Operating Instructions ACTIVE06/07 155
06/07 Operating Instructions ACTIVE 155
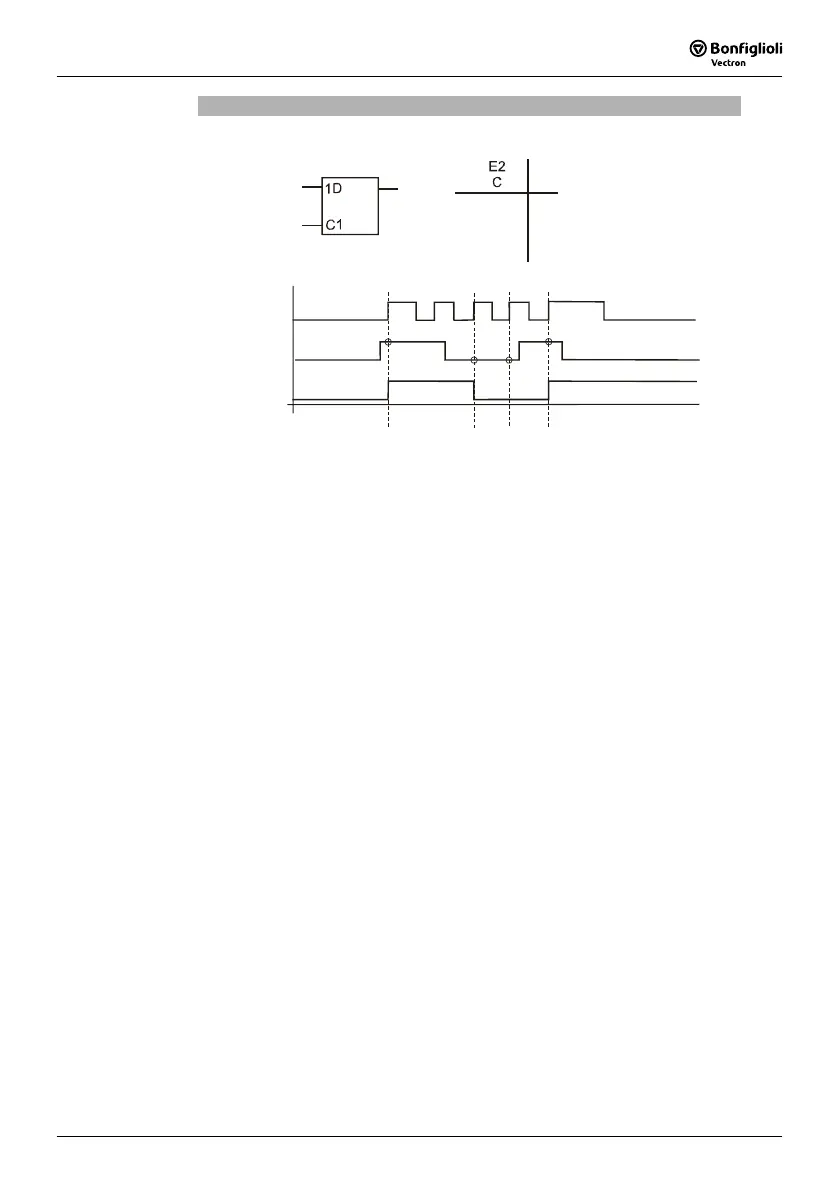
D Flip-Flop
Parameter
Operation Mode Logic = 30
Q
E2; C
E1; D
E1; D
E2; C
Q
E1
D
Q
0
1
0
1
0
0
0–>1
0–>1
Q
n-1
Q
0
1
n-1
Status
hold
sample
hold
sample
E1: data input D; E2: clock input C; Q: output
If logic "0" is present at input 2 (clock input C), the previous logic state is maintained
at the output independent of the status of input 1 (data input D).
If a positive clock edge is received at clock pulse input C, the signal present at data
input D is transmitted to the output. The output maintains its state Q
n-1
until the next
positive clock edge is received.
If a negative clock edge is received, the output signal remains unchanged.

 Loading...
Loading...











