Version 5.2 111 September 2007
SIP User's Manual 5. Web-based Management
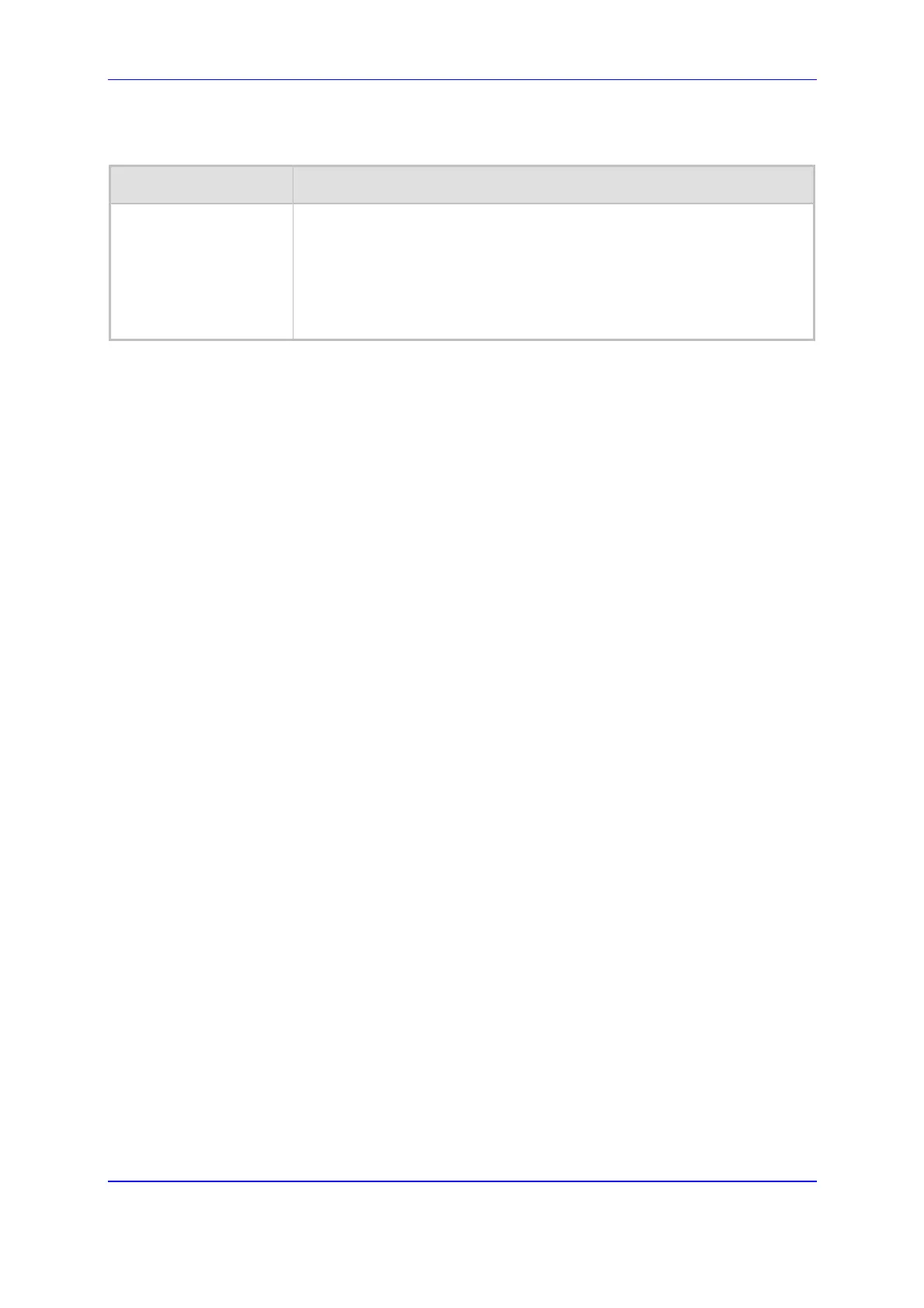
Table 5-13: Supplementary Services Parameters
Parameter Description
Hook-Flash Code
[HookFlashCode]
Determines the digit pattern used by the PBX to indicate a 'Hook-Flash'
event. When this pattern is detected from the Tel side, the gateway
responds as if a Hook-Flash event occurs and sends an INFO message
indicating 'Hook Flash'. If configured and a Hook-Flash indication is
received from the IP side, the gateway generates this pattern to the Tel
side.
The valid range is a 25-character string.
5.5.2.3 Stand-Alone Survivability
The Stand-Alone Survivability option is used to configure the SAS 'survivability' feature
for Small Medium Enterprises (SME) that implement IP Centrex services. In such
environments, the enterprise's incoming and outgoing telephone calls (external and
internal) are controlled by the IP Centrex, which communicates with the enterprise through
the WAN interface. However, to ensure call service survivability in the face of a WAN / IP
or IP Centrex failure, a PSTN backup connection is provided.
This solution is provided by the gateway's integrated SAS (back-to-back User Agent) and a
dedicated connection to the PSTN network. The SAS operates in one of two modes:
Normal Mode:
Initially, the SAS acts as a registrar so that every IP phone or residential gateway
(CPE) within the SME registers to it, while it passes all registration requests to the IP
Centrex. In Normal mode, the SAS functions as a statefull proxy, passing all SIP
requests received from the enterprise to the IP Centrex, and vice versa. In parallel, the
SAS continuously maintains a ‘Keep-Alive’ handshake with the IP Centrex proxy,
using SIP OPTIONS or re-INVITE messages.
Emergency Mode:
The SAS switches to Emergency mode if it determines (from the ‘Keepalive’
responses) that connection with the IP Centrex is lost. This can occur due to IP
Centrex server failure or WAN problems. In Emergency mode, when the IP Centrex
server is down, the SAS controls all internal calls within the enterprise. In the case of
outgoing calls, the SAS forwards them to the local VoIP gateway (this can be an
analog FXO to PSTN or a gateway with digital E1/T1 trunk(s) to PSTN). In this way,
the enterprise preserves its capability for outgoing calls.
When Emergency mode is active, the SAS continuously attempts to access the IP
Centrex proxy using the regular ‘Keepalive’ method. After the connection is re-
established, the SAS switches to pre-Normal mode. In this mode, the SAS maintains
all terminations of existing calls while any new SIP call signaling (issued by new
INVITE session) is transacted to/from the IP Centrex server. This requires the SAS to
maintain a database of current active calls so that after releasing all calls established
during Emergency mode, the SAS can continue functioning in Normal mode.
Alternatively, the SAS can be simplified by carelessly handling existing calls.

 Loading...
Loading...