15-6
Catalyst 2950 and Catalyst 2955 Switch Software Configuration Guide
78-11380-12
Chapter 15 Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
Understanding Optional Spanning-Tree Features
How CSUF Works
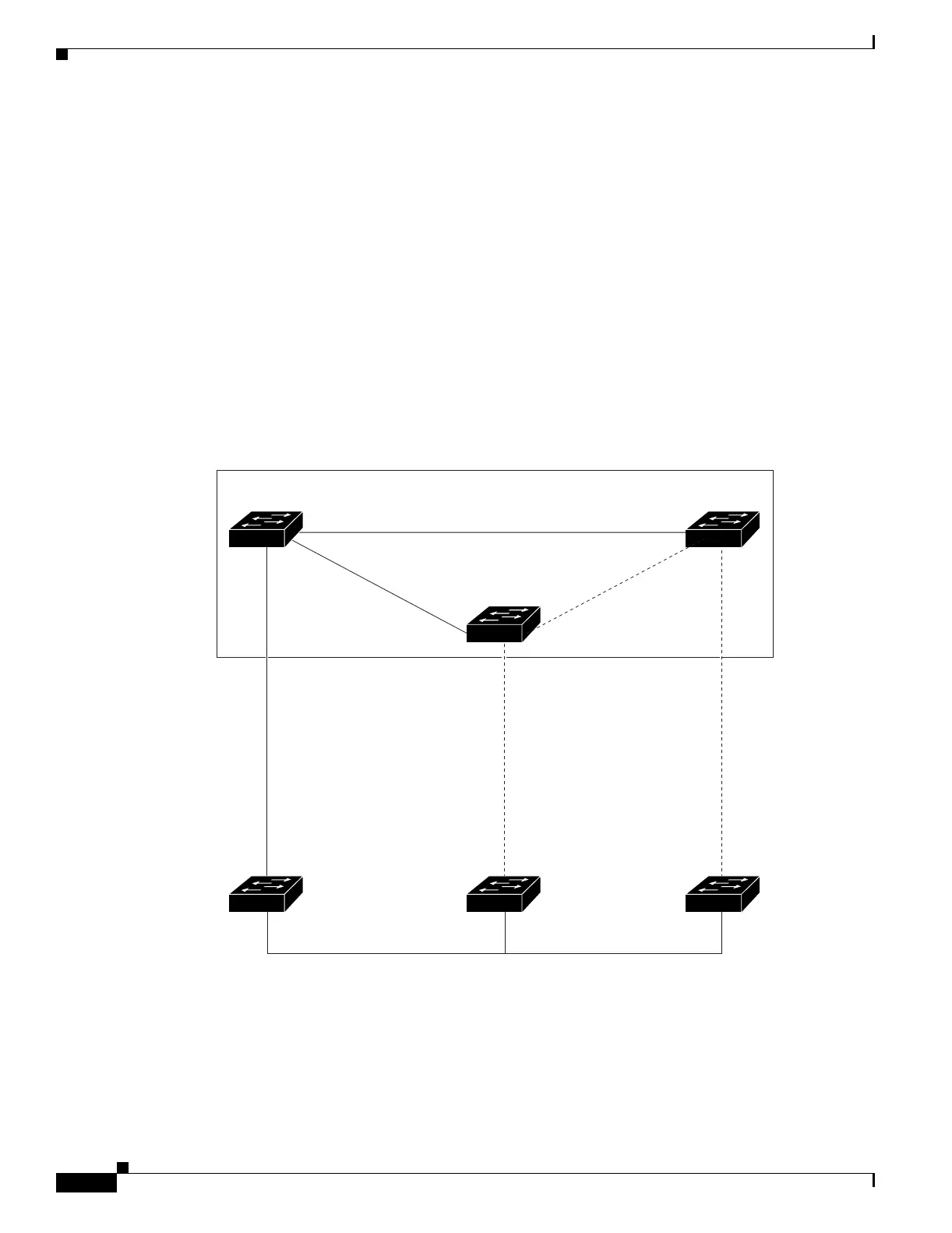
CSUF ensures that one link in the stack is elected as the path to the root. As shown in Figure 15-5,
Switches A, B, and C are cascaded through the GigaStack GBIC module to form a multidrop backbone,
which communicates control and data traffic across the switches at the access layer. The switches in the
stack use their stack ports to communicate with each other and to connect to the stack backbone; stack
ports are always in the spanning-tree forwarding state. The stack-root port on Switch A provides the path
to the root of the spanning tree; the alternate stack-root ports on Switches B and C can provide an
alternate path to the spanning-tree root if the current stack-root switch fails or if its link to the
spanning-tree root fails.
Link A, the root link, is in the spanning-tree forwarding state; Links B and C are alternate redundant
links that are in the spanning-tree blocking state. If Switch A fails, if its stack-root port fails, or if Link
A fails, CSUF selects either the Switch B or Switch C alternate stack-root port and puts it into the
forwarding state in less than 1 second.
Figure 15-5 Cross-Stack UplinkFast Topology
CSUF uses the Stack Membership Discovery Protocol to build a neighbor list of stack members through
the receipt of discovery hello packets. When certain link loss or spanning-tree events occur (described
in “Events that Cause Fast Convergence” section on page 15-7), the Fast Uplink Transition Protocol uses
the neighbor list to send fast-transition requests on the stack port to stack members.
Switch A
Spanning-
tree root
Backbone
Multidrop backbone
(GigaStack GBIC connections)
Stack port
49067
Switch B
Stack port
Forward
Link A
(Root link)
Link B
(Alternate
redundant
link)
Link C
(Alternate
redundant
link)
100 or 1000 Mbps 100 or 1000 Mbps 100 or 1000 Mbps
Forward
Forward
Switch C
Stack port
Stack-root port
Alternate stack-
root port
Alternate stack-
root port
 Loading...
Loading...
















