BENNING IT 130 Measurements
- 57 -
5.10 Single-fault leakage current (ISFL) in IT networks
The IT system is a power supply network which is insulated from the protective conductor. It is
an ungrounded power supply network. Either the network is not connected to earth directly or it
is connected to earth via a relatively high impedance. It is mainly used in areas requiring
additional protection against electrical accidents. A typical area of application are medical
operating rooms.
A first insulation fault between an external conductor and earth represents earthing of this
conductor. In this case, there is neither a potential difference between conductive housings and
earth nor an electric circuit to the transformer closed via earth.
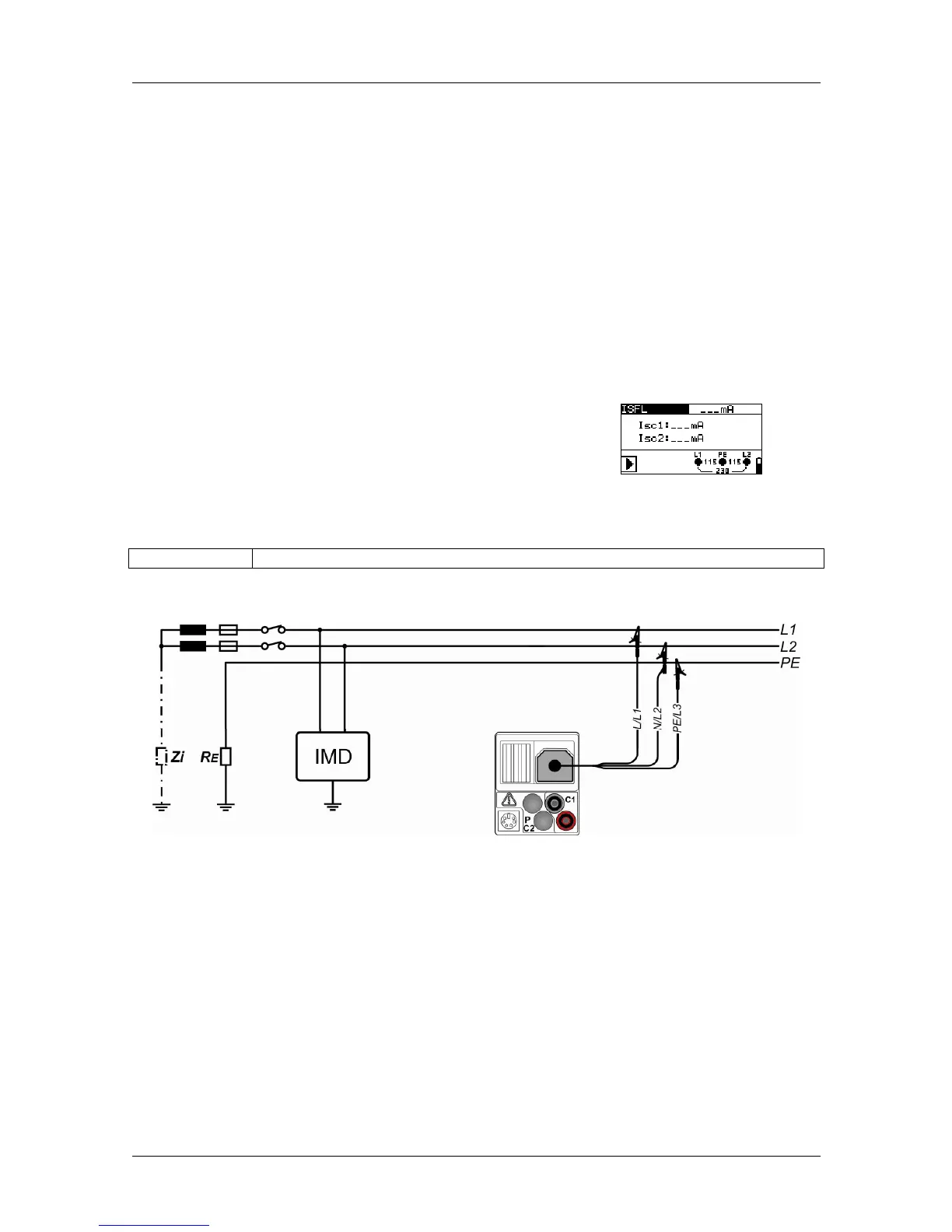
The measurement of the single-fault leakage current is carried out in order to measure the
maximum current which might flow from the tested line (external conductor) to the protective
conductor. This current flows through the insulating resistance and the phase-to-earth
capacities between the other lines (external conductors) and the protective conductor, if the
single fault is applied as short-circuit between the tested line and PE.
Key function as described in chapter
4.2 Function selector switch
Figure 5.41:
Single-fault leakage current (ISFL)
Testing parameters
Limiting value
Maximum single-fault leakage current [without limits (---), 3.0 mA ÷ 20.0 mA]
Connection plan
Figure 5.42: Connection of the three-wire test cable
 Loading...
Loading...