, power factor improvement and harmonic current
distortion reduction.
Install it as close as
possible to the
inverter
NOTE!
For installations that must meet the European standards refer to item 3.3.
 Loading...
Loading...