Voice over IP (VoIP)
110
licences, the available licences will be reassigned with the next incoming or out-
going calls.
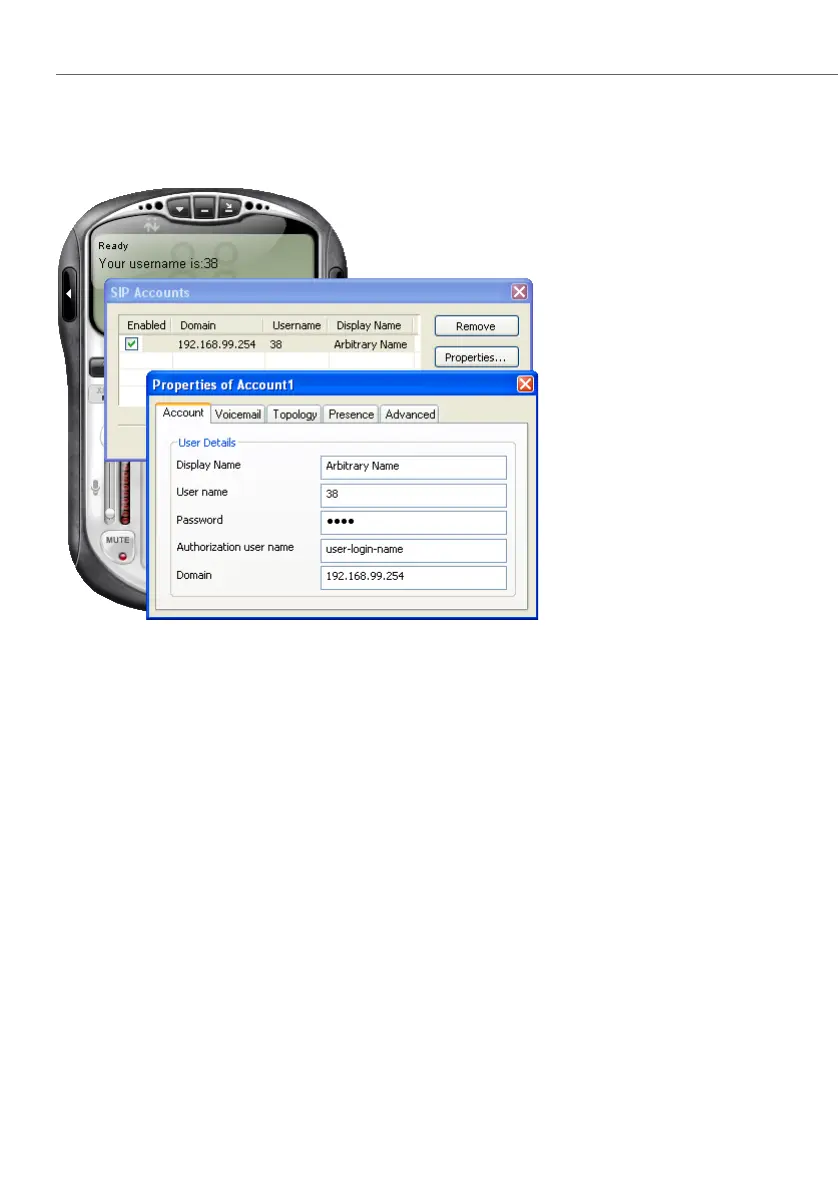
A configuration dialogue of SIP telephony software
Fundamentals
VoIP makes the transmission of voice and telephony signalling via IP (“Internet Pro-
tocol”) possible. After a connection is established, the terminal collects voice data
(PCM data), which is then sent to the receiver using an IP packet. PCM data can also be
compressed to save bandwidth.
Propagation Delay and Bandwidth
IP-based data networks are generally not able to guarantee a specific minimum band-
width and defined propagation delay. A synchronised 64 kbit/s ISDN line guarantees a
fixed data rate as long as the connection exists. In an IP-based data network, the data
rate and propagation delay can vary. Short-term bottlenecks or retransmission due to
errors may be the cause. A data flow interruption of a few seconds is barely noticeable
when fetching a Web page, but it can be seriously interfere with a telephone call.
 Loading...
Loading...