Introductory Theory and Terminology
16 / 86 H171804E_14_001
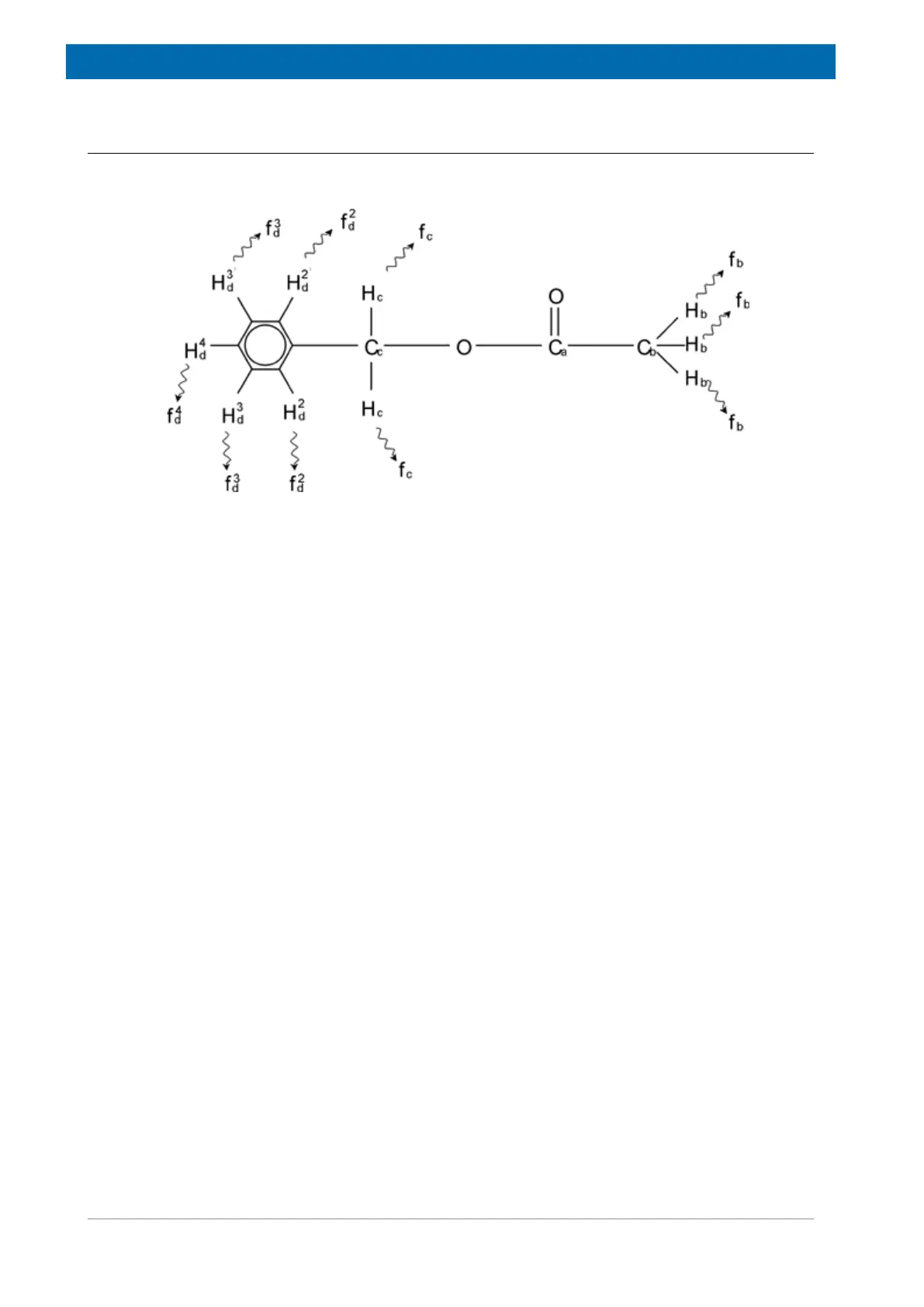
3.5 Proton Spectrum of Benzylacetate
Benzylacetate (C
6
H
5
- CH
2
- O - CO - CH
3
) is a more complicated organic molecule whose
structure is illustrated in the following figure:
Figure3.9: Benzylacetate
We can now distinguish between three different groups of protons that have been labeled
accordingly. For example, the three protons labeled H
b
clearly find themselves in a different
atomic environment to that of the two protons labeled H
c
.
The three H
b
protons are bonded to the carbon C
b
which is single-bonded to another carbon
atom C
a
. The two H
c
protons are bonded to the carbon C
c
which itself is single-bonded to the
benzene ring and an oxygen atom. The third group of protons consists of the five protons H
d
of the benzene ring itself. The figure below is a proton spectrum of benzylacetate in acetone -
d6. In this spectrum we expect three signals corresponding to the three groups of protons.
Note that the position of signals from the benzene ring protons has been shifted slightly from
7.5 ppm (shown in the Spectrum of Benzene figure) to approximately 7.2 ppm (shown in the
figure below).
The benzene ring protons are no longer magnetically equivalent, are to some extent not even
chemically equivalent, and have been labeled accordingly. It is clear from figure 3.10 that the
signal arising from the H
d
protons is a multiplet, but such details will be omitted until the next
section. The three proton peaks shown in this figure have clearly different intensities.
Quantitative analysis of the spectrum is relatively simple, since all the signals are emitted by
the same
1
H isotope i.e. natural abundance and inherent sensitivity to the NMR technique is
the same for each peak. Therefore the area under the benzene, CH
2
and CH
3
peaks should
be in the ratio of 5:2:3 respectively corresponding to the contributing number of protons.
 Loading...
Loading...










