Appendix
App.1-1
IM CA150E
App
Appendix 1 Using a Cold Junction Compensator
Standard thermocouple tables give 0°C as the temperature of the reference
junction. Normally, the input terminal part (reference junction) of a thermometer
(device under calibration) is at room temperature.
(This results in an error equivalent to the difference between 0°C and room
temperature.)
Cold junction compensation involves measuring (detecting) the temperature of
the reference junction, calculating the temperature difference
(thermoelectric power difference) from 0°C, and then carrying out
compensation based on the result.
Use an external RJ sensor (or the built-in RJ sensor) for measuring (detecting)
the temperature of the reference junction.
A cold junction compensator can be used when, for example,
it is not possible to use an RJ sensor.
The use of a cold junction compensator enables the reference junction
to be 0°C.
Cold junction compensator: YOKOGAWA T-MJ or the equivalent
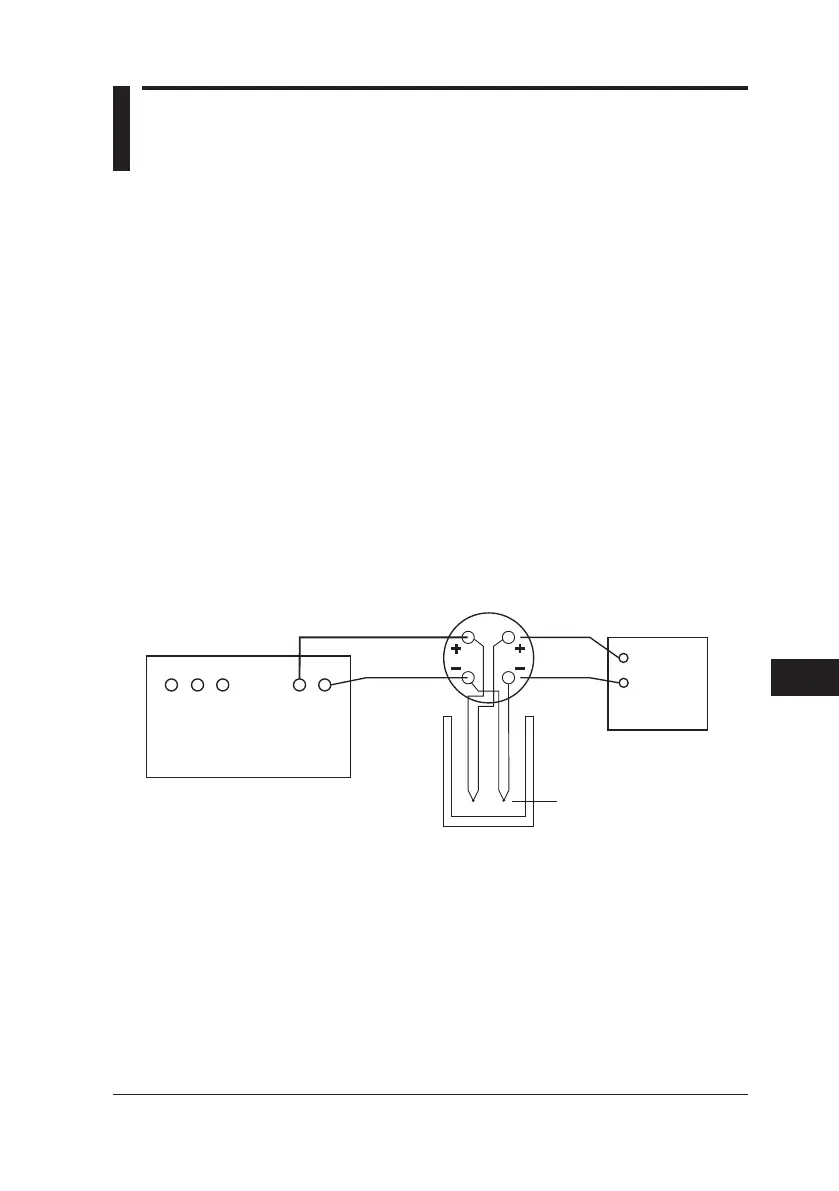
Connecting a Cold Junction Compensator
CA150
H L
SOURCE
H
L
(thermometer)
Lead cables
Cold junction compensator
Thermo
couple
0°C
 Loading...
Loading...