BENNING IT 130 Measurements
- 42 -
The loop resistance is a purely indicative value and is calculated from the contact voltage
(without additional proportional factors).
N
C
L
I
U
R
∆
=
.
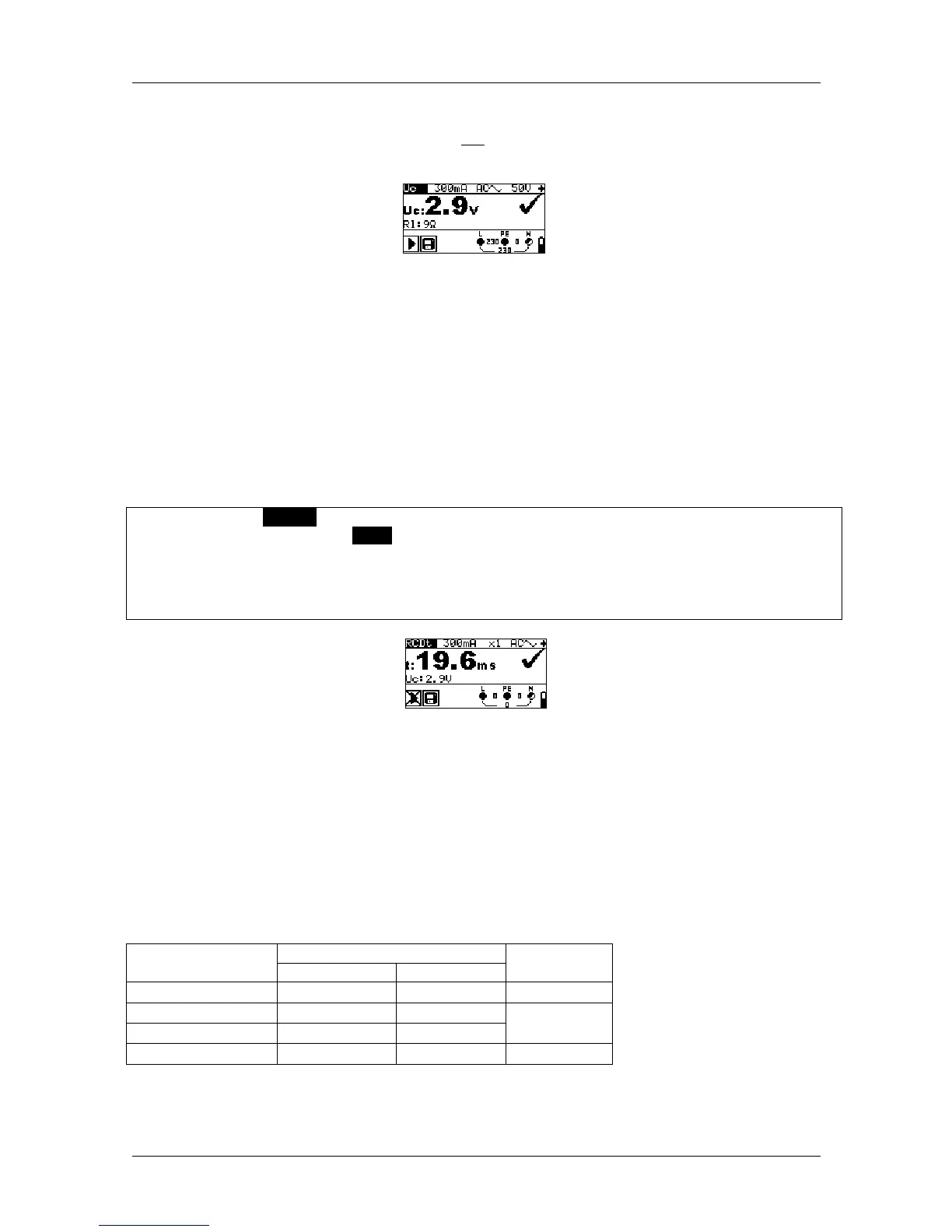
Figure 5.18: Example of a contact voltage measurement
Results displayed:
Uc ........contact voltage
RL ........loop resistance (fault loop resistance)
5.4.2 Tripping time (RCDt)
The tripping time measurement serves to test the sensitivity of the residual current protection
devices (RCDs) at different nominal tripping differential currents I
∆N
.
How to perform tripping time measurements
Select the FI/RCD function by means of the function selector switch.
Set the sub-function to RCDt.
Set the testing parameters.
Connect the test cables to the test object (see figure 5.17).
Press the "TEST" key to start the measurement.
Save the measuring result by pressing the "MEM" key (optional).
Figure 5.19: Example of a tripping time measurement
Result displayed:
t............tripping time
Uc ........contact Voltage
5.4.3 Tripping current (RCD I)
For tripping current measurement, a continuously increasing fault current serves to determine
the limiting sensitivity for RCD tripping. The installation tester increases the fault current in small
steps within the whole range as follows:
Norm EN 60364-4-41, (SETTINGS mode → RCD TESTING):
Increasing fault current
RCD type
Initial value Final value
Curve
shape
AC
0,1×I
∆N
1,1×I
∆N
sinusoidal
A, F (I
∆
∆∆
∆N
≥
≥≥
≥ 30 mA)
0,1×I
∆N
1,5×I
∆N
A, F (I
∆
∆∆
∆N
= 10 mA)
0,1×I
∆N
2,2×I
∆N
pulsating
B, B+
0,1×I
∆N
2,2×I
∆N
DC
 Loading...
Loading...