160 - 8630
GENERAL RULES (APPENDIX)
A PID controller has a proportional, an integral and a differential component (P, I and D components).
P component
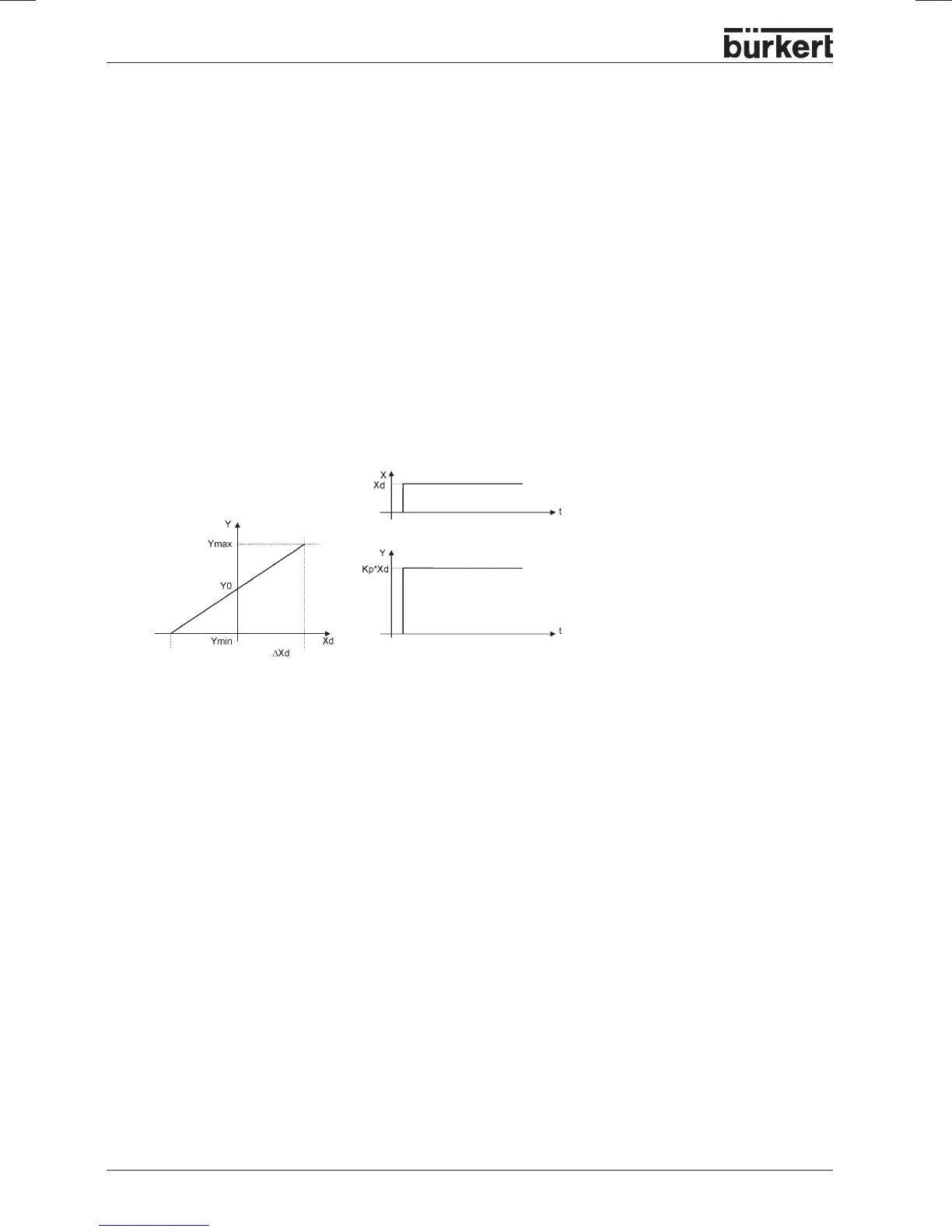
Function: Y = Kp · Xd
Where Kp is the proportional action factor (amplification factor). It is given by the ratio of the correcting
range ∆Y to the proportional range ∆Xd.
Characteristics
A pure P controller works theoretically undamped, i.e. it is fast and dynamically favourable. It has a
residual control difference, i.e. it does not completely eliminate the effects of disturbances and is thus
relatively unfavourable from a static viewpoint.
Characteristics of PID controllers
Characteristic and step response of the P component of a PID controller
Characteristic line Step response
Correcting range ∆Y
Proportional range
 Loading...
Loading...